Understanding Heart Health: A Comprehensive Guide
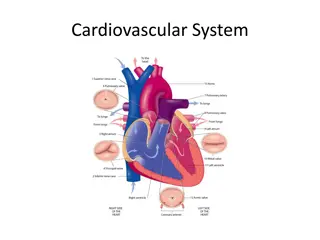
Explore the critical roles of the aorta, pulmonary artery, and coronary arteries in heart function. Discover the impact of a blocked coronary artery and learn about treatments for coronary heart disease. Delve into common heart problems, like leaky valves and irregular heartbeat, and how innovations like pacemakers and valve replacements help address them.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Helping the heart Do Now activity: 1. Identify the role of the aorta and the pulmonary artery 2. Describe the effect a blocked coronary artery can have on the human body. 3. Describe the three types of treatments that can be used on people with coronary heart disease.
Progress indicators GOOD PROGRESS: - Identify some common problems of the heart - Describe the possible ways in which we can help people with heart problems OUTSTANDING PROGRESS: - Explain the advantages and disadvantages of valve replacements and pacemakers
The heart can be affected by a number of problems. Doctors, scientists and even engineers have worked out some amazing ways to help solve them. Leaky valves Pacemaker The resting rhythm of a healthy heart is around 70 beats a minute. It is controlled by a group of cells which act as a pacemaker. If the natural pacemaker stops working properly, it can cause serious problems. Heart valves have to withstand a lot of pressure. Over time they may start to leak or become stiff and not fully open, making the heart less efficient.
Task: Look at the table below, try and shade the boxes which match the with correct malfunction the same colour: Malfunction Cause Result How to fix? Cannot stop this backflow so well. The blood circulation is reduced leading to tiredness and shortness of breath. Installing a pacemaker Hole in the heart Fatty deposits can build up in the walls Septum between the right and left sides of the heart is not complete Heart valves Hole may be closed by surgery. Can cause stroke Blood can flow from one side to the other. Blood going around the body will carry less oxygen, leading to tiredness and shortness of breath. Blocked coronary arteries Electrical signalling to heart not working properly Faulty valves can be replaced by artificial valves. By-pass Fatty deposits can block the arteries, reducing the flow of blood to the heart muscles. surgery involves transplanting a vein from the leg to provide a route past the blockage. Valves are damaged or weak Irregular heartbeat
Self-assessment: Malfunction Cause Result How to fix? Cannot stop this backflow so well. The blood circulation is reduced leading to tiredness and shortness of breath. Installing a pacemaker Hole in the heart Fatty deposits can build up in the walls Septum between the right and left sides of the heart is not complete Heart valves Hole may be closed by surgery. Can cause stroke Blood can flow from one side to the other. Blood going around the body will carry less oxygen, leading to tiredness and shortness of breath. Blocked coronary arteries Electrical signalling to heart not working properly Faulty valves can be replaced by artificial valves. By-pass Fatty deposits can block the arteries, reducing the flow of blood to the heart muscles. surgery involves transplanting a vein from the leg to provide a route past the blockage. Valves are damaged or weak Irregular heartbeat
Artificial pacemakers hearts Task: Use the posters around the room to complete the following: 1. Write a description of how artificial pacemakers and artificial hearts help patients with heart problems. 2. Draw and complete a table which summarises the risks and benefits of each treatment
Self-assessment: 1. Artificial pacemakers are electrical devices which are implanted in your chest and connected to your heart by two wires. The pacemaker sends strong, electrical signal to the heart to stimulate it to beat properly. Artificial hearts are mechanical devices which are attached to the heart to support it whilst the patients waits for a transplant. The artificial heart assists the heart by using air pressure to pump the blood around the body.
Device Advantages Disadvantages Regulates the heart beat so that the patient s heart can pump oxygen around the body efficiently. This means more cells receive more oxygen, more respiration can take place and so the patient has more energy Modern pacemakers are sensitive to the body s needs and only work when the rhythm is disrupted, can stimulate a faster heart beat during exercise. The procedure involves a risk of infection & blood clotting Once you have a pacemaker fitted you will need to have medical check ups for the rest of your life Artificial pacemaker Supports the heart in the absence of a donor, where the patients health might have otherwise deteriorate In some cases artificial hearts have kept patients alive for long periods of time and allowed them to live a relatively normal life at home The procedure involves a risk of infection & blood clotting In most cases, patients with a fitted artificial heart will need to stay in hospital until they receive a donor heart The resources required to develop artificial hearts are expensive and therefore they are not widely used. Artificial heart
Task: Answer the exam-style question in your books: 1. Read the following passage: If a heart valve is replaced it can dramatically improve the blood circulation and this in turn helps the delivery of oxygen to the tissues in the body. The operation to replace a heart valve is a risky and long procedure, whilst it is occurring the patient s blood goes through a bypass machine. One of the risks involved with the procedure is that the artificial valve can fail to work at any point. Another negative effect is if small blood clots start to accumulate on the surface of the valve, these can then break away and be carried around the body in the bloodstream. Using the information above and your own knowledge evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of implanting an artificial heart valve (4 marks)
Any four from (must include at least one advantage and one disadvantage): Advantages: Improved circulation/oxygen supply This means more cell respiration Which released more energy for the body to use More physical activity can be performed Disadvantages Danger of operation Infection risks during surgery Valve may fail and need replacing again Clots could form and block blood vessels Clots can lead to heart attack / stroke
Plenary: 3-2-1 3 facts 2 key words 1 question to test your peers!
Natural pacemaker The resting heart rate is controlled by a group of cells positioned in the right atrium of your heart that act as a natural pacemaker. If the natural pacemaker stops working properly, this can cause serious problems. If the heart beats too slowly the person affected will not get enough oxygen. This could mean that they are very low on energy. If the heart beats too fast, it cannot pump blood properly.
Artificial pacemakers Problems with the rhythm of the heart can be solved using an artificial pacemaker. This is an electrical device used to correct irregularities in the heart rate, which is implanted into your chest. Artificial pacemakers only weigh between 20 and 50g and they are attached to your heart by two wires. The artificial pacemaker sends strong, regular electrical signals to your heart that stimulate the heart to beat normally. Modern pacemakers are often sensitive to what your body needs and only work when the natural rhythm goes wrong. Some even stimulate the heart to beat faster when you exercise. If you have a pacemaker fitted you will need regular medical check ups throughout your life, also there is a risk of blood clotting and infection during the implant procedure. However most people feel that this is a small price to pay for the increase in quality and length of life.
Artificial hearts When an artificial pacemaker is not enough to restores a person s health, a donor heart can be transplanted. When people need a heart transplant they have to wait for a donor heart that is a tissue match. As a result of this wait, many people die before they get a chance to have a transplant. Scientists have developed temporary hearts that can support your natural heart until I can be replaced. These artificial hearts need a lot more machinery to keep them working and most patients need to stay in hospital until they have their transplant. They work by using air pressure to pump blood around the body.
Risks and benefits of artificial hearts In the past few years artificial hearts have improved considerably although there is always a risk of the blood clotting in an artificial heart, which can lead to death. However, this technology does give patients the chance to live a relatively normal life whilst they wait for a transplant. In 2011, a 40 year old patient was able to take his artificial heart home with him in a backpack which kept him alive for 2 years until he received a transplant. Artificial hearts can also be used to give diseased hearts a rest, so that it can recover. Patients have a part or whole artificial heart implanted that removed the strain of keeping the blood circulating for weeks or even months. However, the resources needed to develop artificial hearts and the cost of each one means they are not yet widely used.