JCB T2 T3 Elec Engine 4 Cyl Service Repair Manual Instant Download
Please open the website below to get the complete manualnn//
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Foreword The Operator's Manual You and others can be killed or seriously injured if you operate or maintain the machine without first studying the Operator's Manual. You must understand and follow the instructions in the Operator's Manual. If you do not understand anything, ask your employer or JCB dealer to explain it. SERVICE MANUAL Do not operate the machine without an Operator's Manual, or if there is anything on the machine you do not understand. Treat the Operator's Manual as part of the machine. Keep it clean and in good condition. Replace the Operator's Manual immediately if it is lost, damaged or becomes unreadable. ENGINE JCB T2/3 Elec Engine 4 Cyl Contents 01 - Machine 06 - Body and Framework 09 - Operator Station 15 - Engine 18 - Fuel and Exhaust System 21 - Cooling System 33 - Electrical System 72 - Fasteners and Fixings 75 - Consumable Products 78 - After Sales EN - 9806/7000 - ISSUE 2 - 10/2017 This manual contains original instructions, verified by the manufacturer (or their authorized representative). Copyright 2017 JCB SERVICE All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any other means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying or otherwise, without prior permission from JCB SERVICE. www.jcb.com
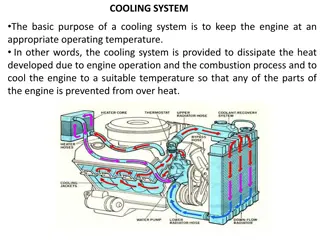
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General 00 - General Introduction Introduction ...................................................... 15-3 Health and Safety ........................................... 15-7 Technical Data ................................................. 15-8 Component Identification ............................... 15-10 Operation ....................................................... 15-14 Fault-Finding .................................................. 15-18 Drain and Fill ................................................. 15-28 Clean ............................................................. 15-28 Check (Pressure) .......................................... 15-30 Remove and Install ....................................... 15-33 Store and Recommission .............................. 15-37 This section contains information about the complete engine assembly. For specific engine technical information refer to the technical data section. Make sure that the correct engine service tools, consumables and torque figures are used when you perform service procedures. Renewal of oil seals, gaskets, etc., and any component showing obvious signs of wear or damage is expected as a matter of course. It is expected that components will be cleaned and lubricated where appropriate, and that any opened hose or pipe connections will be blanked to prevent excessive loss of hydraulic fluid, engine oil and ingress of dirt. Basic Description The JCB ecoMax engine is a 4 cylinder diesel engine in which the fuel is ignited by compression ignition. The engine operates on a four stroke cycle. The engine is started by an electric starter motor. The starter motor turns the engine via a pinion and teeth on the engine flywheel. Refer to: PIL 15-75. When the engine runs the crankshaft drives the camshaft via gears. The camshaft opens and closes the inlet and exhaust valves and via push rods in time with the four stroke cycle. The engine has 16 valves, 2 inlet and 2 exhaust valves for each cylinder. The crankshaft also drives a high pressure fuel pump via gears. The pump is part of the electronically controlled common rail fuel injection system. Refer to: PIL 18-00. Air is drawn into the engine, via the inlet manifold and exhaust gases exit via the exhaust manifold. The engine uses a VGT (Variable Geometry Turbocharger) which pressurises the air at the inlet manifold. Refer to PIL 18-36. A mechanical lubrication oil pump is driven by the crankshaft via gears. The pump pressurises and circulates oil for engine lubrication and cooling purposes. A drive belt driven by the crankshaft, drives a coolant circulation pump, alternator, radiator cooling fan and other ancillaries such as an air conditioning compressor. 15 - 3 9806/7000-2 15 - 3
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Figure 3. 8 5 4 6 3 1 10 2 7 6 9 1 Flywheel 3 Camshaft 5 Exhaust valves (x8) 7 High pressure fuel pump drive gear 9 Lubrication oil pump 2 4 6 8 10 Crankshaft Inlet valves (x8) Push rods (x8) Turbocharger Front end drive belt 15 - 4 9806/7000-2 15 - 4
