Leveraging Lower Bands for RTS/CTS Protection in_mmWave Technology
Multiple contributions aim to reduce complexity and power consumption in IMMW technology. Leveraging lower bands for RTS/CTS protection is discussed as a potential solution to the hidden node problem in mmWave transmissions. Various proposals and challenges related to RTS/CTS for sub-7GHz and mmWave links are explored, highlighting possible solutions for improving transmission reliability.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
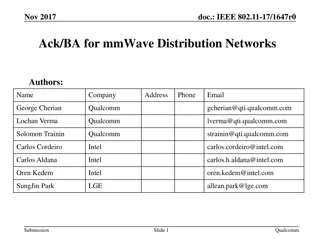
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 mmWave RTS/CTS Date: 2024-01-15 Authors: Name Affiliations Address Phone email llanante@ofinno.com Leonardo Lanante Ofinno Serhat Erkucuk Jeongki Kim Jiayi Zhang Tuncer Baykas Submission Slide 1 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 Abstract Multiple contributions [1-4] agree to aggressively reduce complexity and power consumption of IMMW technology. Some proposals mention that management frames (discovery, association, scheduling) can be supported in the lower bands. In this contribution, we discuss leveraging the lower bands for RTS/CTS protection. Submission Slide 2 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 mmWave Hidden Node Problem mmWave transmissions are much more prone to the hidden node problem than sub-7GHz links due to antenna directionality. Q-omni RTS/CTS range Omnidirectional pattern Directional pattern Submission Slide 3 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 RTS/CTS for sub-7GHz Links Due to generally omnidirectional antenna pattern, RTS/CTS can be reliably received by all STAs in the vicinity of the TXOP holder (AP) and TXOP responder (STA 1) BA CTS AP DATA RTS STA 1 STA 2 hears STA 1 NAV STA 2 STA1 STA3 AP STA2 NAV STA4 STA 3 STA 3 hears AP NAV STA 4 STA 4 hears AP and STA 1 Submission Slide 4 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 RTS/CTS for mmWave Links Due to antenna directionality in mmWave links, RTS or CTS may not be heard reliably by STAs depending on their location. Collisions may still happen even after a successful RTS/CTS exchange. CTS BA AP RTS DATA STA 1 AP STA 2 hears AP NAV STA2 STA1 STA 2 STA3 STA4 NAV STA 3 STA 3 hears STA 1 DATA STA 4 STA 4 doesn t hear AP or STA 1 may result in packet error for AP-STA1 transmission Submission Slide 5 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 Possible solutions 1. All transmissions are scheduled by the AP. Requires developing new or modified MAC protocol (i.e. DMG, E-DMG access, R-TWT) Complexity should be minimized. 2. RTS/CTS transmissions are done omni-directionally May require higher transmit powers to support the same range as a directional RTS/CTS. 3. Leverage sub-7GHz links for NAV protection of mmWave transmissions (e.g. Cross-link RTS/CTS). Crosslink synchronization issues for STAs with different response times need to be studied further. May require new control frames for cross-link operation. Submission Slide 6 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 Cross-link RTS/CTS 1 Duration sub 7GHz = 0 Duration mmWave = T RTS* Sub 7GHz AP DATA mmWave Duration sub 7GHz = 0 Duration mmWave = T CTS* Sub 7GHz STA 1 mmWave BA Sub 7GHz Other STAs NAV( RTS*) NAV( CTS*) mmWave Submission Slide 7 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 Cross-link RTS/CTS 2 Duration sub 7GHz = 0 Duration mmWave = T RTS* retransmit Duration sub 7GHz = 0 Duration mmWave = T RTS* Sub 7GHz AP DATA mmWave Duration sub 7GHz = 0 Duration mmWave = T CTS* CTS* Sub 7GHz STA 1 mmWave BA NAV Sub 7GHz Other STAs NAV( RTS*) NAV( RTS*) NAVTimeout mmWave NAV( CTS*) Submission Slide 8 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 Cross-link RTS/CTS 3 Duration sub 7GHz = 0 Duration mmWave = T RTS* Sub 7GHz AP DATA mmWave Duration sub 7GHz = 0 Duration mmWave = T CTS* ACK Sub 7GHz STA 1 mmWave BA NAV Sub 7GHz Other STAs NAV( RTS*) mmWave NAV( CTS*) Submission Slide 9 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 Summary - mmWave links are prone to hidden node problems. - DMG/EDMG has plenty of mechanisms to solve it but it may result in high complexity. - We presented an alternative mechanism that leverages the sub-7GHz band to provide NAV protections to the mmWave bands. Submission Slide 10 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/0096r0 References [1] https://mentor.ieee.org/802.11/dcn/23/11-23-1819-00-immw- integrated-mmwave-design-considerations.pptx [2] https://mentor.ieee.org/802.11/dcn/23/11-23-2004-00-immw- technical-scope-proposal.pptx [3] https://mentor.ieee.org/802.11/dcn/23/11-23-1878-00-immw-high- level-design-considerations-of-immw.pptx [4] https://mentor.ieee.org/802.11/dcn/23/11-23-1905-00-immw-high- level-thoughts-on-immw.pptx Submission Slide 11 Leonardo Lanante, Ofinno