Photosynthesis in Plants
Photosynthesis is a vital process where plants convert light energy into chemical energy to produce their food. This section covers the two-stage process of photosynthesis, including light reactions and carbon fixation, and explores the factors affecting plant growth. Learn about the importance of photosynthesis, the energy flow it creates, and how plants change light energy into chemical energy essential for all living organisms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
National 5 Biology Unit 3 Life on Earth Section 16 Photosynthesis
Learning Intentions On completion of this unit you should be able to: Describe photosynthesis as a two-stage process By the end of this section you should be able to: Describe the light reactions light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in the chloroplasts and is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP which is used in the production of glucose. The importance of diffusion in the movement of carbon dioxide and oxygen into and out of the leaf cells. Describe the carbon fixation phase as being a series of enzyme controlled reactions which use hydrogen and ATP (produced by the light reactions) with carbon dioxide to produce sugar. State that the chemical energy in sugar is available for respiration, or that it can be converted into other substances, such as starch (storage) and cellulose (structural). Describe limiting factors such as carbon dioxide concentration, light intensity, and temperature and their effects on photosynthesis and plant growth. To analyse limiting factor graphs.
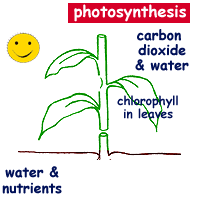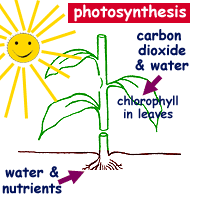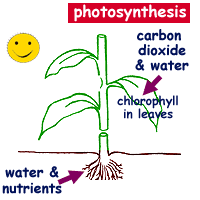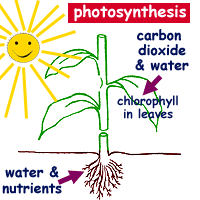
What is photosynthesis? Plants make their own food by photosynthesis. This process is a chemical reaction that uses light energy. light energy The word photosynthesis comes from the Greek language: photo means light synthesis means putting together Photosynthesis just means putting together with light .
Photosynthesis is Important! Why? Energy Flow Green plants are called the producers.
Photosynthesis forward_arrow_colour
Photosynthesis is Important! Plants change light energy to chemical (food) energy If plants didn t do this there would be no animals! Sunlight energy Animals eat plants for the carbohydrate Green plants make carbohydrate Raw materials from the environment
What Kind of Energy Source? Plants make the energy source glucose. This is a carbohydrate. CARBOHYDRATE Hydrogen Oxygen Carbon
Testing for Starch Starch testing animation
The Need for Light The experiment shows the importance of light in photosynthesis using the presence of starch as evidence that photosynthesis has occurred
Photosynthesis Glucose formed during photosynthesis is used by the plant cells to carry out respiration to provide energy for all the cells reactions Some glucose is converted to starch for storage Some glucose is converted to cellulose to build cell walls
Starch Production during 24hours DARK DIM BRIGHT LIGHT DIM DARK Dry mass of leaf Midnight Noon Midnightt Time of Day
Raw Materials The Need for Carbon Dioxide Bell Jar A B Test for Starch
Photosynthesis: word equation activity forward_arrow_colour
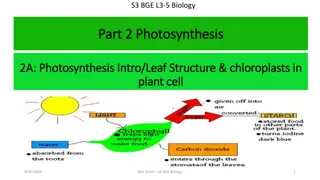
The Structure of a Leaf Leaves Leaves photosynthesis by having a large surface area, and contain stomata (openings) to allow carbon dioxide into the leaf. These design features can result in the leaf losing a lot of water. The cells inside the leaf have water on their surface. Some of this water evaporates, and the water vapour can then escape from inside the leaf by diffusion. To reduce loss the leaf is coated in a wax cuticle to stop the water vapour escaping through the epidermis. Leaves usually have fewer stomata on their top surface to reduce this water loss. are adapted for
Structure Epidermis Function the protective outer layer of cells on the surface of a leaf. Palisade Mesophyll Spongy Mesophyll elongated cells located under the epidermis. contains most of the leaf s chlorophyll. located below the palisade mesophyll. irregularly-shaped cells with many air spaces between. contains some chlorophyll. contains a collection of xylem and phloem vessels. Vein gases dissolve in water vapour for photosynthesis. Moist air space Guard cells Stoma control the opening and closing of stoma. openings in the surface of a leaf for gas exchange.
