Overview of Welding Methods for Joining Metal Parts
Welding is a process of joining metal parts by forming interatomic bonds. Explore various welding methods like fusion, pressure, electric arc, cold, gas, friction, plasma, and ultrasonic welding. Understand electric arc welding principles, including manual metal-arc welding and automatic submerged arc welding. Learn about resistance welding techniques such as butt and flash welding, their advantages, applications, and characteristics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
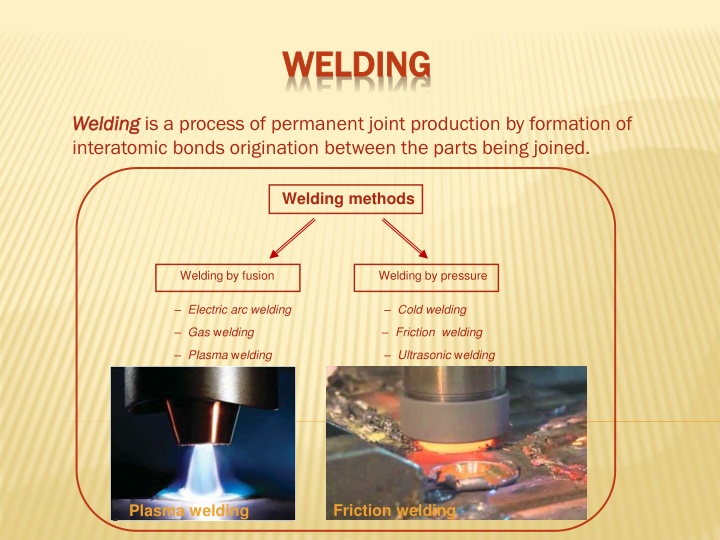
WELDING WELDING Welding Welding is a process of permanent joint production by formation of interatomic bonds origination between the parts being joined. Welding methods Welding by fusion Welding by pressure Electric arc welding Cold welding Gas welding Friction welding Plasma welding Ultrasonic welding Friction welding Plasma welding
WELDING WELDING Electric arc welding U, V b Static volt-ampere arc characteristic ( ); external characteristics of current sources for welding (b) Scheme of direct current welding arc: 1 electrode; 2 base metal; 3 bath of liquid metal; 4 arc column The welding arc is a powerful stable electric discharge burning between electrodes in the atmosphere of ionised gases and vaporised metals.
WELDING: WELDING: Electric arc welding Manual metal-arc welding circuit diagram: 1 A.C. mains supply; 2 neutral; 3 live; 4 fused switch; 5 primary cables; 6 current control; 7 welding set; 8 welding cable; 9 electrode holder; 10 electrode; 11 work-piece; 12 work support; 13 return current cable; 14 and 15 earth Diameter of electrode d is chosen depending on welded metal thickness: where s is the thickness of welded metal, mm.
WELDING WELDING Electric arc welding 2 Automatic submerged arc welding (SAW) Automatic submerged arc welding (SAW): : 1 sliding conductor ; 2 feeder; 3 welding wire; 4 liquid slag; 5 layer of flux; 6 slag crust; 7 welded seam; 8 basic metal; 9 pool of liquid metal; 10 arc zone Advantages Advantages of the process: the most productive way of welding; high quality of a seam; low production cost of 1 m of seam; welding metal up to 20 mm thickness for one pass without cutting of edges. Application Application: : in serial and mass production, such as manufacturing of boilers, tanks, ship hulls, bridge beams, welded pipes with a direct and a spiral seam, wheels.
WELDING WELDING Resistance welding Resistance butt welding (RW) Resistance butt welding (RW): : 1 current supply clips; 2 billets; 3 motionless plate; 4 mobile plate; 5 guide; 6 welding transformer; 7 flexible buses Flash welding (FW) Flash welding (FW) Advantages Advantages of the process: cleaning of surfaces is not necessary; welding parts of a complex section and with the different shape of the section; dissimilar metals can be welded. Application Application: : welding of rings, wheels, the end tool (drills, mills, taps), rods, rails, reinforcement, pipes.