The Building Blocks of the Universe: Protons, Neutrons, Electrons, Atoms, and Beyond
The universe is composed of just seven different things - protons, neutrons, and electrons- the fundamental building blocks of matter. These particles combine to form atoms like hydrogen, helium, and carbon, which are essential components of our bodies. Understanding the structure and properties of these basic units sheds light on the complexity and diversity of the cosmos.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is the universe made of? Image: needpix.com Written by David Ilsley
The whole universe is made of just seven different things Image: pixabay.com
The first three are Protons Neutrons Electrons
A proton is about a trillionth of a millimetre across and weighs about a trillionth of a trillionth of a gram. A neutron is similar in size and mass to a proton. An electron weighs about a thousandth as much as a proton. All protons are the same; all neutrons are the same; all electrons are the same.
Your body is made of about 20 000 trillion trillion protons 20 000 trillion trillion neutrons and 20 000 trillion trillion electrons and nothing else! Image: pngimg.com
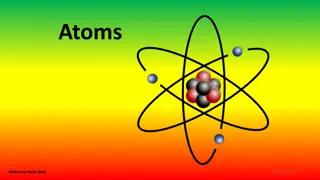
The protons, neutrons and electrons combine to make atoms. About 93% of the atoms in the universe are hydrogen; and over half the atoms in your body are hydrogen. A hydrogen atom is the simplest atom: it consists of one proton with one electron going around it. Image: commons.Wikimedia.org
Protons and electrons are attracted to each other; protons repel other protons; electrons repel other electrons. We say that protons have a positive electric charge and electrons have a negative electric charge. Opposite charges attract; like charges repel. This is what keeps the electron with the proton to make the hydrogen atom. Image: commons.Wikimedia.org
The next simplest atom is helium. A helium atom has two protons and two neutrons in its nucleus and two electrons going around the nucleus. Image: commons.Wikimedia.org Neutrons have no electric charge. Therefore they are not attracted or repelled electrically by protons or by electrons.
Another very common atom in your body is carbon. A carbon atom has 6 protons in its nucleus along with 6 neutrons and 6 electrons going around the nucleus. Image: en.wikipedia.org
There are 94 types of atoms that occur naturally. Each has a different number of protons in the nucleus (from 1 to 94). The number of protons is given above the symbol in the periodic table below. Image: en.wikipedia.org
The human body needs 23 of these 90 different types of atom to function and stay alive. They are: Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Fluorine, Sodium, Magnesium, Silicon, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Chlorine, Potassium, Calcium, Vanadium, Chromium, Manganese, Iron, Cobalt, Copper, Zinc, Selenium, Tin, Iodine.
The big bang made just hydrogen and helium. The Sun produces heat and light by combining hydrogen atoms to make more helium atoms. In red giants, supernovas and neutron star mergers, helium atoms combine to make carbon atoms, oxygen atoms and all the other types of atoms. These are then thrown off into space and are incorporated into new stars and planets. The Earth is made mostly of iron, oxygen, magnesium and silicon.
Quarks Electrons aren t made of anything smaller. But, actually, protons and neutrons are. They are both made of quarks. A proton consists of 2 Up quarks and a Down quark. A neutron consists of 2 Down quarks and an Up quark. We say that a proton has a charge of +1 and an electron has a charge of -1. An Up quark then has a charge of +2/3 and a Down quark has a charge of -1/3.
We will look at quarks in another slideshow on Subatomic Particles. But for now we will consider stuff to be made from protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons can t be separated into quarks anyway. If you try to remove a quark from a proton, it takes so much energy, that the energy you supply turns into more quarks and you just end up with more than one proton.
So . . . Your body and the whole Earth, the other planets and the stars are all made of protons, neutrons and electrons nothing else. But . . . Protons, neutrons and electrons make up only about 4% of the universe. Image: en.wikipedia.org
Remember the universe is made of 7 different things, not 3. As well as protons, neutrons and electrons, the universe also contains photons. Photons are particles of light. Image: commons.Wikimedia.org
Just like matter, light is made of particles. They are called photons. One photon is a very small amount of light: a candle produces about 1024 (a trillion trillion) photons per second. The photons move away from the candle in straight lines at the speed of light (300 000 km/s) until they hit something. Then they can either pass through the obstacle and keep going or get reflected by it or get absorbed by it
The Sun produces about 1045 photons per second. Most of these don t hit anything they keep sailing across the universe at the speed of light for ever. Space is full of photons from stars. If it wasn t, we wouldn t be able to see the stars. Image: commons.Wikimedia.org
Unlike protons, neutrons and electrons, though, photons aren t all the same. Photons can be thought of as waves. The waves have different wavelengths. Image: en.wikipedia.org
Red light photons have a long wavelength about 700 nm Orange light photons have a wavelength about 610 nm Yellow light about 580 nm Green light about 520 nm Blue light about 440 nm Violet light about 400 nm
White light from the Sun is a mixture of these colours. When we shine white light through a prism or through rain drops, it gets split up into the separate colours. Image: commons.Wikimedia.org
Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation ranges in wavelength from many kilometres down to trillionths of a millimetre. Our eyes are sensitive to only a tiny part of this spectrum. Image: commons.Wikimedia.org
As well as visible light, the universe is full of photons of all types of electromagnetic radiation. The universe contains about 1090 photons about 10 billion per cubic metre on average.
The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the universe is only about 1081 about 10 per cubic metre. So there are about a billion times as many photons. So will these account for the other 96% of the universe? No, because photons weigh far far less than protons. Photons add only a small fraction of a percent to the mass of the protons, neutrons and electrons.
The fifth thing that the universe is made of is neutrinos. Neutrinos are very small particles with very little mass and no charge. They travel very close to the speed of light. There are about as many neutrinos in the universe as there are photons.
Neutrinos are produced in nuclear reactions like those going on inside stars. Unlike photons, neutrinos don t generally interact with other particles. So most pass straight through things like humans and the Earth without touching them. About a thousand trillion neutrinos pass through your body every second. Image: flickr.com
As with photons, the total mass of neutrinos in the universe is a lot less than the mass of protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons, neutrons, electrons, photons and neutrinos together still make up less than 5% of the universe. So, what about the other 95%?
Remember that the universe is made of seven things. Number six is . . . Dark Matter
We dont know what dark matter is, but its heavy and there s lots of it. It seems to be evenly distributed in and around each galaxy. We know it s there because of its gravitational effect on the galaxies. It seems to be made of particles, but not any of the types already described. Image: commons.Wikimedia.org
Thats six of the seven things that the universe is made of. Number seven is . . . Dark Energy
Dark energy makes up the other 73% of the mass- energy of the universe. Like dark matter, we don t really understand it. But it is believed to be what causes the universe to expand. Dark energy is distributed evenly through the universe.
In fact, rather than being something distributed through space, it may be just a property of space itself. In other words, space is distributed evenly throughout the universe and one feature of space is that it has dark energy.
We tend to think of space as just nothing. But its not. It s something. Space was created in the big bang Before the big bang there was no space Space is constantly expanding The expansion of the universe isn t caused by the galaxies zooming out into empty space. Instead, space itself expands, taking the galaxies and everything else with it. As space expands, the photons in it stretch and so increase in wavelength. Space is warped by heavy objects.
In fact, it may be better to think that the seventh component of the universe is Space and that space, by its very nature, has dark energy.
So the universe is made of: Space with dark energy 73% by mass Dark matter Protons Neutrons Electrons Photons Neutrinos 23% by mass 4% by mass <1% by mass <1% by mass <1% by mass <1% by mass Image: flickr.com