Nervous system
Neuroglia, also known as neuroglial cells, provide essential support functions for neurons in the nervous system. This includes mechanical support, structural framework, myelin production, and ensuring neuron survival. The classification of neuroglial cells includes Astrocytes, Ependymal cells, Microglia cells, Oligodendrocytes in the CNS, and Schwann cells, Satellite cells in the PNS. Each type plays a specific role in supporting the neurons and maintaining the nervous system's functionality. Astrocytes provide support and form the blood-brain barrier, Ependymal cells line the ventricles, Microglia remove microbes and damaged tissue, Oligodendrocytes produce myelin, and Schwann cells form myelin sheaths around axons.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
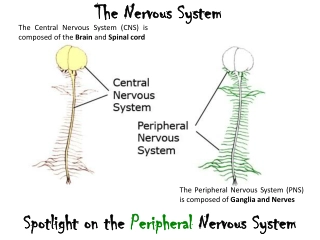
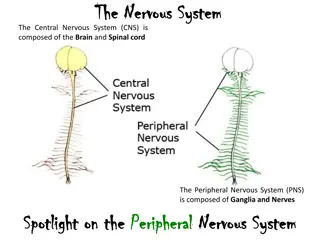
UNIT-I Nervous system (Neuroglia, classification and properties of nerve fibre) Prepared by Sucharita Babu Assistant Professor School of Pharmacy and Life Sciences
Neuroglial Cells Also known as Neuroglia cells or gial cell Neuro-neuron Gial means glue These cells provide mechanical support to the neurons Fill spaces, provide structural framework, produce myelin Neuroglia cell perform support roles for the neurons to ensure their survival.
Classification of Neuroglial cell In CNS Astrocytes Ependymal cells Microglia cells Oligodendrocytes In PNS Schwann cells Satellite cells
Astrocytes : main supporting tissue of the central nervous system star shaped with fine branching processes Found in large numbers adjacent to blood vessels with their foot processes forming a sleeve round them the blood is separated from the neurons by the capillary wall and a layer of astrocyte foot processes which together constitute the blood brain barrier Prevent toxins and poison from eantering brain neurons Ependymal cells These cells form the epithelial lining of the ventricles of tahe brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. Those cells that form the choroid plexuses of the ventricles secrete cerebrospinal fluid.
Microglia It derives from monocytes that migrate from the blood into the nervous system before birth. They are found mainly in the area of blood vessels. They enlarge and become phagocytic, removing microbes and damaged tissue, in areas of inflammation and cell destruction Oligodendrocytes These cells are smaller than astrocytes and are found in clusters round nerve cell bodies in grey matter; where they are thought to have a supportive function The oligodendrocytes form and maintain myelin, having the same functions as Schwann cells in peripheral nerves.
Schwann cells The PNS contain neurological cell as well as schwanncell Form a covering called myelin sheath around axon Basically they perform the same roll as the oligodendrocytes found in CNS Satellite cells Small gial that surround neurons sensory ganglia in theANS . Very sensitive to injury and may exacerbate pathological pain Gives protection to the neuron cells.