https://www.ebooklibonline.com Hello dear friend! Thank you very much for reading. Enter the link into your browser. The full manual is available for immediate download. https://www.ebooklibonline.com
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Internal The following identifies the main internal components of a typical engine assembly. Some variants may differ in detail. Figure 4. 1 3 5 6a 6c 7 9 Rocker assembly Valve spring (x16) Exhaust valve (x8) Piston ring - top compression (x4) Piston ring - oil control (x4) Connecting rod assembly (x4) Main bearing - crankshaft (x5) 2 4 6 6b 6d 8 10 Valve bridge piece (x8) Inlet valve (x8) Piston assembly (x4) Piston ring - 2nd compression (x4) Gudgeon pin (x4) Crankshaft Big end bearing - crankshaft / connecting rod (x4) Flywheel 11 13 Front crankshaft oil seal High duty PTO (Power Take-Off) idler gear (if installed) 12 15 - 5 9806/7000-2 15 - 5
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Figure 5. 2 11 5 10 1 9 1a 8 6 7 4 3 1 2 4 6 8 10 Flywheel Fuel injector (atomiser) (x4) Crankshaft drive gear Camshaft drive gear High pressure fuel pump drive gear Tappet (x8) 1A Flywheel - crankshaft fixing bolts (x8) 3 Flywheel hub 5 High duty PTO idler gear (if installed) 7 Lubrication oil pump 9 Camshaft 11 Push rod (x8) 15 - 6 9806/7000-2 15 - 6
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Health and Safety accordance with local regulations. Use authorised waste disposal sites. Hot Components Touching hot surfaces can burn skin. The engine and machine components will be hot after the unit has been running. Allow the engine and components to cool before servicing the unit. Turning the Engine Do not try to turn the engine by pulling the fan or fan belt. This could cause injury or premature component failure. Notice: The engine and other components could be damaged by high pressure washing systems. Special precautions must be taken if the machine is to be washed using a high pressure system.Make sure that the alternator, starter motor and any other electrical components are shielded and not directly cleaned by the high pressure cleaning system. Do not aim the water jet directly at bearings, oil seals or the engine air induction system. WARNING! To bleed the injectors you must turn the engine. When the engine is turning, there are parts rotating in the engine compartment.Before starting this job make sure that you have no loose clothing (cuffs, ties etc) which could get caught in rotating parts.When the engine is turning, keep clear of rotating parts. Notice: Clean the engine before you start engine maintenance. Obey the correct procedures. Contamination of the fuel system will cause damage and possible failure of the engine. Notice: Do not exceed the correct level of engine oil in the sump. If there is too much engine oil, the excess must be drained to the correct level. An excess of engine oil could cause the engine speed to increase rapidly without control. WARNING! The engine has exposed rotating parts. Switch off the engine before working in the engine compartment. Do not use the machine with the engine cover open. WARNING! Hot oil and engine components can burn you. Make sure the engine is cool before doing this job.Used engine crankcase lubricants contain harmful contaminants. In laboratory tests it was shown that used engine oils can cause skin cancer. Notice: A drive belt that is loose can cause damage to itself and/or other engine parts. WARNING! Do not open the high pressure fuel system with the engine running. Engine operation causes high fuel pressure. High pressure fuel spray can cause serious injury or death. CAUTION! It is illegal to pollute drains, sewers or the ground. Clean up all spilt fluids and/or lubricants.Used fluids and/or lubricants, filters and contaminated materials must be disposed of in 15 - 7 9806/7000-2 15 - 7
