Understanding and Efficiently Managing Urine-Diverting Dry Toilets (UDDT) Systems
This detailed guide explores the principles and practices of using Urine-Diverting Dry Toilets (UDDT), focusing on their construction, usage, and maintenance. Learn about the benefits, challenges, common mistakes to avoid, and essential tips for optimizing UDDT performance. From understanding the type of toilets to be emptied to addressing common mistakes and challenges, this resource serves as a comprehensive reference for promoting proper sanitation practices. Embrace sustainable sanitation solutions with UDDTs for a healthier environment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Water Sector Trust Fund Water Sector Trust Fund How to use, empty and dispose content of a UDDT Version:2.0 Last Update: August 2017 1
Understanding the type of toilets to be emptied What is UDDT?
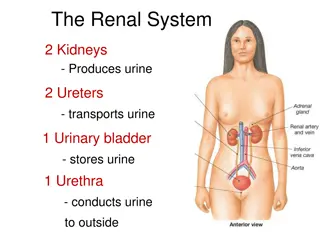
What is UDDT? A urine -diverting dry toilet (UDDT) or a dry toilet is a simple, low-cost, on-site toilet that functions without water and has a divider so that the user, with little effort, can divert the urine away from the faeces. Faeces vault 1 Urine section 1 Faeces vault 2
How is a UDDT used? Every long call visit should be accompanied by pouring ash into the vault Pouring of ash on the faeces allows it to dry fast and raises the PH level which kills most of the disease producing agents (pathogens) found in faeces N/B The use of ash is mandatory in this type of toilet Vault 2 Vault 1 4
Challenges of using UDDTs Requires proper guidance and instructions on use; requires sensitization to gain acceptance It s use requires behavioral adaption change from the masses who think of it as a conventional pit toilet It s use is not obvious to first time users Population pressure can hasten the need for emptying of vaults before the recommended six months period which ensures Posters will be available in all the dry toilets 5
Common mistakes that are made when using a UDDT Careless pouring of ash in the urine hole which often block the urine pipe Dumping solid waste such as sanitary towels and diapers (non- biodegradable items) into the faeces chamber. Defecating in the urine hole which results in blockage of the urine pipe (a mistake mostly made by children) Blocked urine pipe 7
Common mistakes Urinating in the faeces chamber. A mistake mostly made by children and men Anal cleansing water directed to the faeces chamber Bathing inside the toilet 8
How should a UDDT be used? Lift the lid of the big hole (faeces chamber). This lid has a handle which indicates that it is in use (The lid without a handle is not in use) Once you lift the lid with the handle, squat on top of the big hole facing the urinal chamber which is at the centre After use, dispose the used tissue or paper in the big hole 9
How should a UDDT be used? Put a scoop or a cupful of ash into the big hole only N/B No ash should spill in the urine chamber to avoid blockage Replace the lid once done Ensure correct use of each chamber Wash your hands with soap and water after use! Ash bucket. Ash should be poured in the faeces hole after every long call 10
The use of UDDT among children? (1) Children can be instructed best on how to use UDDT by their parents, guardians , teachers etc Children below 3 years should be accompanied by a parent , guardian or teacher while using the toilet to aim for the urine and faecal chambers respectively For children who are too young, contents from potty can be transferred to the faecal chamber 11
The use of UDDT among children (2) N/B There should be no diapers allowed in the faecal chamber but, used tissues paper is however allowed Children should be trained to wash their hands with soap and water after using the UDDT toilet 12
Emptying of vault (1) Once the vault is full, the users are requested to ensure , firstly that the faecal matter as seen from above hole is well covered with ash, the chamber should then be covered with the right lid (the one that has no handle - to indicate that it is currently not in use) The users should then be well informed about the status of the toilet to ensure that the lid is closed tight and to ensure that it is not opened by mistake and left for decomposition for a minimum of 6 months 13
Emptying of vault (2) N/B No one is allowed to use the full vault during the treatment period The longer the sludge stays decomposing, the better and safer for reuse It is recommended that the vault be opened from time to time by the users to monitor the decomposition process and to add more ash to the un decomposed sections After handling the dry matter, sanitation team members are advised to Wash their hands with soap and Water 9/27/2024 14
The dry sludge How does it look like? 15
Any risks faced during the emptying of the vaults? There is a possibility of helminth eggs (worms) transmission since some worms still take a longer time to die even when in an alkaline and tropical climates N/B The risk of worm transmission is present during vault emptying, sludge disposal at treatment site as well as the time for reuse. Hence the use of personal protective equipment (PPEs) and wash your hands with soap and water after handling in still key 16
Risks associated with the reuse of UNTREATED faecal matter There are documented scientific evidence of risks posed by UNTREATED faecal matter ; when used in growing of animal feed, vegetable, fruits and tubers, these risks emanate from pathogens that can be traced from the dried UNTREATED faecal matter. There are however no risks when the UNTREATED sludge is used for tree planting. 17
Risks associated with TREATED faecal matter Treated faecal matter is safe and pose no danger when applied for any reuse The treated dried faecal matter is a great soil conditioner and is better than animal manure since it has more nutrients 18
Challenges in reuse If plastics such as sanitary pads have been thrown in the faeces vaults, the vault contents may need to be sieved or screened prior to agricultural reuse to avoid choking the soil with plastic bags 9/27/2024 19
Benefits of faeces reuse Treated faeces have a high content of organic matter which acts as a good conditioner. It contains nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorous and other micronutrients. If ash has been used, it provides an additional source of potassium! 9/27/2024 20