The Pentose Phosphate Pathway in Metabolism
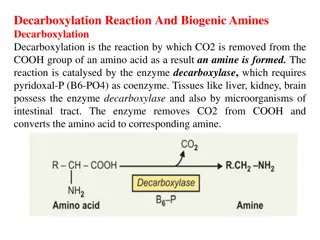
The Pentose Phosphate Pathway, also known as the Hexose Monophosphate shunt, is an alternative route for glucose metabolism that plays a crucial role in NADPH synthesis, fatty acid production, antioxidant activity, and nucleotide formation. This pathway involves oxidative and non-oxidative phases, resulting in the generation of important metabolites such as ribose-5-phosphate and xylulose-5-phosphate. Through a series of enzymatic reactions, glucose-6-phosphate is converted to various carbon sugars and ultimately contributes to the synthesis of essential biomolecules.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pentose Phosphate Pathway www.facebook.com/notesdent al
Introduction Alternative route for the metabolism of glucose Also known as Hexose Monophosphate (HMP) shunt More complex pathway than glycolysis It helps in formation of NADPH for synthesis of fatty acids, steroids, maintaining reduced glutathione for antioxidant activity synthesis of ribose for nucleotide and nucleic acid formation www.facebook.com/notesdental
Pentose Phosphate Pathway Like glycolysis it occurs in cytosol Oxidation is achieved by dehydrogenation using NADP+, not NAD+ Its carried out in 2 step: Irreversible oxidative phase: 3 molecules of glucose-6-phosphate give rise to 3 molecules of CO2 and 3 5-carbon sugars. Reversible nonoxidative phase: Rearranged to regenerate 2 molecules of glucose-6 phosphate and 1 molecule of the glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate www.facebook.com/notesdental
Oxidativephase Dehydrogenation of glucose-6- phosphate to 6- phosphogluconate catalyzedby glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase Followed by hydrolysis of 6- phosphogluconolactone to Ribulose-5-phosphatecatalyzed by 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase Decarboxylation followswith the formation of the ketopentose ribulose-5- phosphate Both this step requires NADP+as hydrogenacceptor www.facebook.com/notesdental
Non-oxidativePhase Ribulose-5-phosphate is the substrate for two enzymes Ribose-5-phosphate ketoisomerase: ribulose 5- phosphate to the corresponding ribose-5- phosphate - used for nucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis Ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase: alters the configuration about carbon giving xylulose 5- phosphate www.facebook.com/notesdental
Non-oxidativePhase Xylulose-5-phosphate (5c) and Ribose-5- phosphate (5c) reacts to give Glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate (3c) and Sedoheptulose-7- phosphate (7c) by the enzymeTransketolase Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (3c) and Sedoheptulose-7-phosphate (7c) is actedby Transaldolase to give Fructose-6-phosphate and Erythrose-4-phosphate www.facebook.com/notesdental
Non-oxidativePhase Erythrose-4-phosphate and Xylulose-5-phosphate reacts in the presence of enzyme Transketolase to give Fructose-6-phosphate and Glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate Mg 2+ and thiamin diphosphate (vitamin B1) as coenzyme Subsequently Fructose-6 phosphate is isomerisedto Glucose-6-phosphate by enzyme Phosphohexose isomerase Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate - reversal of glycolysis and the gluconeogenic enzyme fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase or it proceeds to glycolysis. www.facebook.com/notesdental
Importance of NADPH Bio-synthesis of Fatty acid Certain amino acid involving the enzyme glutamatedehydrogenase Antioxidant reaction Glutathione mediated reaction of H2O2 Detoxification of drugs cytochromeP450 Phagocytosis Integrity of RBC membrane www.facebook.com/notesdental
Importance of Pentose Sugar Ribose-5 phosphate useful for the synthesis of nucleic acid (RNA and DNA) and nucleotide Skeletal muscles capable of synthesizing pentoses www.facebook.com/notesdental
CLINICALASPECTS Genetic defects ofglucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase impairment of the generation of NADPH - X chromosome Mediterranean and Afro-Caribbeanorigin red cell hemolysis (hemolytic anemia) subjected to oxidativestress Infection Drugs such as the antimalarial primaquine, and sulfonamides Fava beans - favism www.facebook.com/notesdental
References Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry, 30E (2015) Biochemistry - U. Satyanarayan and U. Chakrapani 3rdedition Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, Fourth Edition - David L. Nelson, Michael M.Cox Biochemistry - Garrett And Grisham 2nd Ed1998 Biochemistry Stryer 5th Editionrepost Color Atlas of Biochemistry 2005 www.facebook.com/notesdental