Darwin and the Theory of Evolution: A Comprehensive Overview
Darwin's Theory of Evolution encompasses the concepts of organisms changing over time and life evolving through natural selection. Influenced by scientists such as James Hutton, Jean Baptiste Lamarck, and Alfred Russel Wallace, Darwin's theory culminates in the idea of evolution by natural selection, a process where advantageous traits lead to changes in living things over time. This summary provides insights into the development of Darwin's ideas and the contributions of various scientists towards the theory of evolution.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
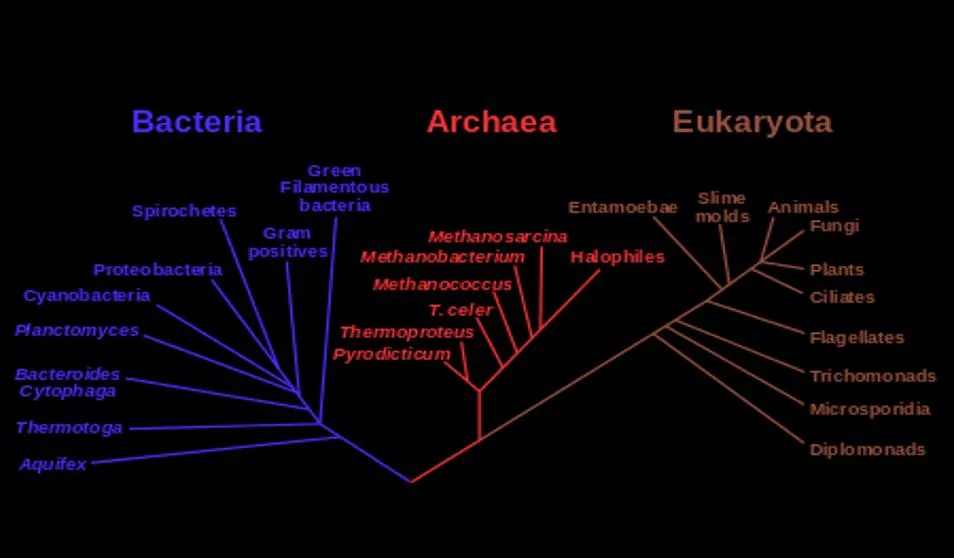
DARWIN AND THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION
Darwins Theory at a Glance Darwin s Theory of Evolution actually contains two major ideas: organisms change over time, life on Earth has changed as descendants diverged from common ancestors in the past evolution occurs by natural selection, the process in which living things with beneficial traits produce more offspring than others do resulting in changes in the traits of living things over time
Where did Darwins Ideas Come From???? Voyage of the HMS Beagle Galapagos Islands
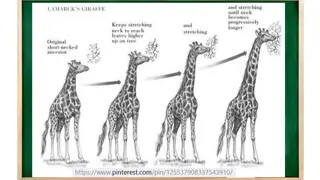
Scientists Who Influenced Darwin s Ideas James Hutton (1726-1797) Scottish geologist; proposed that the Earth is shaped by geological forces t over extremely long periods of time; estimated that the Earth was millions of years old not thousands of years old. Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744 1829) French naturalist.; the first scientists to propose that species change over time. Charles Lyell (1797 1875) English geologist.; book, Principles of Geology, argued that gradual geological processes have gradually shaped Earth s surface Thomas Malthus (1766 1834) English economist; essay titled On Population, argued that human populations grow faster than the resources they depend on. Georges Curvier (1769-1832) French naturalist.; developed support for the idea that fossil remains of unknown organisms were not just the remains of some type of freak of nature but were actually the remains of organisms that had existed at one point in history and had since become extinct. Adam Sedgewick (1785-1873) English geologist; proposed the Devonian period and the Cambrian period of the Earth s geological timescale based on his observations and the data he had collected while studying Welsh rock strata.
Wallaces Theory Wallace s adventures took place 20 years after Darwin s but Darwin had not published his ideas . Did you ever hear the saying that great minds think alike??? It certainly applies to Charles Darwin and another English naturalist named Alfred Russel Wallace. Wallace lived at about the same time as Darwin. He also traveled to distant places to study nature. Wallace wasn t as famous as Darwin. However, he developed basically the same Theory of Evolution. While working in distant lands, Wallace sent Darwin a paper he had written. In the paper, Wallace explained his evolutionary theory. This served to confirm what Darwin already thought.
Darwins Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Darwin spent many years thinking about the work of Lamarck, Lyell, and Malthus, what he had seen on his voyage, and artificial selection. What did all this mean? How did it all fit together? It fits together in Darwin s theory of evolution by natural selection. It s easy to see how all of these influences helped shape Darwin s ideas.
Evolution of Darwins Theory Like Lamarck, Darwin assumed that species can change over time. The fossils he found helped convince him of that. From Lyell, Darwin saw that Earth and its life were very old; there had been enough time for evolution to produce the great diversity of life Darwin had observed. From Malthus, Darwin knew that populations could grow faster than their resources. This overproduction of offspring led to a struggle for existence, in Darwin s words. Darwin coined the term fitness to refer to an organism s relative ability to survive and produce fertile offspring. Nature selects the variations that are most useful. Therefore, he called this type of selection, natural selection. Darwin knew artificial selection could change domestic species over time. He inferred that natural selection could also change species over time. In fact, he thought that if a species changed enough, it might evolve into a new species. From artificial selection, he knew that some offspring have chance variations that can be inherited.; offspring with certain variations might be more likely to survive the struggle for existence and reproduce.
Origins of Species Finally published on 24 November 1859
Lesson Summary Darwin s theory of evolution by natural selection states that living things with beneficial traits produce more offspring than others do. This produces changes in the traits of living things over time. During his voyage on the Beagle, Darwin made many observations that helped him develop his Theory of Evolution. His most important observations were made on the Gal pagos Islands. Darwin was influenced by other early thinkers, including Lamarck, Lyell, and Malthus. He was also influenced by his knowledge of artificial selection. Wallace s paper on evolution confirmed Darwin s ideas. It also pushed him to publish his book, On the Origin of Species. The book clearly spells out his theory. It also provides evidence and logic to support it.