Understanding Adverse Events Following Immunization (AEFI)
Adverse Events Following Immunization (AEFI) are medical incidents that occur after immunization, potentially caused by the vaccine, leading to unfavorable symptoms. Pharmacovigilance plays a crucial role in detecting, assessing, and preventing these events. AEFI can impact immunization programs at various levels, affecting public trust, immunization coverage, and leading to the resurgence of vaccine-preventable diseases. Serious AEFI includes life-threatening events. Clusters of AEFIs signal potential causal relationships between adverse events and vaccines.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Adverse Events Following Immunization Adverse Events Following Immunization (AEFI) AEFI)
Adverse Events Following Immunization Adverse Events Following Immunization (AEFI) (AEFI) The goal of immunization is to protect individuals from specific disease; but may lead to adverse events that require careful monitoring.
Definition of AEFI Definition of AEFI It is a medical incident that takes place after an immunization, causes concern and is believed to be caused by the vaccine. It may be any unfavorable symptoms, disease sings or abnormal laboratory finding. Can be mild or severe. Can occur in clusters or isolated.
Pharmacovigilance Pharmacovigilance Is the science and activities done for detection, assessment, understanding and preventions of adverse events following immunizations and any other vaccine related issues.
Impact of AEFI on Immunization Impact of AEFI on Immunization Programm Programm Can extend from local to national level leading to short or long- lasting consequences. Can affect public trust in immunization services. Decrease in routine & supplementary immunization coverage. Resurgence of vaccine preventable diseases & unnecessary deaths.
Serious AEFI Serious AEFI Life threatening Death Hospitalization Significant disability
signal & cluster A cluster of AEFIs : two or more cases of the same adverse event related in time, place or vaccine administered. Or aggregation of relatively uncommon events in place and/or time in frequency to be grater than expected by chance. A signal defined as: possible causal relationship between an adverse event and a vaccine, the relationship being unknown or incompletely documented previously.
Classification of AEFI Classification of AEFI Vaccine Reaction. Program Error. Immunization anxiety related reaction Co incidental causes Unknown.
Cont. Vaccine quality defect related reaction : AEFI related to quality defects of the vaccine product e.g. failure by the manufacturer to completely inactivate a lot or batch of inactivated polio vaccine leads to cases of paralytic polio.
Cont. Usually present in clusters (routine or campaign vaccination) Easy to be identified if following a correct way of investigations Vaccine specimens, lots and all other information's are needed
Cont. Cont. Suspending vaccination is a rare action usually Manufacturer reports batch problem e.g., - Bell s Palsy with inactivated nasal flu vaccine - Intussusceptions with Rota shield. May need to suspend vaccination temporarily pending investigation outcome
common minor vaccine reaction Local reaction (pain, swelling, redness) Irritability, malaise and systemic symptoms Vaccine Fever >38oC _ BCG 90 95 % _ Hib 5 15 % 2 - 10 % _ adults ~15% children ~ 5% Hepatitis B 1 6 % Measles / MMR /MR 10% 5 15 % 5% (rash) -- Oral poliomyelitis (OPV) < 1 % < 1 % ~ ~ Tetanus / DT / Td 10 10 % 25% Pertussis (whole cell) up to 50% up to 50% up to 55%
Expected rate of serious vaccine reaction Expected rate of serious vaccine reaction Expected per million doses vaccine Reaction Onset interval BCG Supurative lymphadenitis 2-6 months 100 - 1000 BCG Ostitis 1-12 months 1 - 700 Disseminated BCG 1-12 months 2 Hep b Anaphylaxis 0-1 hour 1 2 GBS 1 6 weeks 5 Measles Febrile convulsion 6-12 days 333 Anaphylaxis 0-1 hour 1 50 Thrombocytopenia 15-35 days 33 Encephalopathy 6-12 days 1
Expected rate of serious vaccine reaction Expected rate of serious vaccine reaction Onset interval Expected per million doses vaccine Reaction Pertussis (DTP whole cell) Persistent (> 3 hours) inconsolable screaming 0-24 hours 1000 - 60000 Anaphylaxis 0-1 hour 20 30 - 990 Hypotonic, hypo responsive episode 0-24 hours Seizures 6-12 days 80 570 TT Brachial neuritis 2-28 days 5 10 Anaphylaxis 0-1 hour 1 6 Polio VAPP 4-30 days 1.4-3.4 19
