Photosynthesis in Higher Biology
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into carbohydrates. This revision guide covers the photosynthesis word equation, stages, uses of products, and the role of light and pigments. It explains the absorption of light by leaves and the importance of chlorophyll and accessory pigments in capturing light energy. Understanding the absorption and action spectra is key to comprehending how plants utilize different wavelengths for photosynthesis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Higher Biology Unit 3 3.1 - Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Revision: Answer these questions on photosynthesis from N5? What is the photosynthesis word equation? How many stages are there to photosynthesis? Give 2 examples of the uses of the product of photosynthesis? What is the name of the chemical that traps light during photosyntheis?
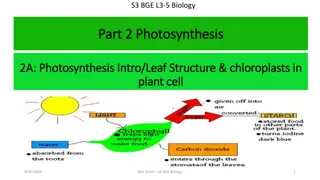
Light Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants trap light energy and use it to produce carbohydrates Light is a form of electromagnetic energy that travels in waves
The distance between two crests on a wave is called the wavelength and is measured in nanometres (nm). (1 nm = 10-9m) Wavelength
Visible Light The spectrum of visible light is a band of light with wavelengths between 380nm and 750nm
Absorption, transmission and reflection When light comes into contact with a substance it can be absorbed, transmitted or reflected
Light absorption by leaves Leaves contain several pigments that absorb light The different pigments in a leaf cell absorb different wavelengths of light
Leaf Pigments The main pigments in leaves are: Chlorophyll a Chlorophyll b Carotene Xanthophyll
Absorption Spectrum This shows the wavelengths of light absorbed by each pigment found in leaves Action Spectrum This shows the effectiveness of different wavelength of light at bringing about photosynthesis
When the absorption and action spectra are compared a close correlation is found to exist Chlorophyll a and b absorb light mainly from the blue and red regions of the spectrum The other pigments absorb light from other regions and pass the energy onto chlorophyll (these are known as accessory pigments)
Having pigments that are able to absorb light at different wavelengths means that the plant is able to photosynthesis more effectively
Photosynthetic pigments are contained within the grana of the chloroplasts This is therefore where absorption of light energy and photosynthesis take place Carbon fixation takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast