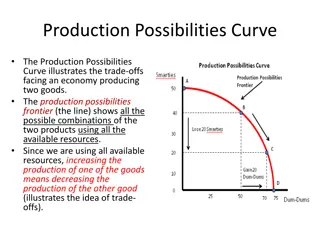
Learning Reminder: Murdock's Serial Position Curve Study and Experimental Practice
Explore the insights of Murdock's serial position curve study and its applications in experimental psychology. Dive into the concepts of alternate and null hypothesis, Sensory Register, and memory experiments. Engage in practical learning through experiment time activities and visual aids like patch, amber, dream, apple, laugh, seven, world, angel, green, music, sugar, and death. Prepare for upcoming lessons on extraneous variables, reliability, validity, and evaluation of studies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Scheme of learning reminder! Lesson 7 Outline Murdock s serial position curve study. As RM has now been combined with other modules. Lessons to follow this one should be: - Lesson 8: Extraneous variables use this study to reinforce - Lesson 9: Reliability and validity use this study to reinforce Lesson 10 Evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
KEY STUDY Murdocks serial position curve study Friday, 19 July 2024 Last week Last lesson Last month What is the difference between an alternate and a null hypothesis? What is the coding, capacity, and duration of the Sensory Register? What are the three different types of experiment usually conducted in psychology? L F N If you were going to conduct an experiment about memory. Which type of experiment do you think would be best? Explain your answer. LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
EXPERIMENT TIME! You are about to see a series of 20 words. They will flash up on the screen for 1 second. After all of the words have been shown, you will have 2 minutes to write down as many as you can remember. You must not share your answers! READY! LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Pens down . How do you do? 1. PATCH 2. AMBER 3. DREAM 4. APPLE 5. LAUGH 6. SEVEN 7. WORLD 8. ANGEL 9. GREEN 10. MUSIC 11. SUGAR 12. DEATH 13. WOMAN 14. TIGER 15. EARTH 16. MONEY 17. SMILE 18. RIVER 19. WATCH 20. BRAIN How many words did you recall? Which section of the list were they from the beginning, the middle, or the end? Why do you think this might have been? LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Keywords Keywords The words recalled from the start of the list are due to the primacy effect. The words recalled from the end of the list are due to the recency effect. Primacy effect refers to what happens first words that appear first in a list are more likely to be recalled than the words in the middle of a list. This is because they have been rehearsed quite well by the time they are recalled and have become long-term memories. Recency effect refers to what has happened most recently the words that appear towards the end of the list will have been heard most recently and will still be in short-term memory. Therefore, recall for these will be best. LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Keywords The effects of serial position When we hear words from the start of the list, we start to rehearse them in our head so that we can recall them later on. This transfers the words to our long-term store. However, as we are rehearsing the first few words, we miss the words from the middle of the list. We are able to recall words from the end of the list as they are still in our short-term store and so are available to be recalled, if we recall them straight away. Serial position effect describes the tendency of people to recall the first and last words in a list of words best. In other words, it is the position of the words that influences the likelihood of their recall. LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Key studies For each key study that we learn about there are some essential pieces of information that you need to know. Aim What was the purpose of the study? What were they trying to find out? Method What did they do? Results What did they find out from their study? Conclusion What can they say in relation to their aim? Did the results support their ideas? (Page 20) LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q1. The dependent variable in Murdocks study was the: a. Position of a word in a list b. Probability of a word being correctly recalled c. Total number of words correctly recalled d. Primacy and recency effects. LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q2. Being able to recall the words at the start of a list refers to the: a. Recency effect b. Primacy effect c. Serial position curve d. Dependent variable of the study. LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q3. How does Murdocks study support the multi-store model: a. Primacy effect shows LTM and recency effect shows STM b. Primacy effect shows STM and recency effect shows LTM c. The serial position curve involves sensory memory d. It doesn t support the multi-store model. LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q4. Information gets into LTM through: a. Attention b. Declarative memory c. Rehearsal d. Visual encoding. LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q5. Coding is mostly acoustic and capacity is between 5 and 9 items. Which memory store is being described? a. Short term memory b. Sensory memory c. Visual memory d. Declarative memory. LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Lets think about what we have learnt today. 1. Tell me something new that you have learnt today. 2. What knowledge/skills have you used today from previous lessons? (Think about other subjects) LO: To describe Murdock s serial position curve study.
Scheme of learning reminder! Lesson 7 Outline Murdock s serial position curve study. As RM has now been combined with other modules. Lessons to follow this one should be: - Lesson 8: Extraneous variables use this study to reinforce - Lesson 9: Reliability and validity use this study to reinforce Lesson 10 Evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
KEY STUDY Murdocks serial position curve study Friday, 19 July 2024 Last week Last lesson Last month What are the three key terms you need to use when describing Murdock s serial position curve study? PE RE SPC What are the 3 processes of memory? (In the correct order). What is the difference between reliability and validity ? Given what you now know about reliability and validity, which one of these would most apply to Murdock s study? Why? LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Evaluating a study G = Generalisable? What is the sample size? Did they use participants from one gender or one culture? Can the results be true for all people in the target population? R = Reliable? Can the results be repeated? Was it a lab experiment? A = Applicable? Have the conclusions changed the way we think? Has it changed anything in society? Have any laws been made as a result? V = Valid? Was the research conducted in a natural setting? Was real everyday behaviour observed? Do we have the real thoughts and feelings of the participants? E = Ethics? Was informed consent given? Right to withdraw? Did participants suffer any physical or psychological harm? Was their data and identity protected? LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Lets recap Aim: To provide evidence for the existence of separate short-term and long- term stores of the multi-store model of memory. Method: Words from 4000 most common words in English were chosen randomly. Participants listened to 20 word lists between 10 and 40 words on them. They recalled the words after each list. Results: Recall was not affected by the number of words in a list but was related to the position of the word in the list (the serial position effect). Murdock found that higher recall for the first few words (primacy effect) and for the last few words (recency effect) that than the middle of the list. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Lets recap Conclusion: Murdock concluded that this does provide evidence for separate short-term and long-term memory stores because: The last few words were still in the short-term memory store (within 18-30 secs) The first few words had been transferred to long-term memory because they had been rehearsed. The words in the middle were forgotten because they were neither in the short-term or long-term memory store. The results confirm the serial position effect, word position determines the likelihood of recall. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Evaluation Controlled lab study P - One strength of the study relates to it being well-controlled. E Familiarity of the words was the same throughout each list. The words were read at the same speed so that participants had no opportunity to practice some lists more than others. E This means that we can be more confident that it was the position of the word on the list that affected recall and not other extraneous variables. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Evaluation Artificial task P - One weakness of the study is that the task was artificial. E Memorising lists of words represent only a small part of what we use our memories for. This therefore, only tells us about one aspect of memory how we deal with memorising words. But we do a lot of other things with our memory like learning how to play basketball or remembering whether we like someone or not. E So this means that this way of studying memory is artificial and restrictive. It does relate to some aspects like how to learn for an exam but it does not explain many other aspects of life. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Evaluation Supporting research P - One strength of this study is research with amnesiacs supports the conclusions. E Research has shown that people who have amnesia and can t store long-term memories also do not show a primacy effect but they do show a recency effect. E This confirms that the primacy effect is related to long-term memory. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Use this guide to help you prepare for writing your first 9 mark question. You can briefly fill it in if it will help you focus your writing. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Evaluating Murdocks serial position curve study. Outline and evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study. (9 marks) Para 1: The aim of Murdock s study was to Para 1: Aim/Method Para 2: Results/conclusion Para 3-5: evaluation Para 2: Murdock found that Para 3: One strength of Murdock s study is that Para 4: One weakness of Murdock s study is that Para 5: Another strength of Murdock s study is that One weakness of Murdock s serial position curve study is that it was conducted in a laboratory. EVIDENCE This means that LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q1. The dependent variable in Murdocks study was the: a. Position of a word in a list b. Probability of a word being correctly recalled c. Total number of words correctly recalled d. Primacy and recency effects. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q2. Murdock used lists of words, which means that the study: a. Was a laboratory experiment b. Was not very well controlled c. Tested a wide range of memory skills d. It only tells us about some of the ways that memory is used in everyday life. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q3. How does Murdocks study support the multi-store model: a. Primacy effect shows LTM and recency effect shows STM b. Primacy effect shows STM and recency effect shows LTM c. The serial position curve involves sensory memory d. It doesn t support the multi-store model. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q4. Murdock used lists of words, which means that the study: a. Was a laboratory experiment b. Was not very well controlled c. Tested a wide range of memory skills d. It only tells us about some of the ways that memory is used in everyday life. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Q5. Information gets into LTM through: a. Attention b. Declarative memory c. Rehearsal d. Visual encoding. LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.
Lets think about what we have learnt today. 1. Tell me something new that you have learnt today. 2. What knowledge/skills have you used today from previous lessons? (Think about other subjects) LO: To evaluate Murdock s serial position curve study.