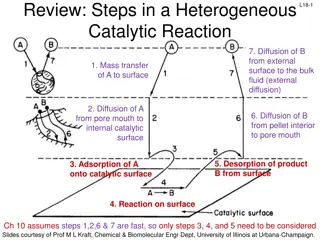
Steps in Research Process: A Comprehensive Guide
Research is a systematic process aimed at investigating specific problems or questions to generate new knowledge or validate existing theories. The research process involves eight essential steps, including identifying the problem, evaluating literature, formulating hypotheses, designing the research, collecting and analyzing data, interpreting results, and report writing. Each step plays a crucial role in guiding the research direction and ensuring the study's success.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SeminarPpt.com Seminar On Step in Research Process Submitted to: Seminarppt.com Submitted By Seminarppt.com
Table of Contents 1. 2. Introduction to Research Steps in Research Step 1: Identify the Problem. Step 2: Evaluate the Literature. Step 3: Create Hypotheses. Step 4: The Research Design. Step 5: Data Collection. Step 6: Data Analysis. Step 7: Interpretation of Results. Step 8: The Report-writing and presentation. 3. 4. Future Research Directions Conclusion
Introduction to Research Research is a systematic and organized effort to investigate a specific problem or question. It aims to generate new knowledge, validate existing theories, or find solutions to issues.
Steps in Research There are Eight steps in Research and they are: Step 1: Identify the Problem. Step 2: Evaluate the Literature. Step 3: Create Hypotheses. Step 4: The Research Design. Step 5: Data Collection. Step 6: Data Analysis. Step 7: Interpretation of Results. Step 8: The Report-writing and presentation.
Steps in Research Step 1:Identifying the problem This step involves defining the research problem clearly and concisely. A well-defined problem sets the direction for the entire research process and determines the scope of the study.
Steps in Research Step 2:Literature Review A literature review involves examining existing research related to your topic. It helps to identify gaps in current knowledge, provide context for your study, and justify the need for your research.
Steps in Research Step 3:Formulating Hypothesis A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It provides a focus for the research and a basis for collecting and analyzing data.
Steps in Research Step 4:Research Design Research design is the blueprint for conducting the research. It includes selecting the research methods, deciding on the sampling techniques, and planning how data will be collected and analyzed.
Steps in Research Step 5:Data Collection Data collection involves gathering information from various sources. It can be done through surveys, interviews, experiments, observations, or secondary data sources.
Steps in Research Step 6: Data Analysis Data analysis involves processing the collected data to uncover patterns and relationships. Statistical tools and software are often used to analyze quantitative data.
Steps in Research Step 7: Interpretation of Results Interpreting results means making sense of the data collected and analyzed. It involves explaining what the results mean in the context of the research question and hypothesis.
Steps in Research Step 8: The Report-writing and presentation. Reporting and presentation involve communicating the research findings to a wider audience. This can be done through written reports, academic papers, or presentations at conferences.
Limitations of Research Every research study has limitations. Sample Size: A small sample size may limit the generalizability of findings. Methodological Constraints: Limitations in research design or data collection methods can impact results. External Variables: Factors outside the control of the researcher that may influence outcomes.
Future Research Directions Addressing Gaps: Exploring areas not covered or inadequately addressed by the current study. New Variables: Investigating additional variables or different contexts to expand understanding. Methodological Improvements: Utilizing more advanced or diverse research methods to enhance the reliability of results. Longitudinal Studies: Conducting long-term studies to observe changes and trends over time.
Case Study Example A case study example provides a practical application of the research process. It illustrates how theoretical concepts are implemented in real-world scenarios. For instance: Topic: The impact of digital marketing on consumer behavior. Approach: A mixed-methods study combining surveys and in- depth interviews with consumers. Findings: Insights into how social media influences purchasing decisions and the effectiveness of different marketing strategies.
Conclusion The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the research, reinforces the importance of the study, and provides recommendations for practice or further research. It highlights the significance of the results and how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
References References Wikipedia.org Google.com Seminarppt.com Studymafia.org











![[PDF⚡READ❤ONLINE] Gemini 4: An Astronaut Steps into the Void (Springer Praxis B](/thumb/21620/pdf-read-online-gemini-4-an-astronaut-steps-into-the-void-springer-praxis-b.jpg)