Periodic Trends: Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
The Periodic Table displays a systematic organization of elements based on their increasing atomic number, leading to periodic patterns in their physical and chemical properties. Key trends like Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy provide insights into the size of atoms and the energy required to remove electrons. The Atomic Radius increases down a group and decreases across a period due to changes in energy levels and electron density. Conversely, Ionization Energy decreases down a group and increases across a period as valence electrons are held closer to the nucleus. Understanding these trends enhances our comprehension of elemental behavior and properties.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
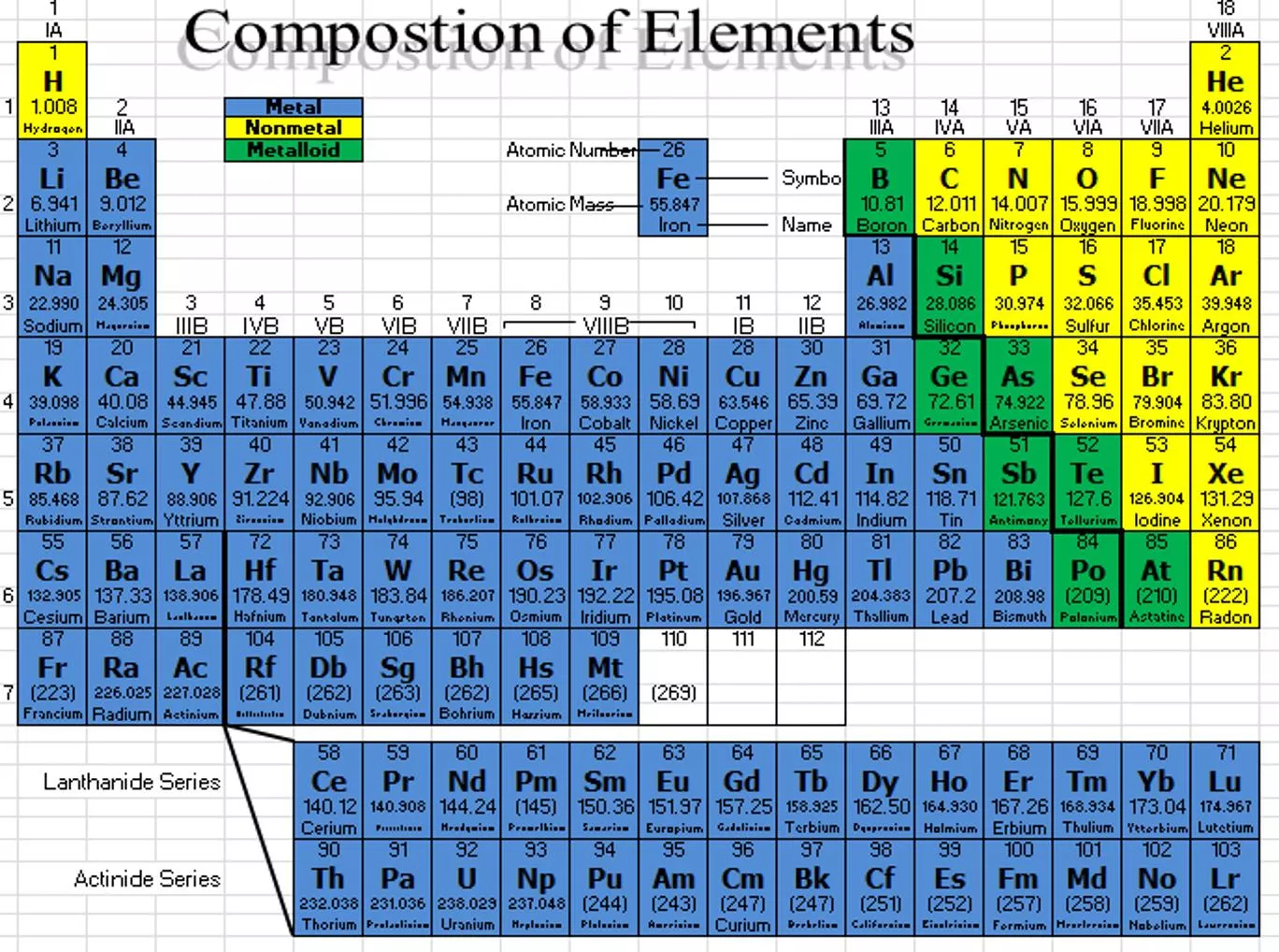
Periodic Law When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties.
There are many trends in the periodic table, but you must know the reasoning behind 3 of them
Atomic Radius: Gives us an idea of the size of an atom The trend: A.R. increases as you move down a group A.R. decreases as you move across a period from left to right
Why? As atomic # increases, the number of protons and electrons increases To accommodate the electrons, there must be more energy levels. This is why A.R. increases as you move down a group. As you go across a period, an atom is not gaining energy levels The atom is still gaining protons and electrons, though, so the atom becomes more and more dense This causes the electrons to be drawn closer to the positive nucleus. This is why A.R. decreases as you move across a period.
Ionization Energy The energy required to remove an electron from the valence shell of an atom The trend: I.E. decreases as you go down a group I.E. increases as you go across a period from left to right
Draw the arrows for the trend on the periodic table sheet!
Why? As you go down a group, the atomic radius increases This means that the valence electrons in a large atom are further away from the nucleus, than the valence electrons in a small atom If the valence electrons are far away from the positive nucleus, it will take less energy to remove them. Large atoms tend to be lower down in a group. This is why I.E. decreases as you go down a group. As you go across a period, atomic radius decreases This means the electrons will be held closer and closer to the positive nucleus as you go across the period This means that atoms of elements to the right of the periodic table will have valence electrons that are harder to remove. This is why I.E. increases as you go across a period.
Electronegativity the tendency of an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with other elements The trend: E.N. decreases as you go down a group E.N. increases as you go across a period left to right
Draw the arrows for the trend on the periodic table sheet!
Why? As you go down a group, the atomic radius increases This means that in elements lower down in the group, the additional electrons will not feel a strong attraction to the nucleus, which is already surrounded by electrons. This is why E.N. decreases as you go down a group. As you go across a period, the atomic radius decreases This means that in elements further to the right, additional electrons will feel a stronger attraction to the nucleus than in elements further to the left. This is why E.N. increases as you go across a period.