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Technical Data Table 4. Description Engine Variants SK Engine Turbocharged with Intercooler US-EPA Tier 2, EU Stage II 2200 RPM (Revolu- tions Per Minute) (Dry weight-No cool- ing fan drive) 457kg SE Engine Turbocharged with Intercooler US-EPA Tier 3, EU Stage IIIA 2200 rpm DE Engine Turbocharged with Intercooler US-EPA Tier 2, EU Stage II 2200 RPM DK Engine Turbocharged with Intercooler US-EPA Tier 3, EU Stage IIIA 2200 RPM Emission compli- ance Rated speed Weight (Dry) (Dry weight-No cool- ing fan drive) 457kg 4 103mm 132mm In line (Dry weight-No cool- ing fan drive) 477kg 4 106mm 135mm In line (Dry weight-No cool- ing fan drive) 477kg 4 106mm 135mm In line Number of cylinders 4 Nominal bore size Stroke Cylinder arrange- ment Combustion Cycle Firing order Displacement Compression ratio Engine Compres- sion 103mm 132mm In line 4-stroke 1-3-4-2 4.399L 17.1: 1 Compression vari- ance between each cylinder should be no greater than 3.5bar (50.7psi) Clockwise 4-stroke 1-3-4-2 4.399L 17.1: 1 Compression vari- ance between each cylinder should be no greater than 3.5bar (50.7psi) Clockwise 4-stroke 1-3-4-2 4.765L 17.1: 1 Compression vari- ance between each cylinder should be no greater than 3.5bar (50.7psi) Clockwise 4-stroke 1-3-4-2 4.765L 17.1: 1 Compression vari- ance between each cylinder should be no greater than 3.5bar (50.7psi) Clockwise Direction of rotation (viewed from front {crankshaft pulley} end) Valves Valve clearances measured at the tappet end of the rockers (measured cold) - Inlet - Exhaust Lubricating oil pres- sure (Dependent on engine temperature and speed) Filter type 4 per cylinder 4 per cylinder 4 per cylinder 4 per cylinder 0.15 0.2mm 0.43 0.5mm 1.6 6.5bar (23.2 94.2psi) 0.15 0.2mm 0.43 0.5mm 1.6 6.5bar (23.2 94.2psi) 0.15 0.2mm 0.43 0.5mm 1.6 6.5bar (23.2 94.2psi) 0.15 0.2mm 0.43 0.5mm 1.6 6.5bar (23.2 94.2psi) Screw-on canister (with drain facility) 1.6bar (23.2psi) Screw-on canister (with drain facility) 1.6bar (23.2psi) Screw-on canister (with drain facility) 1.6bar (23.2psi) Screw-on canister (with drain facility) 1.6bar (23.2psi) Pressure to open by-pass valve Oil pressure relief valve setting Oil pressure switch setting Oil pump 6bar (87.0psi) 6bar (87.0psi) 6bar (87.0psi) 6bar (87.0psi) 0.6bar (8.7psi) falling Integral unit with re- lief valve 0.6bar (8.7psi) falling Integral unit with re- lief valve 0.6bar (8.7psi) falling Integral unit with re- lief valve 0.6bar (8.7psi) falling Integral unit with re- lief valve (1) 15 - 8 9806/7000-2 15 - 8
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Description Combustion system Common rail direct SK Engine SE Engine Common rail direct Injection High pressure with electronically con- trolled fuel metering DE Engine Common rail direct Injection High pressure with electronically con- trolled fuel metering DK Engine Common rail direct Injection High pressure with electronically con- trolled fuel metering Injection High pressure with electronically con- trolled fuel metering High pressure fuel pump (1) The oil pump is a non-serviceable part 15 - 9 9806/7000-2 15 - 9
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Component Identification Figure 6. Engine - As viewed on the left hand side C D E C C F C G B H A J 7 K L K M 6 5 N 4 P Q R S 3 T U 2 V W 1 X Z Y A Rocker cover C Fuel injectors and high pressure fuel pipes B Lubrication oil filler cap D TMAP (Temperature Manifold Air Pressure) sensor F High pressure fuel pipe - rail feed H Fuel pressure sensor K Knock sensor (x2) M Timing gear case P Flywheel housing R IMV (Inlet Metering Valve) T Low duty PTO (Power Take-Off) (blanking cover if no device is installed) V Fuel filter E Tappet covers (x4) G Fuel injection common rail J Air Inlet manifold L High pressure fuel pump N Low pressure fuel line (to tank) Q Fuel temperature sensor S Flywheel position sensor U Cam shaft position sensor (mounted on the side of the crankcase) W ECM (Engine Control Module) Y Oil drain plug (sump) X Lubrication oil sump Z Bedplate 15 - 10 9806/7000-2 15 - 10
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General 1 Lubrication oil dipstick 3 Oil pressure switch 5 Lubrication oil filler cap 7 Fuel pressure dump valve 2 Oil filter housing drain plug 4 Lubrication oil filter 6 Lubrication oil cooler housing Figure 7. Engine - As viewed on the right hand side B C A D V E U F G T H J K L S R Q P N M A Rocker cover C Turbocharger oil feed line E CCV (Crankcase Ventilation) filter vent to atmosphere (If installed) G Turbocharger oil drain line J Coolant inlet / radiator hose connector L Bedplate N CCV filter oil drain hose (If installed) Q CCV filter assembly (If installed) S Heavy duty PTO (blanking cover if no device is installed) U Timing gear case B Turbocharger D Exhaust manifold F Alternator H Coolant pump housing (crankcase) K Crankcase M Lubrication oil sump P Oil drain plug (sump) R Starter motor T Flywheel housing V CCV hose (If installed) 15 - 11 9806/7000-2 15 - 11
