Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A Comprehensive Overview
PCOS, the most common endocrine disease in women of reproductive age, is characterized by various symptoms including abnormal metabolism of androgens and estrogen, insulin resistance, and hyperinsulinemia. This syndrome is associated with multiple theories explaining its occurrence, and its proposed mechanisms include anovulation and elevated androgen levels. PCOS affects a significant percentage of women, leading to infertility and other complications affecting reproductive health.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PCOS: PCOS: - - is referred to poly cystic ovary syndrome. is referred to poly cystic ovary syndrome. It is the most common endocrine disease seen among women in their most common endocrine disease seen among women in their reproductive age, reproductive age, it is also called it is also called Stien belonged to the one who discover it in belonged to the one who discover it in 1935 nominated as hyper androgenic chronic nominated as hyper androgenic chronic unovulation cystic cystic ovary disease, ovary disease, and and scleroting scleroting ovarian disease. ovarian disease. It is the Stien Leventhal Leventhal syndrome, 1935. .It is also It is also unovulation, , poly syndrome, poly Epidemiology Epidemiology It is seen among It is seen among 5 5- -10 age. age. It is seen among It is seen among 50 50 50% % of women consulting for miscarriages had certain degree of women consulting for miscarriages had certain degree of poly cystic ovarian changes. of poly cystic ovarian changes. 10% % among women in their reproductive among women in their reproductive 50% % of infertile women. of infertile women.
Aetiology Aetiology & &pathophysiology pathophysiology It is an autosomal dominant disorder with multi It is an autosomal dominant disorder with multi- -genicity different theories that explain its occurrence. different theories that explain its occurrence. Women with polycystic ovarian syndrome ( Women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) abnormalities in the metabolism of androgens and estrogen abnormalities in the metabolism of androgens and estrogen and in the control of androgen production. and in the control of androgen production. PCOS is also associated with peripheral insulin resistance and PCOS is also associated with peripheral insulin resistance and hyper hyper insulinemia insulinemia, , and obesity amplifies the degree of both and obesity amplifies the degree of both abnormalities. abnormalities. Hyperinsulinemia Hyperinsulinemia may also result in suppression of hepatic generation of sex hormone of hepatic generation of sex hormone binding globulin ( which in turn may increase which in turn may increase androgenicity androgenicity due to increase free androgen in the circulation. androgen in the circulation. genicity with with PCOS) have have may also result in suppression binding globulin (SHBG), due to increase free SHBG),
A proposed mechanism for anovulation and elevated androgen A proposed mechanism for anovulation and elevated androgen levels suggests that, levels suggests that, under the increased stimulatory effect of under the increased stimulatory effect of luteinizing hormone ( luteinizing hormone (LH) LH) secreted by the anterior pituitary, secreted by the anterior pituitary, stimulation of the ovarian theca cells is increased. stimulation of the ovarian theca cells is increased. These cells, in turn, in turn, increase the production of androgens ( increase the production of androgens (eg androstenedione androstenedione). ). Because of a decreased level of follicle Because of a decreased level of follicle- - stimulating hormone ( stimulating hormone (FSH) FSH) relative to LH, relative to LH, the ovarian cells cannot aromatize the androgens to estrogens, cells cannot aromatize the androgens to estrogens, which lead to decreased estrogen levels and consequent anovulation. to decreased estrogen levels and consequent anovulation. Growth hormone ( Growth hormone (GH) GH) and insulin and insulin- -like growth factor may also augment the effect on ovarian function may also augment the effect on ovarian function These cells, eg, , testosterone, testosterone, the ovarian granulosa which lead granulosa like growth factor 1 1 ( (IGF IGF- -1 1) )
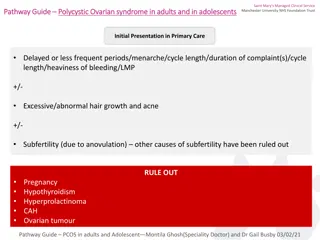
Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms The major features of PCOS include menstrual dysfunction, The major features of PCOS include menstrual dysfunction, anovulation, anovulation, and signs of hyper and signs of hyper- -androgenism Other signs and symptoms of PCOS may include the following: Other signs and symptoms of PCOS may include the following:- - Hirsutism, Hirsutism, infertility, infertility, obesity and metabolic syndrome, obesity and metabolic syndrome, diabetes, Obstructive sleep apnea Obstructive sleep apnea androgenism. . diabetes,
Diagnosis Diagnosis On examination, On examination, findings in women with PCOS may include the findings in women with PCOS may include the following: following:- - Virilizing Virilizing signs like signs like hirsutism hirsutism, , male type of baldness, male type of baldness, hoarseness of voice, voice, acne and hypertension acne and hypertension Enlarged ovaries: Enlarged ovaries: May or may not be present; May or may not be present; evaluate for an ovarian mass testing. ovarian mass testing. Exclude all other disorders that can result in menstrual irregularity Exclude all other disorders that can result in menstrual irregularity and hyper androgenic, and hyper androgenic, including adrenal or ovarian tumors, including adrenal or ovarian tumors, thyroid dysfunction, dysfunction, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, hyper acromegaly, acromegaly, and Cushing syndrome. and Cushing syndrome. hoarseness of evaluate for an thyroid hyper prolactinemia prolactinemia, ,
Baseline screening laboratory studies for women suspected of Baseline screening laboratory studies for women suspected of having PCOS include the following: having PCOS include the following:- - * *Thyroid function tests e. Thyroid function tests e.g. g. TSH, TSH, free thyroxin * *Serum prolactin level Serum prolactin level * *Total and free testosterone levels Total and free testosterone levels * *Free androgen index Free androgen index * *Serum HCG level Serum HCG level * *Serum Serum 17 17- -hydroxyprogesterone ( hydroxyprogesterone (17 * *Urinary free cortisol ( Urinary free cortisol (UFC) UFC) and and creatinine * *Low Low- -dose dexamethasone suppression test to exclude dose dexamethasone suppression test to exclude adrenal adrenal cause, cause,unresponsiveness unresponsiveness of the patient to dexamethasone suppression test reflect the possibility of dexamethasone suppression test reflect the possibility of adrenal tumor. adrenal tumor. free thyroxin 17- -OHPG) OHPG) level creatinine levels level levels of the patient to
* *Serum insulin like growth factor ( Serum insulin like growth factor (IGF) Other tests used in the evaluation of PCOS include the Other tests used in the evaluation of PCOS include the following: following:- - * *Androstenedione Androstenedione level, level, FSH and LH levels, FSH and LH levels, GnRH testing, testing, Glucose level, Glucose level, Insulin level and lipid test because of Insulin level and lipid test because of those patients usually had dyslipidemias those patients usually had dyslipidemias Ovarian ultrasonography, Ovarian ultrasonography, preferably using trans preferably using trans- -vaginal approach approach Presence of Presence of 8 8- -10 10 luteinized un ruptured follicles of varying size luteinized un ruptured follicles of varying size up to up to 10 10mm size with elongated enlarged ovaries indicate PCO mm size with elongated enlarged ovaries indicate PCO changes. changes. Pelvic CT scan or MRI to visualize the adrenals and ovaries Pelvic CT scan or MRI to visualize the adrenals and ovaries An ovarian biopsy may be performed for histologic confirmation An ovarian biopsy may be performed for histologic confirmation of PCOS; of PCOS; however, however, ultrasonographic ultrasonographic diagnosis of PCOS has generally superseded generally superseded histo histo- -pathologic diagnosis. pathologic diagnosis. An endometrial biopsy may be obtained to evaluate for endometrial endometrial biopsy may be obtained to evaluate for endometrial disease, disease, such as malignancy such as malignancy IGF) 1 1 level level GnRH stimulation stimulation vaginal diagnosis of PCOS has An