The Two Stages of Photosynthesis There are two stages of chemical reactions that make up the process of photosynthesis. The first stage in photosynthesis is called Photolysis. The second stage is called Carbon Fixation
Photolysis The first stage of photosynthesis is photolysis - the splitting of water Light energy is captured by the chlorophyll in chloroplasts and used to split water into oxygen gas and hydrogen The oxygen diffuses out of the cell. http://www.twigonglow.com/films/photosynthesis-1186/
Photolysis The sun Light energy absorbed by chlorophyll Hydrogen acceptor NADP ADP + Pi Water (H2O) H2 ATP O2 Reduced hydrogen acceptor NADPH (energy) passed to second stage released as gas passed to second stage
Carbon Fixation The second stage of photosynthesis is carbon fixation. Carbon Dioxide undergoes a series of enzyme controlled reactions and combines with the hydrogen from photolysis to form glucose. This also requires the ATP which was formed in photolysis. Both stages of photosynthesis occur in the chloroplast
Carbon Fixation Energy Hydrogen ATP ADP + Pi Reduced hydrogen acceptor (loaded with H2) Glucose Stored as starch or used to make cellulose CO2
Starch and Cellulose Name Structure Long chains of glucose molecules made into spherical grains Starch Cellulose Long chains of glucose molecules made into ribbon-like strands Properties Storage carbohydrate Structural carbohydrate Build cell walls Function Store of food that can be converted back to sugar for energy when needed
Limiting Factors in Photosynthesis A limiting factor is some factor which when in short supply prevents photosynthesis proceeding more quickly The rate of photosynthesis can be measured by The production of oxygen The uptake of carbon dioxide The production of carbohydrate
Limiting Factors The rate of photosynthesis may be limited by Light Intensity Carbon dioxide concentration Temperature Removing any limiting factor allows early crops to be produced
The Elodea Bubbler Elodea is a type of pondweed. It is a good plant to use to study the effects that limiting light has on photosynthesis Use this Multimedia Science school to perform a virtual version of this experiment or look at the demo set up to answer the questions.
Questions for the Elodea Bubbler experiment Plot your results on a graph. How does the distance from the light source relate to the light intensity? What gas do you think the bubbles contain? Using your data and your graph, describe the trend that it shows. Why do you think this trend occurs? Can you think of any other factors, apart from light intensity, which could affect the rate of photosynthesis in Elodea? How do factors affect photosynthesis? How could you improve this experiment to achieve more precise, accurate and reliable results?
Results Rate of photosynthesis [number of bubbles/min] 0 6 15 26 35 38 38 Light Intensity 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
Light intensity as a Limiting Factor Look at this graph. What does the graph show us about light intensity as a limiting factor?
Light Intensity as a Limiting Factor Without enough light, a plant cannot photosynthesise very quickly, even if there is plenty of water and carbon dioxide. Increasing the light intensity will boost the speed of photosynthesis to a certain rate where it will then level off. At this point it cannot increase anymore.
Results Carbon Dioxide Concentration [%] Rate of photosynthesis [number of bubbles/min] 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0 1 2 3 5 6 6
Carbon dioxide concentration as a limiting factor State the relationship between carbon dioxide concentration and the rate of photosynthesis. Answer: As the concentration of Carbon dioxide increases the rate of photosynthesis increases up to a maximum rate. After this point the carbon dioxide is no longer the limiting factor.
Carbon dioxide concentration as a limiting factor Sometimes photosynthesis is limited by the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air. Even if there is plenty of light, a plant cannot photosynthesise if there is not enough carbon dioxide available.
Results Temperature [oC] Rate of photosynthesis [number of bubbles/min] 0 5 0 6 9 13 18 18 18 9 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Temperature as a limiting factor What does this graph tell us about temperature as a limiting factor on the rate of photosynthesis?
Temperature as a limiting factor If it gets too cold, the rate of photosynthesis will decrease. Plants cannot photosynthesise if it gets too hot.
Word ATP Meaning carbon dioxide carbon fixation cellulose chlorophyll Diffusion chloroplast glucose
Light Reactions limiting factor oxygen
Stomata and Guard Cells Turgid full of water stoma is open Flaccid stoma is closed Guard cells surround each stoma. They regulate the rate of transpiration by opening and closing the stomata. As the water is used up