Analysis of Urine Composition in Volunteers Under Various Conditions
This study involved measuring the volume and composition of urine from four groups of volunteers under different conditions: control, water intake, saline intake, and Lasix administration. The data recorded included urine volume, osmolality, pH, Na+ concentration, flow rate, and Na+ excretion rate, with the aim of understanding the mechanisms behind the observed results.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
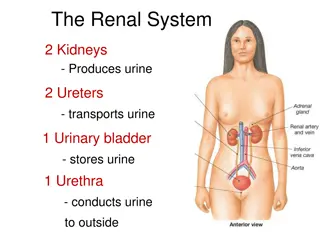
To measure the volume and determine the composition of urine excreted by 4 groups of volunteers, as follows: Control. Drinking one liter of water. Drinking one liter of normal saline. Taking lasix (a diuretic) 40 mg. To explain the mechanisms behind the different data.
Control Water Saline Lasix lasix. . Control Water Saline Lasix lasix ..Nothing. .drink drink ..take ..Nothing. .drink 1 1L water. drink 1 1L saline. ..take 20 L water. L saline. 20mg mg 11 11am am 1 1pm pm 1:30 1:30pm pm 2 2pm pm 2:30pm 2:30 pm 3 3pm pm 2 2nd sampl e e 3 3rd sampl e e 4 4th sampl e e 5 5th sampl e e nd rd th th Empty Bladder ( (1 1st st sample) Empty Bladder sampl sampl sampl sampl Empty bladder Empty bladder sample) Urine volume, Urine volume, osmolality osmolality, and , and pH. pH.
Recording and Analysis Recording and Analysis of Data of Data Sample no Sample no 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 10 10am am 10.30 10.30am am 11 11am am 11.30am 11.30 am Time 120 120 30 30 30 30 30 30 Duration (min) Record the data obtained for each sample in the tables provided. Urine volume. Osmolality. pH. [Na+] [K+] Volume Volume ( (m ml) ) 102 102 0.85 0.85 Flow rate (ml/min) 132 132 Na+ Conc. (mmol/L) Total Na+excretion (mmol Rate of Na+ excretion ( mol/min) Calculate: Flow rate. Na excretion. Total Na excretion
Urine flow rate = Volume/time (ml/min). Sodium excretion(mmoles) = Na conc. Volume of Urine 1000 Urine Na conc. (mmol/L). Flow rate (ml/min). Volume of Urine (ml) Sodium excretion rate ( mol/ml) =Sodium conc.XVolume of Urine Time
Sample no Sample no 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 10am 10 am 11am 11 am 12am 12 am 1 pm 1 pm Time 120 120 60 60 60 60 60 60 Duration (min) Volume Volume ( (m ml) ) 102 102 58 58 0.85 0.85 ? ? Flow rate (ml/min) 132 132 107 107 Na+ Conc. (mmol/L) 13.5 13.5 ? ? Total Na+excretion (mmol 112.2 112.2 ? ? Rate of Na+ excretion ( mol/min)
Urine Flow Rate Urine Flow Rate 9 8 7 Urine flow rate (ml/min) Urine flow rate (ml/min) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 10:30 11:00 Time 11:30 00:00 Time
Sodium Concentration Sodium Concentration 140 120 100 Na concentration (mmol/L) Na concentration (mmol/L) 80 60 40 20 0 10 10:30 11:00 Time 11:30 00:00 Time
urine osomality urine osomality 300 250 200 urine osomality urine osomality 150 urine osomality 100 50 0 1st sample 2nd sample 3rd sample 4th sample 5th sample
Comparison among the groups
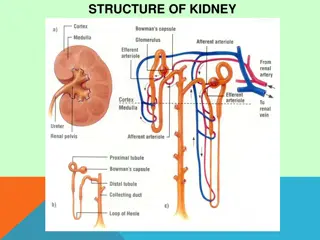
Deprive of H2O 1 Plasma Osmolarity 2 3 Stimulates Osmoreceptors in anterior hypothalamus Thirst 3 ADH secretion from posterior pituitary H2O drinking 4 H2O permeability in late distal tubule and collecting duct 5a Plsma Osmolarity Toward Normal H2O reabsorption 5b Urine osmolarity and urine volume 6
m 1 Drink H2O Plasma Osmolarity and Volume 2 3 Inhibits osmoreceptors in anterior hypothalamus Thirst 3 ADH secretion from posterior pituitary H2O permeability in late distal tubule and collecting duct H2O drinking 4 5a H2O reabsorption and excretion 5b Plasma osmolarity toward Normal Urine Osmolarity and urine volume 6
Isotonic Saline (0.9%) 1 liter Volume of E.C.F. Osmolality same (as isotonic saline) ( total solute amount Stretch on right atrium (volume receptors in right atrium) ANP (Atrial Natriuretic peptide Na excretion by Kidneys
Increase in Blood flow to kidneys (due to relaxation of smooth muscles of blood vessels) Increase in GFR Increase in Na loss in urine Decrease in Aldosterone Decrease in Na reabsorption in DCT (increase in Na loss in urine)
m 1 tab of Lasix (furosemide) (40mg) with 25ml of water Action starts 1-2 hours and lasts for 4-6 hours (1/2 life of furosemide is 6hr) Acts on thick asending limb of loop of Henle and blocks the Na-K-2Cl co-transport (called loop diuretic Na exrection in urine and water excretion (osmotic drag)