Management Management Lifestyle modifications are considered first Lifestyle modifications are considered first- -line treatment for women with PCOS. women with PCOS. Such changes include the following: Such changes include the following:- - - -Diet with low fat like fruits, Diet with low fat like fruits, vegetables, vegetables, grains and so on Exercise Exercise- - - -Weight loss Weight loss - - Stop smoking because this will increase androgen secretion. Stop smoking because this will increase androgen secretion. - -For those who seek fertility we can start ovulation induction by For those who seek fertility we can start ovulation induction by using one of the methods of induction like the use of clomiphene using one of the methods of induction like the use of clomiphene citrate citrate 50 50mg twice daily from mg twice daily from 2 2- -5 5th day of menstrual cycle or the use of use of gonadotrophin gonadotrophin accompanied with metformin capsule twice accompanied with metformin capsule twice daily to reduce weight and help to treat PCOS. daily to reduce weight and help to treat PCOS. line treatment for grains and so on . . th day of menstrual cycle or the
Spirolonactone Spirolonactone as potassium sparing diuretics can also be as potassium sparing diuretics can also be given given Certain drugs can be given to decrease weight, Certain drugs can be given to decrease weight, usually those of nutrient derivatives. of nutrient derivatives. Surgery includes two methods: Surgery includes two methods:- - A A- -Laparoscopic ovarian drilling. Laparoscopic ovarian drilling. B B- -Traditional old method ( Traditional old method (wedge resection of both wedge resection of both ovaries). ovaries). This method carries the risk of This method carries the risk of peritubal and hence will lead to future tubal blockage this is done by and hence will lead to future tubal blockage this is done by removal one third of the affected ovary and removal the thick removal one third of the affected ovary and removal the thick tunica albugenia which cover the affected ovary in a wedge tunica albugenia which cover the affected ovary in a wedge form. form. It is an old surgery rarely done now a days although no It is an old surgery rarely done now a days although no definite studies show its inferiority to the above methods, definite studies show its inferiority to the above methods, but because of the big abdominal incision, because of the big abdominal incision, longer hospital stay & the post the post- - operative operative peri peri tubal adhesion. tubal adhesion. usually those peritubal adhesion adhesion but longer hospital stay &
For those who don For those who don t want fertility then they may be given oral contraception t want fertility then they may be given oral contraception for cycle regulation. for cycle regulation. Cosmetic by hair bleaching and so on Cosmetic by hair bleaching and so on . . Androcure ( Androcure (cyproterone acetate) cyproterone acetate) as an anti as an anti- -androgenic compounds can be given to treat Hirsutism. given to treat Hirsutism. PROGNOSIS PROGNOSIS 1 1- - Evidence suggest that women with polycystic ovarian syndrome ( Evidence suggest that women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) may be at increased risk for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. may be at increased risk for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. Women with hyper Women with hyper- -androgenism androgenism have elevated serum lipoprotein have elevated serum lipoprotein 2 2- - Approximately Approximately 40 40% % of patients with PCOS have insulin resistance that is of patients with PCOS have insulin resistance that is independent of body weight. independent of body weight. These women are at increased risk for type These women are at increased risk for type 2 2 diabetes mellitus and consequent cardiovascular complications diabetes mellitus and consequent cardiovascular complications 3 3- - Patients with PCOS are also at an increased risk for endometrial Patients with PCOS are also at an increased risk for endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma. hyperplasia and carcinoma. The chronic anovulation in PCOS leads to constant endometrial stimulation The chronic anovulation in PCOS leads to constant endometrial stimulation with estrogen without progesterone, with estrogen without progesterone, and this increases the risk of and this increases the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and future endometrial carcinoma. endometrial hyperplasia and future endometrial carcinoma. androgenic compounds can be PCOS)