Understanding Operational Amplifiers: Basics and Feedback Mechanisms
Operational amplifiers are versatile linear devices used for amplification, signal processing, and mathematical operations. They consist of high-impedance inputs and an output port, enabling various functions such as addition, subtraction, and differentiation. Incorporating feedback mechanisms like negative feedback can enhance amplifier performance, improve fidelity, and extend frequency response limits.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Operational Amplifier Basics O Operational amplifiers are linear devices that have all the properties required for nearly ideal DC amplification and are therefore used extensively in signal conditioning, filtering or to perform mathematical operations such as add, subtract, integration and differentiation.
An Operational Amplifier is basically a three-terminal device which consists of two high impedance inputs, one called the Inverting Input, marked with a negative or minus sign, ( ) and the other one called the Non-inverting Input, marked with a positive or plus sign ( + ). The third terminal represents the operational amplifiers output port which can both sink and source either a voltage or a current. In a linear operational amplifier, the output signal is the amplification factor, known as the amplifiers gain multiplied by the value of the input signal.
The output voltage signal from an Operational Amplifier is the difference between the signals being applied to its two individual inputs. In other words, an op-amps output signal is the difference between the two input signals as the input stage of an Operational Amplifier is in fact a differential amplifier . Feedback Feedback amplifire amplifire: :- -
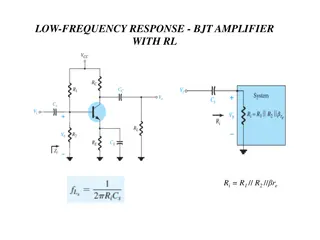
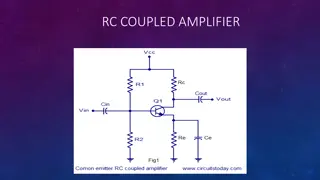
Negative Feedback Negative Feedback Negative feedback is accomplished by adding part of the output signal out of phase with the input signal. The methods of providing negative feedback are similar to those methods used to provide positive feedback. The phase relationship of the feedback signal and the input signal is the only difference . Negative feedback in a common-emitter transistor amplifier is shown in the figure below . The feedback network of C2 and R2 couples part of the output signal of Q1 back to the input. Since the output signal is 180 out of phase with the input signal, this causes negative feedback .
Negative feedback is used to improve fidelity of an amplifier by limiting the input signal. Negative feedback can also be used to increase the frequency response of an amplifier. The gain of an amplifier decreases when the limit of its frequency response is reached. When negative feedback is used, the feedback signal decreases as the output signal decreases . At the limits of frequency response of the amplifier the smaller feedback signal means that the effective gain (gain with feedback) is increased . This will improve the frequency response of the amplifier .