Understanding Photosynthesis: Role of NADP and Division into Light and Dark Stages
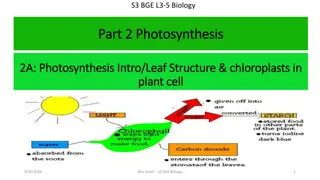
In photosynthesis, NADP plays a crucial role in carrying hydrogen into the dark stage for carbon dioxide reduction. The process is divided into light and dark stages where different components like chlorophyll, chloroplasts, and electron transfer mechanisms are involved. This division ensures efficient capture and utilization of light energy to produce carbohydrates essential for plant growth.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
2.2.9.H Photosynthesis Follow-Me iQuiz
Q. Explain the part played by NADP-in photosynthesis. Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Give a brief explanation of the division of photosynthesis into light and dark stages. Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In which of the stages of photosynthesis does ATP form? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the role of ATP in cells? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is an energised electron? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In which stage of photosynthesis does carbon dioxide provide carbon for carbohydrate formation? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. ATP is an abbreviation. What does it stand for? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Explain briefly the role of ATP in the energy exchanges of a cell. Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the fate of the ATP produced in the light-dependent stage? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Why is the dark stage given the alternative name of the light- independent stage? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name a gas that is essential for the dark stage. Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. To what group of biomolecules do the main products of the dark stage belong? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What happens to water molecules when they reach the sites of photosynthesis? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State a precise role for carbon dioxide photosynthesis: Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the fate of the NADPH produced in the light- dependent stage? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Where in a plant cell does photosynthesis take place? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Suggest a role for NAD / NADP+ in cell activities. Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. During the first stage of photosynthesis where do the energised electrons come from? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the fate of the oxygen produced in the light- dependent stage? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. During photosynthesis compounds of the general formula Cx(H2O)y are formed. What name is given to this group of compounds? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. From which simple compound does the plant obtain the H used to make C6H12O6? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name the simple compound that supplies the necessary energy for the second stage reactions. Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Give the name of the second stage of photosynthesis. Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
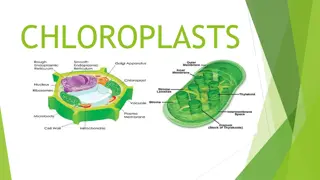
Q. Where in the cell is chlorophyll found? Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Respired or released into atmosphere Adenosine triphosphate Light not required Light not required Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Stores or provides energy Carbohydrates Light stage Light stage Carbon dioxide Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide Light essential; Independent of light Light essential; Independent of light Chlorophyll To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Chlorophyll Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Monosaccharides; Polysaccharides; Carbohydrates Chloroplast(s) To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Chloroplast(s) P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed P ~ P bond stores energy and releases it when needed Dark stage Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Capturing/transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Dark stage Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons oxygen Photolysis; Split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Water
CONGRATULATIONS You re Brilliant
Incorrect Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again