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Figure 8. Engine - As viewed on the crankshaft pulley (front) end A B C D E F G N H J M L K A Coolant thermostat housing / radiator hose connector C Cab heater water hose connector E Inlet manifold induction heater (if installed) G Crankcase J Bedplate L Crankshaft pulley N Alternator B Coolant temperature sensor D Rocker cover F Cylinder head H Drive belt tensioner and pulley K Lubrication oil sump M Coolant pump 15 - 12 9806/7000-2 15 - 12
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Figure 9. Engine - As viewed on the flywheel (rear) end B C D A E F L G K H J A Rocker cover C Crankcase pressure relief valve E Cylinder head G Flywheel housing J Crankshaft position sensor L High pressure fuel pump drive gear cover B CCV chamber D Engine electrical harness F CCV hose H Crankshaft position target disc K Flywheel 15 - 13 9806/7000-2 15 - 13
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Operation The Four Stroke Cycle - 4 Cylinder Engine It is important to note that number 1 cylinder is firing and about to start its power stroke. Rotating the crankshaft a further full rotation would position the pistons as described but the engine would be at a different stage in its four stroke cycle, with number 1 cylinder about to start its Induction stroke. This section describes the cycle sequence, for the 4 cylinder engine. With the crankshaft positioned as shown, the pistons in numbers 1 and 4 cylinders are at top dead centre and pistons in numbers 2 and 3 cylinders are at bottom dead centre. The stages in the four stroke cycle for each cylinder are as follows: Table 5. The Four Stroke Cycle Stage num- ber 1 Piston operation Valve operation The piston is at the top of its Compression stroke and is about to start its Power stroke. The piston is at the bottom of its Power stroke and is about to start its Exhaust stroke. The piston is at the bottom of its Induction stroke and is about to start its Compression stroke. The piston is at the top of its Exhaust stroke and is about to start its Induction stroke. Inlet and exhaust valves closed 2 Inlet valves closed, exhaust valves about to open Exhaust valves closed, inlet valves about to close 3 4 Valve Operation Exhaust valves about to close, inlet valves about to open Firing Order From the stages described, it can be seen that number 1 cylinder will be next to fire. Number 3 cylinder is starting its compression stroke and is next in the cycle, followed by cylinders 4 and 2. A cylinder is said to be firing, when the fuel / air mixture ignites and the piston is about to start its power stroke. The firing order is therefore; 1, 3, 4, 2. 15 - 14 9806/7000-2 15 - 14
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Figure 10. CYL1 CYL2 CYL3 CYL4 1 2 5 A C B C B C B C B G H J K 4 3 F 745620 745620 G H J K C B B C A A A A C B C B CYL1 CYL3 A C 1 3 5 Cylinder number 1 Cylinder number 3 Camshaft Camshaft lobe - Exhaust valve operation Exhaust valves Crankshaft Camshaft drive gear CYL2 CYL4 B F 2 4 Cylinder number 2 Cylinder number 4 Camshaft lobe - Inlet valve operation Front of engine Inlet valves Crankshaft gear 15 - 15 9806/7000-2 15 - 15
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Four Stroke Cycle revolution of the crankshaft, thus, in one cycle of a four stroke engine, the crankshaft revolves twice. Induction Figure 11. As the piston travels down the cylinder, it draws filtered air through inlet valves into the cylinder. Compression When the piston reaches the bottom of its stroke the inlet valves close. The piston then starts to rise up the cylinder compressing the air trapped in the cylinder. This causes the temperature and pressure of the air to rise. Fuel is injected into the cylinder when the piston is near to top dead centre. 3 2 Power C B The piston continues to rise after the start of fuel injection causing a further increase in pressure and temperature. 4 The temperature rises to a point at which the fuel/air mixture ignites. A cylinder is said to be firing, when the fuel/air mixture ignites. 1 This combustion causes a very rapid rise in both temperature and pressure. The high pressure generated propels the piston downward turning the crankshaft and producing energy. 746030 1 2 3 4 A B C BDC Bottom dead centre TDC TDC (Top Dead Centre) Induction stroke Compression stroke Power stroke Exhaust stroke Camshaft Camshaft lobe - Inlet valve operation Camshaft lobe - Exhaust valve operation Exhaust Once the piston has reached the bottom of its travel, the exhaust valves open and momentum stored in the flywheel forces the piston up the cylinder expelling the exhaust gases. In a running engine these four phases are continuously repeated. Each stroke is half a 15 - 16 9806/7000-2 15 - 16
