Pioneers in Biology: Linnaeus, Darwin, and Cell Theory
Carl Linnaeus revolutionized taxonomy by classifying numerous animals in his work Systema Naturae. Charles Darwin's evolutionary theory proposed that all species evolve from a common ancestor through natural selection. The cell theory, proposed by Schwann and Schleiden in 1838, established cells as the basic units of living tissues, influencing various biological disciplines.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
3.Classification and Taxonomy (Carl Linnaeus -1707 1778) Linnaeus was a Swedish famous botanist, physician, and zoologist who is considered to be the father of modern taxonomy. During his life, and especially during the 1750s, he classified an extraordinary number of animals that he collected on his own. One of his most prominent works Systema Naturae, where he introduced his taxonomy.
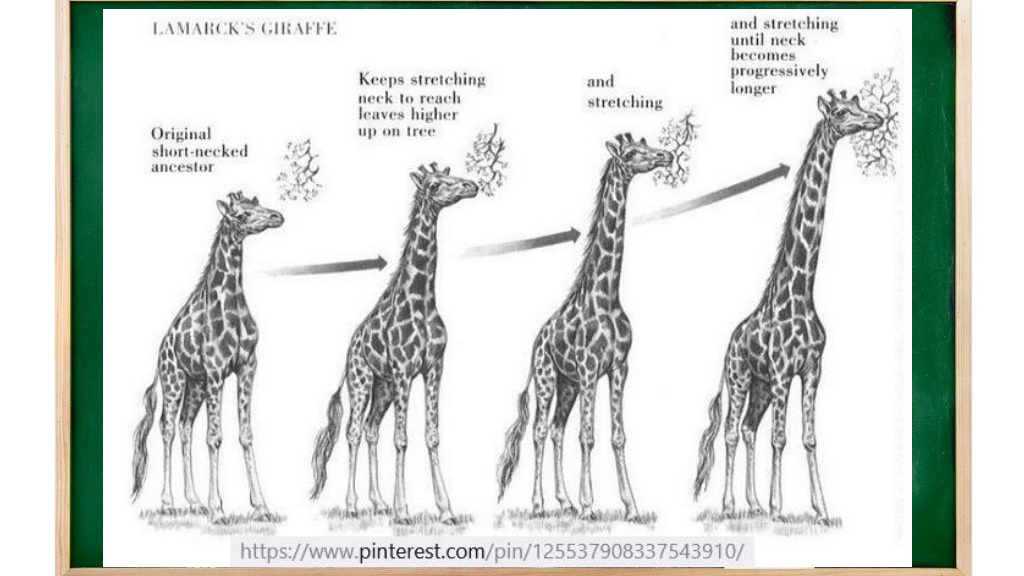
4. Evolutionary Theory Charles Darwin (1809 1882) Darwin is, by far, the most famous of all the zoologists on this list. This English scientist is best groundbreaking book On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, published in the 19th century. known for his
According to Darwin, all species have come from a common ancestor and have evolved through the process of natural selection. His continuous insights and studies on different classes resulted in an immense collection of data, which was later published through his books. of animals have
5.The Schwann and Matthias 1838) cell concept (cell-theory Jakob Schleiden : Theodor 1837- fundamental according to which cells are held to be the basic units of all living tissues. First proposed by German scientists: ( Theodor Schwann Schleiden in 1838,) scientific theory of biology and Matthias Jakob
5.The Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden : 1837-1838) cell concept (cell-theory Theodor the theory that all plants and animals are made up of great conceptual advance in biology and resulted in renewed attention to the living processes that go on in cells. cells marked a
5.The Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden : 1837-1838) cell concept (cell-theory Theodor This concept influenced many biological disciplines, including embryology, in important in determining the way in which a fertilized egg develops into a new organism. that cells of which are
5.The Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden : 1837-1838) cell concept (cell-theory Theodor The unfolding of these events called epigenesis by Harvey was described notably the German-trained embryologist Karl von Baer, who was the first to observe a mammalian egg within an ovary. Another German-trained embryologist, Christian Heinrich Pander, introduced in 1817 the concept of germ, or primordial, tissue layers into embryology by various workers, comparative
This biological disciplines, including that of embryology, in which cells are important in determining the way in which a fertilized egg develops into a new organism. concept influenced many
This concept influenced many biological disciplines, including that of embryology, in which cells are important in determining the way in which a fertilized egg develops into a new organism. The unfolding of these events called epigenesis described by various workers, notably the German- trained comparative embryologist Karl von Baer, who was the first to observe a mammalian egg within an ovary. Another German-trained embryologist, Christian Heinrich Pander, introduced in 1817 the concept of germ, or primordial, tissue layers into embryology. by Harvey was
The cell concept, which asserts that all living organisms are composed of cells and that the cell is the fundamental unit of life, has significantly influenced zoology classification. It has provided a basis for understanding comparing organisms, and utilizing molecular techniques. Zoologists use cellular characteristics to assess evolutionary relationships, construct phylogenetic trees, animals within the taxonomic microscopy and genetics grounded in the cell theory have enabled zoologists to refine classifications and explore cellular details. In essence, the cell theory has fundamentally shaped zoology's approach to classifying classification systems with evolutionary relationships and cellular characteristics cellular structure, and organize Advances hierarchy. in animals, aligning