LBNF Excavation Cost Reconciliation Report Dec 2018
In December 2018, Fermilab conducted a Cost Reconciliation for the LBNF Excavation project. The report covers Deliverables, Significant Developments post 30% completion, changes in excavation processes, and new criteria for key receivers' vibrations. The document includes details on modifications, realignments, and adjustments made to the excavation plan. It also outlines the increased cavern rock bolt spacing, updated cavern benching, shotcrete criteria, rock reinforcement, and blast door specifications. Various structural reconfigurations and new provisions for equipment installation were implemented to enhance the excavation process.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
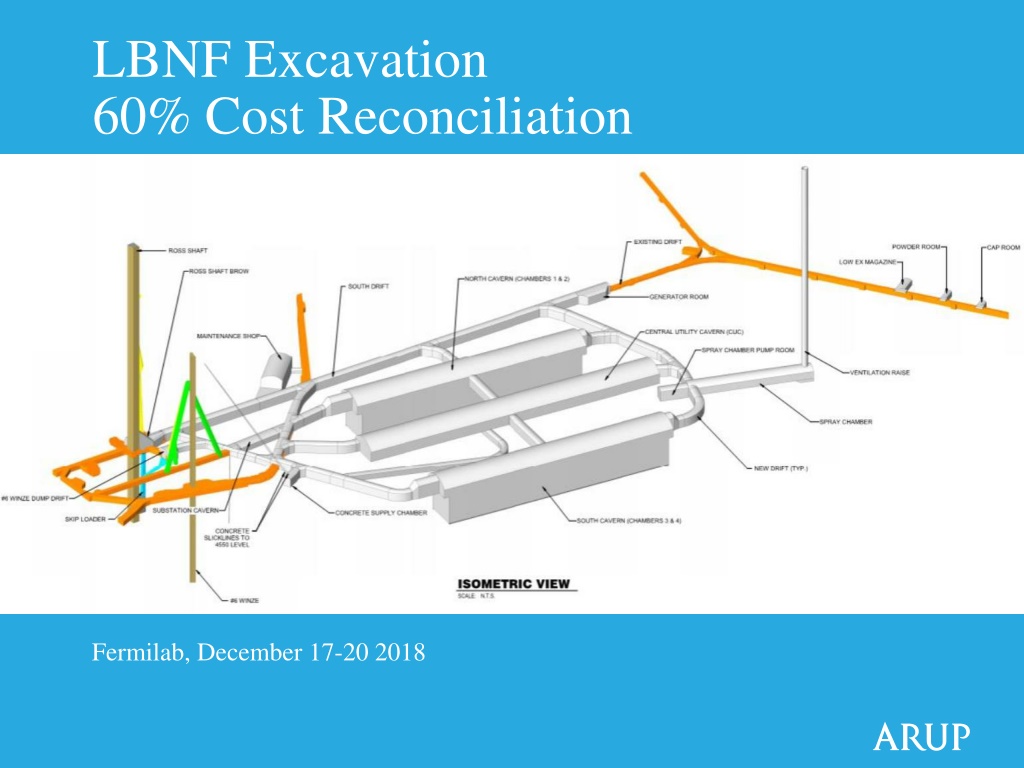
LBNF Excavation 60% Cost Reconciliation Fermilab, December 17-20 2018
60% Deliverables Drawings Specifications Geotechnical Baseline Report Basis of Design Report Not reissued (no changes): GDR GIR 2
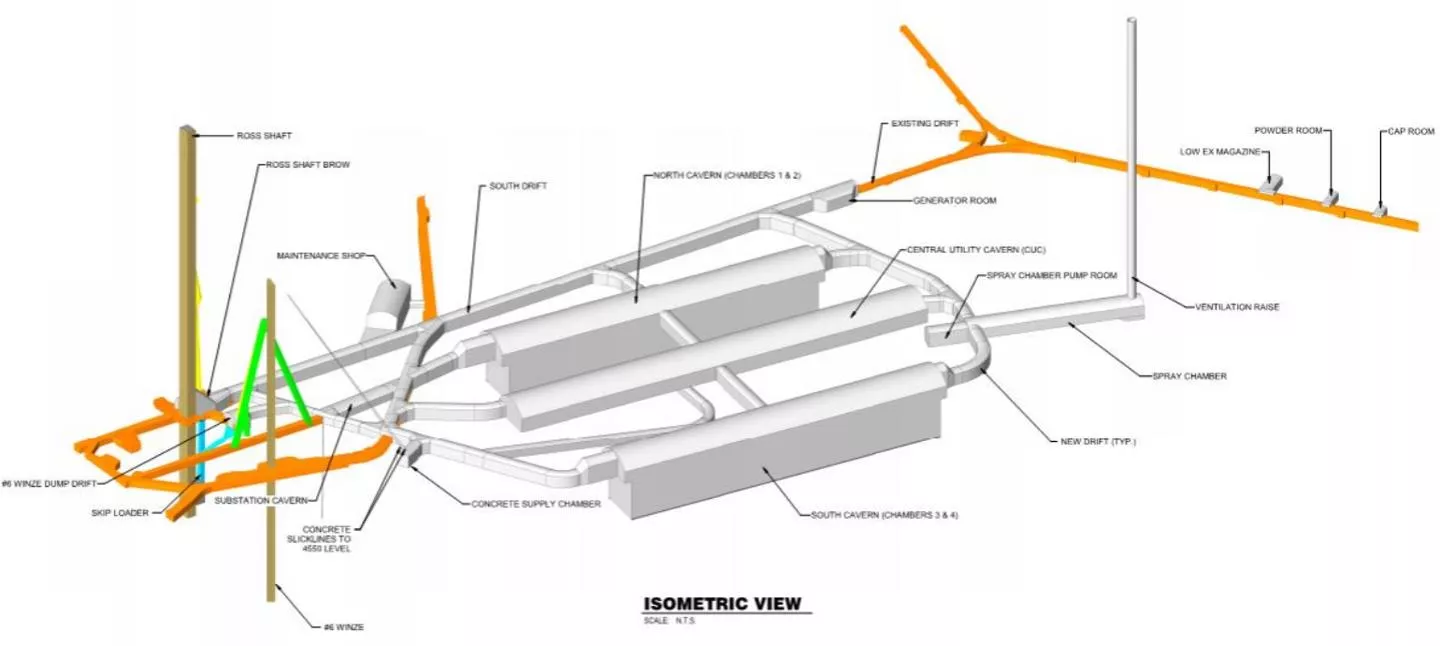
Changes/Significant Developments after 30% Re-arrangement of eastern drift configuration deletion of secondary access drift to spray chamber raise bore Relocation and decoupling of Maint Shop from Substation room Addition of Pump Room opposite of spray chamber to house mech equip and associated pipe trench Location defined for three (3) rooms for explosive mag along #4 Winze drift Alignment of mucking ramp to the bottom of the caverns updated. This was confirmed to be constructed and utilized by CM/GC to facilitate construction and mucking of the chambers during construction. 3
Changes/Significant Developments after 30% Increase in cavern rock bolt spacing (4 ft. to 5 ft.) Reconfigured cavern benching sequence to allow for mass excavation within center cut Differentiation of shotcrete waviness criterion between caverns and drifts (requirements relaxed in drifts) Proof testing of each installed Mezzanine Anchor required (to 80% yield) Cavern top heading height increased to accommodate proper install of 20 ft. rock reinforcement. Better clarity around Ross Shaft Brow enlargement removal of bottom 3 sets Shotcrete thickness fixed at 4 (Instructed for Cost Estimate) 5