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Figure 12. 717620 1 2 3 4 B C A A A A C B B C B C 1 Induction stroke 3 Power stroke A Camshaft C Camshaft lobe - Exhaust valve operation 2 Compression stroke 4 Exhaust stroke B Camshaft lobe - Inlet valve operation 15 - 17 9806/7000-2 15 - 17
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Drain and Fill Clean Notice: Clean the engine before you start engine maintenance. Obey the correct procedures. Contamination of the fuel system will cause damage and possible failure of the engine. Notice: The engine and other components could be damaged by high pressure washing systems. Special precautions must be taken if the machine is to be washed using a high pressure system. Make sure that the alternator, starter motor and any other electrical components are shielded and not directly cleaned by the high pressure cleaning system. Do not aim the water jet directly at bearings, oil seals or the engine air induction system. Refer to Engine, Oil Filter, (PIL 15-21-00). Before carrying out any service procedures that require components to be removed, the engine must be properly cleaned. Cleaning must be carried out either in the area of components to be removed or, in the case of major work, or work on the fuel system, the whole engine and surrounding machine must be cleaned. Stop the engine and allow it to cool for at least one hour. DO NOT attempt to clean any part of the engine while it is running. 1. Make sure that the electrical system is isolated. 2. Make sure that all electrical connectors are correctly coupled. If connectors are open fit the correct caps or seal with water proof tape. 3. Cover the alternator with a plastic bag to prevent water ingress. 4. Seal the engine air intake, exhaust and breather system. 5. Make sure that the oil filler caps and dipstick are correctly installed. 6. Use a low pressure water jet and soft bristle brush to soak off caked mud or dirt. 7. Apply an approved cleaning and degreasing agent with a brush. Obey the manufacturers instructions. 8. Use a pressure washer to remove the soft dirt and oil. Important: DO NOT aim the water jet directly at oil seals or electrical connectors and electronic components such as ECU (Electronic Control Unit)'s, alternator or fuel injectors. DO NOT place the jet nozzle closer than the specified distance to any part of the engine or exhaust system. Length/Dimension/Distance: 600mm 15 - 28 9806/7000-2 15 - 28
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General 9. When the pressure washing is complete move the machine away from the wash area, or alternatively, clean away the material washed from the machine. 10. Before working on specific areas of the engine use a compressed air jet to dry off any moisture. When the area is dry use a soft clean brush to remove any sand or grit particles that remain. 11. When removing components be aware of any dirt or debris that may be exposed. Cover any open ports and clean away the deposits before proceeding. Additional cleaning must be carried out prior to working on the high pressure fuel system. Refer to Fuel System - Clean (PIL 18-00). 15 - 29 9806/7000-2 15 - 29
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Check (Pressure) Special Tools Description Pressure Gauge (0-40 Bar) Dummy Injector rotating in the engine compartment.Before starting this job make sure that you have no loose clothing (cuffs, ties etc) which could get caught in rotating parts.When the engine is turning, keep clear of rotating parts. Part No. 892/00278 Qty. 1 892/12347 1 1. Make sure that the engine is safe to work on. Refer to (PIL 01-03). Engine Compression Test 2. Get access to the engine. This test is used to diagnose suspected poor compression in one or more of the engine cylinders. Use a dummy injector to do the test. 3. Remove all four fuel injectors, refer to (PIL 18-18). Several factors can