Understanding Diode Clamps and Rectifiers in Electronics Lab
Explore the functionality of diode clamps and various rectifiers including half-wave and full-wave in an Electronics Lab setting. Learn modifications to make clamps work for both positive and negative voltages.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
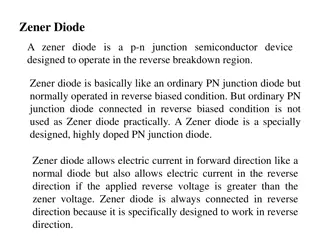
EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Lecture 3 Review of Lab 2 Simplest Active device: DIODE EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 1
Review of Lab 2 Vin Vout 1. One Diode (voltage) clamp D1 Fig 1 0V Vin Vout D2 2. Two Diode (voltage) limiter D1 Fig 2 3. One Diode half-wave rectifier Fig 3 1 Fig 4 D2 D1 3 Vin OUT Vout 4. Four diode full-wave rectifier D4 D3 2 4 EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 2
What happens in a diode clamp? Vin Vout D1 Vin Fig 1 0V If Vin < 0.7V, Vout = Vin 0.7V Vout If Vin > 0.7V, Vout = 0.7V Follow up questions: 1. This circuit only clamps the positive part of Vin What modification would cause it to clamp the negative part of Vin? 2. What modification would make it clamp both positive and negative ? EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 3
What happens in a diode clamp? Vin Vout D1 Vin Fig 1 0V If Vin > 0.7V, Vout = Vin Vout If Vin < 0.7V, Vout = 0.7V 0.7V What modification would cause it to clamp the negative part of Vin? EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 4
Diode Limiter http://www.falstad.com/circuit/e-diodelimit.html Half wave Rectifier http://www.falstad.com/circuit/e-rectify.html EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 5
Full wave rectifier http://www.falstad.com/circuit/e-fullrect.html DSO-1 1 D2 D1 DSO-2 3 Vin OUT Vout D4 D3 2 4 EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 6
Full wave rectifier with measurements of Vin Vout http://www.falstad.com/circuit/e-fullrect.html DSO-1 1 D2 D1 DSO-2 3 Vin OUT Vout D3 2 4 EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 7
Full wave rectifier Looks like a negative clamp from Vin http://www.falstad.com/circuit/e-fullrect.html DSO-1 1 D2 D1 3 Vin OUT Vout D3 2 4 Vin 0.7V EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 8
Full wave rectifier Looks like a half-wave rectifier from Vout http://www.falstad.com/circuit/e-fullrect.html 1 D2 D1 DSO-2 3 Vin OUT Vout D3 2 4 Vout Note: D1 and D3 function as positive clamps (like Slide 4) but are irrelevant, because the half-wave rectification makes sure that Vout is always positive. EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 9
Full wave rectifier Looks like a half-wave rectifier from Vout http://www.falstad.com/circuit/e-fullrect.html 1 D2 D1 DSO-2 3 Vin OUT Vout D3 2 4 Vout Notice the green dots which represent 0V EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 10
Prep for Lab 3 We have used working definitions of Diode operation: Cathode to Anode voltage > 0.7V ON Cathode to Anode voltage < 0.7V OFF This is not good enough for detailed circuit building & analysis Vout 0.7V EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 11
I-V characteristics of two terminal devices As the voltage across a diode increases from 0.65V to 0.75V it changes smoothly from: - A state of not conducting current (I) - To a state of conducting current (V) We will learn how to determine the I-V characteristics of any two terminal device without using graph paper! EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 12
Useful reference for this course Foundations of Analog and Digital Electronics by Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang http://www.allaboutcircuits.com EP215 Electronics Lab 1 Slide 13