Changes/Significant Developments after 30% Added frequency based vibration criterion for key sensitive receivers (#6 Winze, Ross Shaft) Use of double blast doors on Ross Campus side to alleviate excess overpressure The #6 Winze and west lab access drift blast doors must have a minimum opening of 9 ft. x 9 ft. The trolley drift, east lab access, and behind Ross Shaft blast door have a minimum opening of 5 ft. wide by 7.5 ft. high. Instruments which are desired to be retained for the operational stage of the experiment (long term) have been identified. Seismograph locations are revised based on a list of sensitive receivers developed between Arup and FRA. 7
Changes/Significant Developments after 30% Slabs within the CUC have been leveled and revised to show a solid slab on top of a mud slab, with a vapor membrane included in areas below the mechanical mezzanine, and to a solid slab for other areas. Local pad supports for dewars are shown, but the extent and size are not yet fully understood. Slabs within the experiment cavern have been updated to include a Cavidrain sub-slab drainage system that extends to the perimeter walls. A granular layer and perforated pipes were previously shown in 30% FD. The use of Cavidrain provides several advantages for the project including reduced long term clogging from groundwater related mineralization, and easier installation compared to mass gravel. A mud slab has been added below the structural slab to smooth out irregularities within the blasted invert. 9
Changes/Significant Developments after 30% Monorails: The design has been updated to incorporate comments from FRA. This includes changing the beam size, and raising the beams to be as high as possible. Rail: Additional details for rails provided. 11