Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is a chronic disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis that primarily affects the respiratory system. This overview covers the epidemiology, transmission methods, causative agents, pathogenesis, diagnostic methods, management, prevention, and control of tuberculosis. The importance o
2 views • 35 slides
Staining techniques
Explore a series of images illustrating various staining techniques used in histopathology, including fixation, different types of staining methods like Gram staining and acid-fast staining, as well as vital and supra-vital staining. Learn about the principles and applications of these techniques in
2 views • 42 slides
Understanding Johne's Disease in Ruminants: Causes, Transmission, and Clinical Findings
Johne's Disease, caused by Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, is a chronic bacterial infection affecting the lower intestinal tract of ruminants. It is characterized by chronic diarrhea and emaciation, mainly seen in mature animals. The mode of transmission includes contaminated food/water, intrauterin
0 views • 12 slides
Overview of Cutaneous Tuberculosis: Causes, Classification, and Clinical Features
Cutaneous tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its manifestations depend on the host's immunity, route of entry, and bacterial load. It is classified into exogeneous and endogenous sources, with various types such as tuberculides and tuberculous chancre. Clinical features include
0 views • 31 slides
Overview of Antitubercular Drugs: Introduction, Classification, and Applications
Tuberculosis is a chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium bovis in ruminants and Mycobacterium avium in dogs and pigs. These bacteria have a unique waxy appearance due to their cell wall composition, providing a shield against pharmacological compounds. Antitubercular drugs play a cruc
3 views • 28 slides
Understanding Host-Parasite Relationship in Microbiology
In microbiology, the host-parasite relationship is crucial for understanding diseases caused by pathogens. This lecture covers definitions of terms like pathogenicity, pathogen, disease, resistance, susceptibility, infection, virulence, and transmissibility. It also delves into the division of host
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Mycobacterium: Causes and Impact of Tuberculosis
Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria known for causing serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (TB) and leprosy. Tuberculosis, caused mainly by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is a chronic infection that affects the lungs and various organs, especially prominent in developing regions d
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Paratuberculosis (Johne's Disease) in Animals
Contagious and fatal, Paratuberculosis, or Johne's Disease, affects the small intestine of ruminants due to Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. It spreads through fecal-oral route, affecting animals' immunity, causing weight loss, decreased milk production, and diarrhea. The infection l
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Tuberculosis: A Comprehensive Overview of the Disease
Tuberculosis, a chronic disease affecting both humans and animals, is caused by pathogenic Mycobacterium spp. This article covers the etiology, synonyms, history, and geographic distribution of tuberculosis, along with key terms like anthropozoonosis and zooanthroponosis. Learn about the tubercle ba
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Mycobacteria: Human TB, Bovine TB, and Atypical Mycobacteria
The article explores characteristics and differences between Human TB, Bovine TB, and Atypical Mycobacteria, discussing their growth, biochemical reactions, pathogenicity, and disease manifestations. Additionally, it highlights the properties of Mycobacterium leprae, emphasizing its unique morpholog
0 views • 7 slides
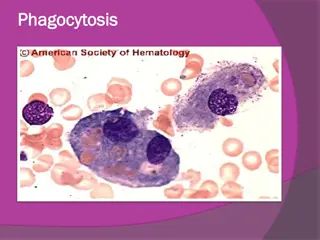
Understanding Phagocytosis, Inflammation, and Granulomas in Tuberculosis
Phagocytosis is a crucial process where cells engulf and digest pathogens. Inflammation responses involve various immune cells like neutrophils, plasma cells, lymphocytes, and macrophages. Granulomas, typical in diseases like tuberculosis, are mass accumulations in chronic inflammation. Tuberculosis
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Tuberculosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Measures
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria and primarily affects the lungs but can impact other body parts. TB can be latent or active, with symptoms like fever, weight loss, and coughing. Prevention involves protective strategies during autopsies and universal precautions. E
0 views • 10 slides
Mantoux Test: Procedure and Administration Guidelines for TB Screening
The Mantoux test, a standard method for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, involves injecting Tuberculin Purified Protein Derivative (PPD) into the skin. This test is administered to individuals including children and those with TB exposure history. Proper injection technique and site s
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Special Pathogens for Infection Prevention and Control
Pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Clostridium difficile, and antibiotic-resistant organisms like MRSA and VRE pose significant challenges to infection prevention programs. This content discusses the impact of these pathogens, transmission of tuberculosis, and clinical forms of TB. Antibi
0 views • 51 slides