Understanding Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Through Experiment
Explore the concepts of endothermic and exothermic reactions with a detailed experiment to determine which solute dissolves most endothermically and exothermically in water. Discover the roles of heat transfer in chemical reactions using potassium chloride, calcium chloride, sodium carbonate, and sodium bicarbonate.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS DoneBy : Markella Bursheh, Ziena Khraim, Mariam Nimri, Olivia Qudah.
What are Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions? Which solute dissolves the most endothermically and which dissolves the most exothermically in water?
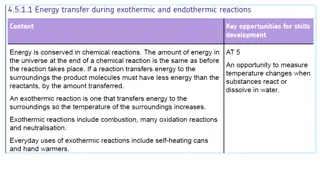
What are Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions: What are Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions: An exothermic reaction is one that gives off heat. This heat is transferred to the surroundings. An endothermic reaction is one in which heat has to be supplied to the system from the surroundings.
Let us do an experiment to determine which solute dissolves the most endothermically and which dissolves the most exothermically in water. Let us do an experiment to determine which solute dissolves the most endothermically and which dissolves the most exothermically in water. Materials for Each Group: Potassium chloride Calcium chloride Sodium carbonate Sodium bicarbonate Water 5 small cups Permanent marker or masking tape and pen Graduated cylinder Thermometer Gram balance
Procedure Procedure 1. Label the small plastic cups Potassium Chloride, Calcium chloride, Sodium carbonate, and Sodium bicarbonate. 2. Weigh 2 g of each solute and place them in their labeled cups. 3. Add 10 mL of water to the small unlabeled cup and place a thermometer in the water. Record this initial temperature in a chart. 4. Pour the potassium chloride into the water and swirl the cup. Watch the thermometer.
5. When the temperature stops changing, record the final temperature. 6. Repeat steps 3 5 for each solute. Expected Results Expected Results Potassium chloride dissolved the most endothermically, and calcium chloride dissolved the most exothermically.
5. When the temperature stops changing, record the final temperature. 6. Repeat steps 3 5 for each solute. Expected Results Expected Results Potassium chloride dissolved the most endothermically, and calcium chloride dissolved the most exothermically.
Changes in temperature: Changes in temperature Solute dissolved in water at room temperature Potassium Chloride KCL Calcium Chloride CaCl Sodium Chloride NaCl Sodium Bicarbonate NaHCO3 Solute dissolved in water at room temperature Potassium Chloride KCL Calcium Chloride CaCl Sodium Chloride NaCl Sodium Bicarbonate NaHCO3 Initial Temp ( C) Initial Temp ( C) Final Temp ( C) Final Temp ( C) Change in Temp ( C) Change in Temp ( C) Endothermic or exothermic? Endothermic or exothermic? 22 14 -8 endothermic endothermic 22 45 23 exothermic 22 32 10 exothermic 22 18 -4 endothermic endothermic
Chemical properties of different materials: Chemical properties of different materials: Solute Solute Properties Properties In its solid form, potassium chloride can be easily dissolved in water and the resulting KCl solution is said to have a salty taste. The primary application of this ionic salt is in the agriculture industry, where it is used in the production of crop fertilizers. Potassium Chloride Potassium Chloride Molecular Formula Molecular Formula KCl KCl Calcium Chloride It is highly soluble in water and it is deliquescent. It is a salt that is solid at room temperature, and it behaves as a typical ionic halide. It has several common applications such as brine for refrigeration plants, ice and dust control on roads, and in cement. Molecular Formula Calcium Chloride Molecular Formula CaCl2 CaCl2
Sodium Chloride Sodium Chloride Sodium chloride, a white crystalline solid, contains a density of 2.165 g/mL, a melting point of 801 C, and a boiling point is about 1,413 C. It is also available as aqueous solutions with different concentrations, which are known as saline solutions. It is used as a food preservative and as a seasoning to enhance flavor, and is used in healthcare to help prevent patients from becoming dehydrated. Molecular Formula Molecular Formula NaCl NaCl Sodium Bicarbonate Sodium Bicarbonate Sodium bicarbonate is a white, crystalline powder that is commonly used as a pH buffering agent, an electrolyte replenisher, systemic alkalizer and in topical cleansing solutions. Molecular Formula Molecular Formula NaHCO3 or CHNaO3 NaHCO3 or CHNaO3
Done By: Done By: Markella Bursheh Zeina Khraim Mariam Nimri Olivia Qudah