Understanding Prezygotic Reproductive Isolating Mechanisms
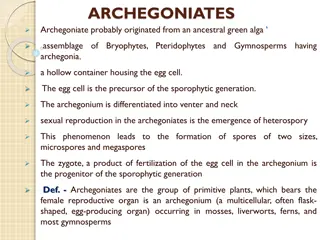
Prezygotic reproductive isolating mechanisms prevent mating or fertilization between different species before it can occur. Examples include habitat isolation, behavioral isolation, and temporal isolation. These mechanisms play a significant role in maintaining species integrity and preventing the formation of hybrids.
- Reproductive Isolation
- Prezygotic Mechanisms
- Species Integrity
- Hybrid Prevention
- Biological Barriers
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PREZYGOTIC Katelin King Amarita Singh Iann Tharp
ASSERTION Prezygotic is one of the two general categories of reproductive isolating mechanisms. Prezygotic takes effect before fertilization occurs.
EXAMPLE & EXPLAIN 1) Habitat Isolation- populations live in different habitats and they don t meet or have the opportunity to mate. Elephants in Africa cant mate with Elephants in Asia. 2) Behavioral Isolation- Little or no sexual attraction between males and females. Normally Humans don t have the urge to mate with other species. 3)Temporal Isolation- where mating or flowering occur at different seasons or times of day. Western spotted skunk and eastern spotted skunk cant mate because one mates in the summer and the other in the winter.
SIGNIFICANCE If the first three barriers fail there are still two other barriers that work to prevent fertilization and reproduction of a cross breed.