Understanding Mycobacterium: Causes and Impact of Tuberculosis
Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria known for causing serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (TB) and leprosy. Tuberculosis, caused mainly by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is a chronic infection that affects the lungs and various organs, especially prominent in developing regions due to its association with HIV. The high lipid content in the cell wall of mycobacteria makes them resistant to Gram staining, requiring alternative detection methods. Despite being aerobic and nonmotile, mycobacteria are significant pathogens affecting billions worldwide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mycobacterium assist. Prof. Zainab Abdul jabar Aldhaher
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly 2 billion people, one-third of the world s population, have disease caused by mycobacteria, particularly tuberculosis. Mycobacteria are widespread both in the environment and in animals and cause two major human diseases tuberculosis and leprosy. They are aerobic, acid-fast bacilli (not stained by the Gram stain because of the high lipid component of the cell wall). The major medically important pathogens are: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the agent of tuberculosis; one of the top three infectious diseases affecting humans globally
Pathogenicity This organism is the agent of tuberculosis, a chronic, granulomatous, slowly progressive infection, usually of the lungs; eventually, many other organs and tissues may be affected. A pandemic disease, tuberculosis is especially common in the developing world owing to HIV infection (15 20% of individuals with HIV disease may have tuberculosis).
Mycobacterium Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria, given its own family, the Mycobacteriaceae. The genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including: tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) leprosy (Mycobacterium leprae).
mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) is a pathogenic bacterial species in the genus Mycobacterium and the causative agent of most cases of tuberculosis (TB)First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch,
M. tuberculosis has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface (primarily mycolic acid), which makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, so acid-fast detection techniques are used, instead. The physiology of M. tuberculosis is highly aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen.
Microbiologic characteristics Mycobacteria are aerobic and nonmotile bacteria. Mycobacteria do not contain endospores or capsules and are usually considered Gram- positive. All Mycobacterium species share a characteristic cell wall, thicker than in many other bacteria, which is hydrophobic, waxy, and rich in mycolic acids/mycolates.
Many Mycobacterium species adapt readily to growth on very simple substrates, using ammonia or amino acids as nitrogen sources and glycerol as a carbon source in the presence of mineral salts. Optimum growth temperatures vary widely according to the species and range from 25 C to over 50 C. Some species can be very difficult to culture (i.e. they are fastidious),
M. tuberculosis requires oxygen to grow. It does not retain any bacteriological stain due to high lipid content in its wall, and thus is neither Gram-positive nor Gram-negative; hence Ziehl- Neelsen staining, or acid-fast staining,
M. tuberculosis divides every 1520 hours, which is extremely slow compared to other bacteria, which tend to have division times measured in minutes (Escherichia coli can divide roughly every 20 minutes). It is a small bacillus that can withstand weak disinfectants and can survive in a dry state for weeks. Its unusual cell wall, rich in lipids (e.g., mycolic acid), is likely responsible for this resistance and is a key virulence factor.
symptoms Fever Malaise tired, achy Lung degeneration pneumonia Chronic cough Septicemia, multiple organ failure Weight loss despite increased appetite consumption
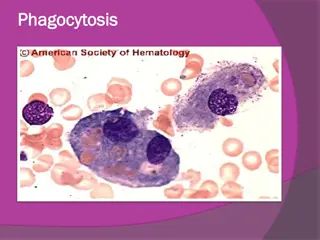
Virulence Factors Waxy cell wall. Major factor is ability to invade and survive within macrophages as surface protein called exported repetitive protein prevents phagosome from joining with lysosome. It produces no exotoxins or no LPS.
Pathogenicity The organism generally transmitted by droplets from person with active case of tuberculosis. The microorganism is very stable in sputum droplets and can remain viable in very even dry sputum for up 6 days. M. tuberculosis in droplets is then inhaled and reach the highly aerobic environment of the lung where it produce non specific pneumonitis.
Inflammation occurs such that more phagocytes travel to the site this is called an exudative lesion end up with a mass of live and dead bacteria, live and dead phagocytes surrounded by an outer layer of macrophages called a granuloma due to large number of granulocytes, granuloma becomes surrounded by fibrin which calcifies called a tubercle, can be seen by chest X ray. The infection may stop at this point and the individual may have no more symptoms
The tubercle can break though the lung into blood vessels and then be disseminated throughout the body becomes systemic infection, 50% mortality rate. Tubercle can be coughed up and swallowed, becoming systemic via the gastrointestinal tract Tubercle can burst years after primery infection Reactivation TB
diagnosis 1. demonstration of acid fast bacilli in smear made from sputum sample is indicative of tuberculosis. 2. M.tuberculosis can be culture from suptum or other contaminated fluids onto egg yolk containing agar or onto oleic acid albumin agar following 2-4 weeks of incubation. The L wenstein Jensen medium, is a growth medium specially used for culture of Mycobacterium species, notably Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
LwensteinJensen medium L wenstein-Jensen agar
When grown on this medium appears as brown, granular colonies (sometimes called "buff, rough and tough"). The medium must be incubated for a significant length of time, usually four weeks, due to the slow doubling time of M. tuberculosis (15 20 hours) compared with other bacteria. 3. Chest X ray 4. Tuberculin skin test (Mantoux Test) Purified protein derivative (PPD), part of cell wall is injected under the skin, 24 48 hours measure the size of the welt that forms. Cell have been primed and recognize the PPD.
o Positive reaction means you have been exposed to the organism: Could have active infection Could have been infected but were one of the 90% who are Asymptomatic. You have been immunized
Antigenic structure: The mycobacterial antigens have been classified as: 1- Soluble (cytoplasmic) and insoluble (cell wall lipid bound). 2- Carbohydrates or proteins 3- by their distribution within the genus
Treatment Antibiotic sensitivity and control Long-term therapy (6 9 months) with antituberculous drugs (isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol). As drug resistance is growing and a persistent problem, combination therapy should always be given. Tubercle bacilli resistant to a number of antituberculous drugs (multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB)) is a growing problem. Hence, regimentation of drug delivery is a cornerstone of managing the disease, which is achieved by a global programme termed directly observed therapy (DOT). Prevention is by bacille Calmette Gu rin (BCG) vaccination containing live attenuated organisms, in childhood.
vaccine BCG (Bacilli Calmete Guerin) vacine Made to stimulate the cell mediated immune response as M. tuberculosis is largely an intracellular pathogen Uses live attenuated M. bovis, causes TB in cows Most effective in children, given as part of early childhood regime in endemic regions Some cases of human contracting M. bovis from vaccine, or from drinking unpasteurized milk from infected cow.