Program error Program error Usually related to handling or administration of the vaccine e.g.: Injection in wrong place Sterilization issues by handling needles incorrectly Using incorrect diluents Drugs substituted for vaccine or diluents Storage and transport problems Ignoring contraindications
Coincidental Events Coincidental Events Something not related to program error or to individual reaction to vaccine It is medical event that would have occurred even if the individual had not been immunized Strong evidence for Coincidental Event is that the same event has been reported in people who have not been immunized
Immunization anxiety reaction - This reaction is unrelated to the content of the vaccine - arising from anxiety about the act of the vaccination itself eg . Vaso vagal syncope in adolescent following vaccination Usually occur during mass vaccinations
BCG BCG Koch s phenomenon: Accelerated reaction (10 days-Diagnostic tool) Complications: Erythema nodosum, abscess, ulceration, local lymphadenopathy and generalized T.B
Unknown/ Unclassified Unknown/ Unclassified Unknown category when after intensified correct investigations no cause identified. This an area for research and reinvestigation which might reclassify latter to one of the categories above . Can be due incomplete data
What/when to investigate What/when to investigate Serious AEFIs. Clusters and events above the expected rate AEFIs possibly caused by program error (e.g. bacterial abscess, severe local reaction, high fever or sepsis, BCG lymphadenitis, toxic shock syndrome) Significant events of unexplained cause occurring within 30 days after vaccination Events causing significant parental or community concern
AEFI surveillance tools AEFI field guide lines
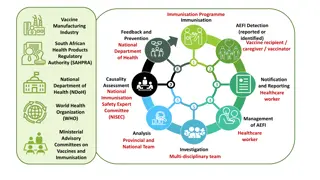
Objectives of AEFI Surveillance System Objectives of AEFI Surveillance System Detect, correct, and prevent program errors. Identify problems with vaccine lots or brand. Prevent false blame from coincidental events. Maintain confidence by properly responding to parent/community concerns while increasing awareness (public and professional) about vaccine risks. Estimate rates of occurrence on AEFI in the local population, compared with trial and international data (particularly for new vaccines being introduced)
AEFI Surveillance System AEFI Surveillance System Types of reports :- Urgent notification of serious cases. Weekly report from sentinel sites integrated with measles and AFP. monthly aggregated data from states. Investigation form for the cases should be investigated.
AEFI surveillance tools Immediate notification form
AEFI surveillance tools AEFI investigation form
AEFI surveillance tools Monthly report from vaccination site to locality
General rules General rules Treat the patient. Communicates with patients/parents, health workers EPI and community. Analyze data. Do corrective measures. Summarize and report findings to: National stakeholders International Causality assessment Take action
Investigation Key Points Investigation Key Points Understand the safety profile of commonly used vaccines & background rates of AEFI. Safety profile of vaccines depends in some cases on risk factors of person being vaccinated. Understand possible mechanisms, treatment and prevention of vaccine reactions. Verify reported event(s) early in investigation. Establish that onset occurred after vaccination.
Immunization errors leading to adverse Immunization errors leading to adverse events events Adverse event immunization error Non-sterile injection reuse of disposable syringe or needle improperly sterilized syringe or needle contaminated vaccine or diluents reuse of reconstituted vaccine at subsequent session (e.g. local suppuration at injection site, abscess, cellulitis, systemic infection, sepsis, toxic shock syndrome, transmission of blood borne disease (HIV, hepatitis B or hepatitis C) Vaccine prepared incorrectly vaccine reconstituted with incorrect diluent drugs substituted for vaccine or diluent Local reaction or abscess from inadequate shaking. Effect of drug (e.g. muscle relaxant, insulin).
Immunization errors Immunization errors Adverse event immunization error Immunization injected in wrong site: subcutaneous instead of intradermal for BCG too superficial for toxoid vaccine (penta, TT) buttocks. Local reaction or injection site abscess Local reaction or injection site abscess Sciatic nerve injure Increased local reaction from frozen vaccine (and ineffective vaccine). Vaccine transported/stored incorrectly AEFI Surveillance 2012 Contraindications ignored. Avoidable severe vaccine reaction