The Nervous System: Structure and Functions
The nervous system plays a crucial role in gathering, processing, and responding to information from both internal and external sources. Neurons, the basic building blocks of the nervous system, transmit nerve impulses through specialized structures like axons and dendrites. Different types of neurons, such as sensory, interneurons, and motor neurons, work together to ensure proper communication within the body. The synapse, the junction between neurons, allows nerve impulses to travel by releasing chemicals to bridge the gap. Understanding the structure and functions of the nervous system is essential for grasping how our body processes information and coordinates responses effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Unit 7: The Nervous System (Ch.18)
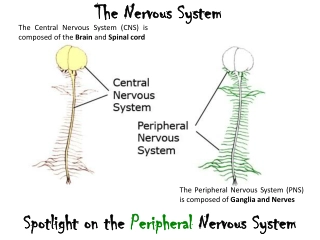
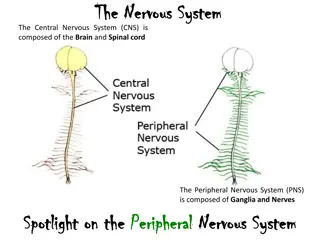
Functions the nervous system gathers, processes, and responds to information Receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. Directs the way in which your body responds to information. Stimulus- something that causes a reaction. Response- what you do in reaction to a stimulus. Helps maintain homeostasis. Protects from harm and directs signals to eat, sleep, etc.
The Neuron Neuron- nervous system cell. Nerve impulse- the signal that neurons carry. Neuron has a large cell body that contains organelles and threadlike extensions called dendrites, and a long axon.
- How the Nervous System Works The Neuron The Neuron The structure of a neuron allows it to carry nerve impulses. Axon- carries impulses away from the neuron. Dendrite- carries impulses towards the neuron.
Kinds of Neurons Sensory Neuron- picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment. Interneuron- carries impulses from one neuron to another. Motor Neuron- sends an impulse to a muscle or gland.
The Synapse Synapse- the gap between two neurons. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the impulse across the gap.
- How the Nervous System Works How a Nerve Impulse Travels How a Nerve Impulse Travels For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the impulse across the gap.