Key Considerations for a Successful Audit Process in Nairobi
Understanding the importance of audit file preparation and key considerations for a successful audit process in Nairobi. Key staff participation, management of audit process, sharing draft financial statements for quality review, and following Act requirements are crucial steps for a successful audit.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
www.pwc.com Audit Process and File Presentation at KSG, Nairobi 3rd 7thDecember 2018 Presenter: Fitzgerald Oyoo
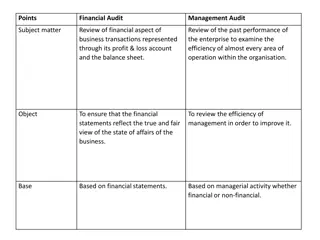
Why Audit File The purpose of preparing the audit file is to prepare adequately for the audit in order to satisfy the most robust audit procedures. The objective is to: - Highlight any audit issues before the auditors do; - Respond adequately to audit queries; and - Prepare in advance standard information asked for by auditors This goes a long way in giving the auditors confidence in your accounting records and reducing the issues identified during the audit. PwC 2
Key considerations Participation of key staff in the entrance meetings: County Executive CEC, Chief Officer Finance and Head of Treasury and for the County Assembly: County Assembly speaker, Director of Finance; Management and coordination of the audit process- provide ample working space for the auditors: Kericho tea, county water e.t.c Have regular meetings with the auditors- assess if they have sufficient documentation- get to know the auditors and call them by their names; Provide all the required documents while the auditors are still on site- do not give the impression of manufacturing the same during the audit- Involve all key stakeholders including the internal audit function in the financial statement processing- they can give the FS an initial assessment PwC 3
Key considerations (cont) Share the draft financial statements with the National Treasury for quality review before submission to the Office of the Auditor General. PwC 4
Preparing the Audit File In preparing the audit file, Accounting Officers should ensure that the requirements of the Act have been adequately addressed. Section 163 of the PFM Act basically talks of the schedules that should be prepared in addition to the financial statements. The Act states, The County Treasury shall include in the consolidated financial statements- a statement of all money paid into and paid out of the County Exchequer Account; a summary of - the appropriation accounts and statements prepared by accounting officers under section 164, and - the statements prepared by receivers of revenue under section 165; PwC 5
Preparing the Audit File (cont) a statement of payments ,if any, made out of the County Exchequer Account that are authorised by legislation other than an Appropriation Act; a statement of the total amount of debt of the county government that is outstanding at the end of the financial year; a statement of the debt guaranteed by the national government at the end of the financial year; such other statements as the county assembly may require; and a statement on the summary of the accounts from the county assembly. PwC 6
Listing of Important Schedules to be contained in the Audit File Bank reconciliations for all the bank accounts prepared and reviewed with outstanding reconciling issues resolved . Extracted and Reconciled reports from IFMIS i.e Statement of Assets, Statement of Receipts and Payments, Statement of Cashflows, Statement of Budget Execution (Statement of Appropriation) and the notes to the statements (extract from IFMIS). A complete and valid Trial Balance preferably from IFMIS Exchequer Receipts reconciled with the County Revenue Allocation Act (CARA) Reconciled Inter - Entity Confirmations between sending and receiving entity- transfers to the County Assembly, to and from National Government PwC
Listing of Important Schedules to be contained in the Audit File (cont ) Well supported Imprest Register: Date, amount, employee number- an ageing of the imprests Summary of the fixed assets register : Serial No. description, asset type, date of acquisition, amount Pending Bills Listing Source Documents to support receipts and Expenditure Items Support for Journal Vouchers PwC
Sample Audit File Index A: Trial Balance and Financial Statements A/1 2014_Final Draft Financial Statements A/2 2014_Draft Financial Statements Crossed referenced to the Trial Balance A/3 2014_ Final Trial Balance A/4 2013_ Audited and Signed Final Financial Statements A/5 2013_Final trial balance (to confirm opening balances) PwC
Sample Audit File Index (cont) B: Management Letter B/1 2014_Final Management Letter B/2 2013_Final Management Letter PwC
Sample Audit File Index (cont) C: Cash and Bank Balances C/1 List of bank accounts (bank name, branch, account number, balance as per trial balance) C/2 Lead Schedule C/3 Reconciliations/analysis for all trial balance ledger balances C/4 Bank reconciliations at 30 June 2014 C/5 Bank confirmations at 30 June 2014 C/6 Cash book and bank statements, if necessary PwC
Audit process Entrance meeting with the client management and the auditor is a must Coordination of the audit process by key client staff and the auditor is a key to a successful audit. Regular progress meetings during the audit. Provide all supporting documentation on site Involvement of the internal audit function during the audit process. Hold an exit meeting with the auditor and auditee management Prepare an audit file in advance PwC
What should be in an audit file Cash and bank Bank reconciliations ensuring reconciling items are valid for all bank accounts Bank statements Bank confirmations Basically whether the cash is existent, owned by the entity and valid. PwC
What should be in an audit file (cont) Receivables Aged debtors summary Staff receivables and other receivables listings Provision for bad debts listing Subsequent settlement details Looking into existence, ownership, valuation, validity Distinction of receivables from amounts due from the related parties Debtor confirmations PwC
What should be in an audit file (cont) Property, Plant and Equipment An updated fixed assets register clearly showing cost brought forward, additions, revaluations and disposals. Title/ ownership documents( looking at ownership, existence) should be included in the file. Depreciation policy and computation of the depreciation charge for the year. Supporting documentation to additions and approval Schedule for disposals and loss/ gain arising there on. PwC 15
What should be in an audit file (cont) Property, Plant and Equipment Schedule for disposals and loss/ gain arising there on. Impairment review record for PPE Accounting for revaluation; review of work done by experts; valuation report should be included in the file Disclosure in the financial statements comparative breakdown for both cost and accumulated depreciation. Insurance proof that insurance cover exist for the assets and its adequate. PwC 16
What should be in an audit file (cont) Investments Movement schedule showing balances brought forward, acquisition, disposal proceeds from investments. Schedule of all government securities indicating maturity analysis. Documents of title such as share certificates, CDSC account statements Valuation of investments PwC 17
What should be in an audit file (cont) Inventory Stock take report as at the year end date Inventory valuation report Aged inventory listing Stock provisions List of obsolete stock PwC 18
What should be in an audit file (cont) Trade payables Listings to trade payables, accruals and provisions Supplier statement files Supplier statement reconciliations Aged creditors listing Leave pay and gratuity provisions workings Details of contingent liabilities and provisions disclosed/ made PwC 19
What should be in an audit file (cont) Taxation Tax computation for the current financial year Annual returns filled with the Kenya Revenue Authority Deferred tax computation Withholding tax payment Schedule Instalment tax returns PwC 20
What should be in an audit file (cont) Revenue Summary of income from operating and non-operating revenue Schedule for all revenue streams Supporting documents such as contracts/donor agreements Revenue recognition policy Confirmation of donated income PwC 21
What should be in an audit file (cont) Expenditure Expenses classification, breakdown and schedules Supporting documentation such as invoices, contracts Payroll Summary of statutory deductions Directors emoluments Compensation to key management staff PwC 22
THANK YOU PwC 23