Overview of Histology: Study of Tissues and Organs
Histology involves studying the tissues of the body and how they form organs. Tissues consist of cells and extracellular matrix, with functions like support, nutrient transport, and waste removal. The human body comprises epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues, each with specific functions and structures. Epithelial tissue forms protective linings, aids in absorption and secretion, and plays crucial roles in sensory perception and regeneration. Understanding the basics of tissue types and functions is essential for comprehending the body's biological processes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
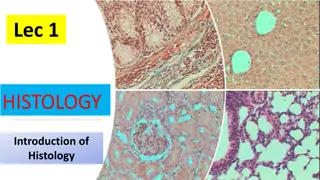
Histology Histology : is the study of the tissues of the body and how these tissues are arranged to constitute organs. Tissues have two interacting components: A. Cells . B. Extracellular matrix (ECM).which is consist of many kinds of macromolecules. The (ECM) function : 1. Supports the cells and the fluids that transports nutrients to the cells . 2. Carries away their catabolites and secretory products.
Types of Tissue Despite its complexity, the human body is composed of only four basic types of tissue: 1) Epithelial tissue. 2) Connective tissue. 3) Muscular tissue. 4) Nervous tissue. 1. Epithelial tissue it is a tissue in which cells are bound tightly together structurally and functionally to form a sheetlike or tubular structure with little extracellular material between the cells
All epithelial cells in contact with connective tissue at basal surfaces which referred as the Basement membrane which is a thin extacellular layer of specialized proteins , its components: a. Attach epithelia to connective tissue. b. Regulate (filter) substances passing from connective tissue to epithelia. c. Guide tissue during regeneration after injury.
Functions of epithelial tissue 1. Covering. 2. Lining. 3. Protecting surfaces. 4. Absorption. Ex. Intestinal lining 5. Secretion. Ex. Parenchymal cells of glands 6. Specific cells of certain epithelia may be contractile or specialized sensory cells. Ex1. Taste buds Ex. Epidermis Ex2. Olfactory epithelium 7. Because epithelial cells line all external and internal surfaces of the body, all substances that enter or leave tissues and organs must cross an epithelium.