Process Control Actuators Overview
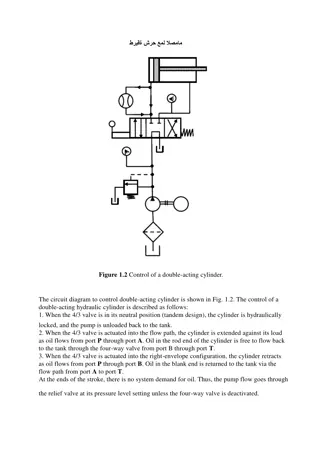
Explore the role of actuators in process control systems, including control valves and pumps. Learn about pneumatic control valves, centrifugal pumps, peristaltic pumps, and AC motors controlled by frequency converters. Understand the key components and principles involved in motor control with frequency converters in industrial applications.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Course: Process Control, NMBU Dec 2017 - April 2018 Actuators By Finn Aakre Haugen, PhD, TechTeach (finnhaugen@hotmail.com) F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017. 1
2 Where is the actuator in the control loop? Valves Pumps Motors Heaters d u y ySP PID Actuator Process controller Control loop ym,f ym Meas.- filter Sensor F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017.
Control valve 3 Here is a pneumatic control valve, using air pressure to manipulate the valve opening. Valves are used to manipulate gas and liquid flows. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Control_valves] F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017.
Principal design of a pneumatic control valve: Control valve Air pressure supply Reguleringsventil Forsyningstrykk 1,2 bar Control air pressure 4-20 mA 0,2-1 bar P I Styresignal (p drag fra reg.) Control signal (from controller) IP-omformer (fra str m til trykk) IP-converter (from current (I) to pressure (P)) Spring Indicator displaying valve opening Packing box Plug Fluid outlet Seat Fluid inlet F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017. 4 [http://nn.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reguleringsventil + FH]
5 Centrifugal pump: The most common pump type in industry. F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pump]
6 Peristaltic pump (displacement pump): Applied for small, precise liquid flows, in dosing applications. Rotational speed is manipulated with voltage or current. F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pump]
7 AC-motors (Fans; Pumps; Conveyors; Compressors.) AC-motors are controlled (manipulated) by frequency converters. F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_heating]
Example: Motor control The purpose of a frequency converter is to convert the "fixed" alternating mains voltage (e.g. 230 V, 50 Hz) to an alternating voltage with variable amplitude and frequency appropriate to control the rotational speed of an AC-motor. Nettspenning (3 faser) Frekvens- omformere PLS AC-motorer Digital kommunikasjon Amplitude og frekvens manipuleres av frekvensomformeren 8 F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017.
9 Actuator: Heating element (resistor) Varmeelementer Varmetr d Bruk av varmetr d It can be manipulated using PWM... (next slide) [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_heating] F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017.
10 Principle of pulse-width modulation (PWM) : Purpose of PWM: To deliver approximately continuous (analog) power to a process using relatively quick On/Off- switching of the power source. Typical applications are electrical heaters and motors. F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017.
11 Application of PWM for temperature control The SSR (Solid State Relay) switches the mains in/out over the heating element. In average the process receives power which is proportional to the control signal from the PID controller, hence analog power supply, even if the power is actually turned on/off! Process 230 V Tp Uhigh ~ Temp.- setpoint uPID [%] SSR D = Approx. analog power supply to process (due to PWM) Heating element (resistor) uPID [%] PID PWM Scaling (Solid State Relay) TT F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017.
12 Simulator of PWM-controlled actuator in a PID control system (download and unpack zip-file, then run exe-file) F. Haugen. Process Control. NMBU. 2017.