The Nervous System: Functions, Sense Organs, and Reflex Actions
The nervous system, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, is crucial for sensing and responding to stimuli in our environment. Sense organs like the eyes, ears, and skin help detect changes, while reflex actions provide immediate responses. Synapses and neurotransmitters play a role in transmitting messages within the nervous system.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
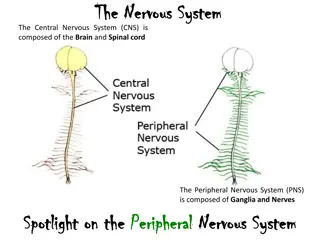
What is the nervous system made up of? The brain The spinal cord The nerves (neurones) The central nervous system (or CNS for short) is made up of the brain and the spinal cord.
What is the job of the nervous system? Our survival depends on us being sensitive to our surroundings. We need to be able to detect any changes and be able to respond to them.
What are our sense organs? The sense organs are: These organs sense: The eyes The ears The nose Tongue skin Light Sound and balance Smell Taste Pressure, pain, temperature
How does our nervous system work then? Our sense organs contain special receptor cells which will detect a change in our surroundings (a stimulus) The receptor cells will change the stimulus into an electrical impulse which is passed along nerve cells The message will usually go to the brain which will then process it The brain then sends a message along nerves to an effector organ (usually a muscle or a gland) The effector organ will then give a response (e.g. a muscle will move, or a gland will produce a hormone)
Response Stimulus Receptor Effector Motor neurone Sensory neurone Central Nervous system
Synapses When a nerve ending meets up with another nerve ending we get a microscopic space This space is called a synapse The electrical message travelling along a nerve has to cross the synapse as a chemical message When the chemical (neurotransmitter) reaches the other nerve ending it causes an electrical impulse to travel along the next nerve cell
Reacting without thinking Sometimes a stimulus requires an immediate response. This is called a reflex action. It is an involuntary response and we do it without thinking. These automatic responses do not have to be learned. They can be very important in preventing injury to ourselves.
A reflex arc The nerve pathway taken in a reflex action is called a reflex arc. The nervous message goes to the spinal cord, then a message passes from the spinal cord directly to an effector to give an immediate response.
The knee jerk reflex action Sometimes called a relay or Connector neurone
Examples of responses Involuntary actions Voluntary actions Your heart beat Breathing Blinking Removing hand from hot object Choking Salivating Eating a cake Riding a bicycle Walking Playing the piano Coming to school
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.