Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 1 Summary
Exploring Unit 1 of Chemistry revision, we delve into bonding of the first 20 elements, trends in the periodic table, structure and bonding concepts, and oxidation and reduction reactions. Topics covered include melting points, boiling points, covalent radius, ionization energy, types of bonding, intramolecular and intermolecular forces, and redox equations. Understand the principles behind various chemical phenomena to enhance your knowledge in chemistry.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
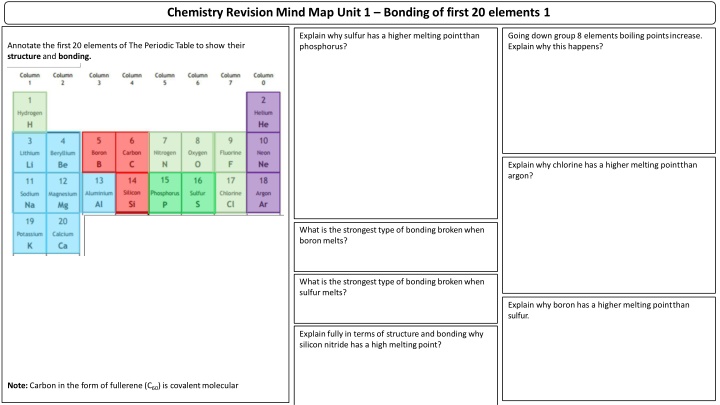
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 1 Bonding of first 20 elements 1 Explain why sulfur has a higher melting pointthan phosphorus? Going down group 8 elements boiling pointsincrease. Explain why this happens? Annotate the first 20 elements of The Periodic Table to show their structure and bonding. Explain why chlorine has a higher melting pointthan argon? What is the strongest type of bonding brokenwhen boronmelts? What is the strongest type of bonding brokenwhen sulfurmelts? Explain why boron has a higher melting pointthan sulfur. Explain fully in terms of structure and bonding why silicon nitride has a high meltingpoint? Note: Carbon in the form of fullerene (C60) is covalentmolecular
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 1 Trends in The Periodic Table 2 The covalent radius is a measure ofwhat? Calculate the energy required for the followingreaction; Na+ (g) Na 3+ (g) + 2e- Explain why the first ionisation of sodium is much lower than the second ionisationenergy Explain the trend in covalent radius as you go across a period Explain the trend in ionisation energy across a period Explain the trend in covalent radius as you go down agroup Explain the trend in ionisation energy down agroup Explain why the covalent radius of sodium is larger thanthe ionic radius Explain the termelectronegativity Explain why there is a large difference between the thirdand fourth ionisation energies ofaluminium? Explain the trend in electronegativity across aperiod Define the term first ionisation energy Explain the trend in electronegativity down agroup Write the equation to show the third ionisation energy of chlorine.
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 1 Structure and Bonding 3 What is a covalent bond Decide if each of the following are polar or non-polarmolecule and explain youranswer Explain how London dispersion forcesarise What is a polar covalent bond What is a non-polar/pure covalent bond Explain how permanent dipole- permeantdipole interactionarise Annotate HCl below to show the partial charge on each atom and the location ofelectrons. H - Cl Name the three types of intramolecular bonding. Are these types of bondingstrong? Explain how Hydrogen bondingarises. If a compound has the greatest ionic character, what does this mean in terms of electronegativitydifference? What is a polar molecule Explain why ethanol is soluble inwater. Name the three types of intermolecular bonding. Which isthe strongest? What is a non polar/pure molecule
Chemistry Revision Mind Map Unit 1 Oxidation and Reduction 4 In a redox equation what is always cancelledout: Oxidation involves the electrons. of Name three compounds which are strong oxidising agents? Reduction involves the electrons. of What is a use of hydrogen peroxide as an oxidisingagent? Write the ion electron equation for the following reaction: What is an oxidisingagent? Potassium permanganate reacting with iron metal producing Iron(III) oxide in the presence of an acidic solution. What does the term electronegativitymean? What is a reducing agent? If an element is very electronegative will it be an oxidising agent or reducingagent? Where in your data booklet will youfind strong reducing agents? In the followingequation: Mg (s) + Zn2+ (aq) Mg2+ (aq) + Zn (s) For the following redoxequation: 1. Write the oxidationreaction Where in your data booklet will youfind strong oxidising agents? C6H12O6 + Cu2+ + H2O C6H12O7 + Cu+ + 2H+ 2. Write the reductionreaction Write the ion-electron equation for the oxidationreaction: Name a compound which is a strong reducing agent? 3. Name the oxidisingagent Write the ion-electron equation for the reductionreaction: 4. Name the reducingagent

![[PDF⚡READ❤ONLINE] Zen Mind, Beginner's Mind: 50th Anniversary Edition](/thumb/20459/pdf-read-online-zen-mind-beginner-s-mind-50th-anniversary-edition.jpg)