Understanding Optical Fiber Communication Systems
Explore the world of optical fiber communication systems, from the basics of communication to the intricate workings of optical fibers. Learn how information is exchanged, the components of optical fibers, and the functions of optical communication systems. Discover how light signals travel through fiber-optic cables and the essential role of transmitters and receivers in the process.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MADE BY: seminartopics.info
What is Communication ?? Exchange of information
What is Optical Fiber ? Optical fibers are thin, transparent strands almost the size of a human hair made from a dielectric cylinder surrounded by another transparent dielectric cylinder
Optic Fiber Optic fiber is made up of 3 parts : Core, Cladding and jacket The inner most part is the core which contains one or more thin fibers that are made up of plastic or glass Each of the fiber in the core is covered by a cladding which has different optical properties from the core The outer most part of the optical fiber is made up of plastic or other materials ,which is called the jacket
How does it work ? You hear about fiber-optic cables whenever people talk about the telephone system, the cable TV system or the Internet. Fiber-optic lines are strands of optically pure glass as thin as a human hair that carry digital information over long distances. The light in a fiber-optic cable travels through the core by constantly bouncing from the mirror-lined walls, total internal reflection. The reflections inside the walls are possible because of high refractive index material of the inner cylinder.
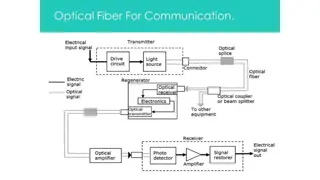
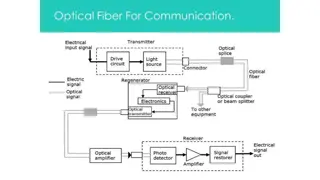
Optical communication system Transmitter. Converts electrical signal into light signal. Optical fiber. Conducts the light signal over the distance. Optical regenerator. May be required to boost the light signal for longer distances. Optical receiver. Converts light signals back to electrical signal.
Typical Optical communication system. Electric Signal OUT Electric signal In LIGHT Signal OPTICAL TRANSMITTER OPTICAL RECEIVER OPTICAL FIBER
http://www.dki.dk/images/Transceiver.gif Transmitter The transmitter is like the sailor on the deck of the sending ship. It receives and directs the optical device to turn the light "on" and "off" in the correct sequence, thereby generating a light signal. http://www.usswisconsin.org/Pictures/1940%20Pic/097%20Signal%20light%2024inc..JPG Produces and encodes the light signals. 9
Optical Regenerator Signal loss occurs when the light is transmitted through the fiber, especially over long distances Optical Regeneratorsis spliced along the cable to boost the degraded light signals. Consists ofoptical fibers with a special coating (doping). Regeneratoris a laser amplifier for the incoming signal. 10
Optical Receiver http://www.dki.dk/images/Transceiver.gif Optical receiver is like the sailor on the deck of the receiving ship. Takes the incoming digital light signals, decodes them and sends the electrical signal to the other user's computer, TV or telephone (receiving ship's captain). The receiver uses a photocell or photodiode to detect the light.
How Are Optical Fibers Made? Optical fibers are made of extremely pure optical glass. Making a preform glass cylinder Drawing the fibers from the preform Testing the fibers http://www.fiberdyne.com/products/images/lc.jpg 12
How Does an Optical Fiber Transmit Light? Shine a flashlight beam down a long, straight hallway Total internal reflection. Light signal degrades within the fiber Signal degrades depends on the purity of the glass and the wavelength of the transmitted light 850 nm = 60 to 75 percent/km 1,300 nm = 50 to 60 percent/km 1,550 nm is greater than 50 percent/km 13
Advantages of using optical fiber Less expensive. Less volume (thinner than copper wires). Higher capacity. Less signal degradation. No interference between two signals. Low power. Lightweight. Flexible.
Applications Some applications use fiber optics for the communication Communication Medical Industry Sensors Military Application