influence the compression pressure, the following conditions are assumed: 3.1. Make sure that the injectors are labelled for correct fitting at a later stage. The valve clearances have been set correctly, refer to (PIL 15-30). The correct engine oil has been used, refer to (PIL 75-03). The engine oil level is correct, refer to (PIL 15-21). The correct type of diesel fuel has been used and the system correctly primed, refer to (PIL 75-18). The battery and starting circuit is fully charged and in good condition, e.g. good earth paths, cable connections tight etc. 4. Install the dummy injector in one of the vacant cylinder injector bores.Refer to Figure 13. Special Tool: Dummy Injector (Qty.: 1) 5. Install a pressure test gauge into the dummy injector fitting. 5.1. Note: The dummy injector is drilled and tapped 1/8-28 BSP x 8.00mm deep to accept a standard pressure gauge fitting. 6. Remove the ESOS (Engine Shut-Off Solenoid) to prevent accidental start of the engine. refer to (PIL 15-86). When comparing the figures recorded in the following procedures, there should be a minimum variation of 3.5bar (50.7psi) between each cylinder. If the variation is greater than this figure, then remove the cylinder head, refer to (PIL 15-06) and closely inspect the cylinder bores, pistons and piston rings for signs of wear or damage. Repair as necessary. 7. Operate the starter motor to crank the engine. 7.1. Do not crank for longer than 20 seconds. 7.2. Record the gauge reading. 8. Do the step 3 to 6 again for the remaining three cylinders. WARNING! To bleed the injectors you must turn the engine. When the engine is turning, there are parts 15 - 30 9806/7000-2 15 - 30
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Figure 13. 0 50 0 0 50 50 A A Dummy injector 15 - 31 9806/7000-2 15 - 31
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Engine Oil Pressure 5. Start the engine, increase the engine revs to the rated speed. Record the pressure gauge reading, refer to Technical Data (PIL 15-00), for the recommended circuit pressure. Use the following procedures to measure the engine oil pressure. Refer to Oil Sump (PIL 15-45) for a full explanation of the lubricating oil circuit. Several factors can influence the engine oil pressure, the following conditions are assumed: 6. Remove the pressure gauge and install the pressure switch. High Lubrication Oil Pressure The correct engine oil has been used, refer to Consumable Products, Oil (PIL 75-03). The engine oil level is correct, refer to Oil Filter, Check Level (PIL 15-21). High oil pressure will be evident when starting in cold conditions. Typically the pressure will be 1 2bar (14.5 29.0psi) and higher in cold operation, the pressure should drop when the engine reaches normal operating temperature. 1. Make sure that the engine is safe to work on. If the engine has been running, let it cool before you start the service work. If the pressure remains high when operating temperature is achieved, check the oil level, if this is correct, suspect the oil pump relief valve is at fault. 2. Get access to the engine. 3. Disconnect the electrical connector to the oil pressure switch, and remove the switch from the oil cooler housing. Low Lubrication Oil Pressure Several factors can be the cause of low lubricating oil pressure: 4. Install a suitable test gauge into the vacant pressure switch port (M10 x 1.5mm thread). Make sure that the gauge has a sealing washer as shown. Special Tool: Pressure Gauge (0-40 Bar) (Qty.: 1) Low oil level - typically evident as a loss of pressure when operating on uneven ground or on a gradient. Blocked oil filter - a blocked filter will show as a gradual loss of pressure. Blocked suction strainer (pick-up pipe) - typically evident as low pressure on start up, if the blockage frees itself in the sump, the pressure will pick up to normal. Coolant in the oil - coolant in the lubricating oil will show as a milky discolouration of the oil and an increase in oil level. Check for damaged core plugs, lubricating oil cooler, cylinder head and/ or gasket. Fuel in the oil - fuel in the oil will result in thin' black lubricating oil, the oil will also have a diesel fuel smell. Check the fuel injection pump (FIP) shaft seal refer to (PIL 18-18), piston ring wear, lift pump diaphragm damage or injector leakage if fuel is evident in the oil. Figure 14. A B A Oil pressure switch B Sealing washer 15 - 32 9806/7000-2 15 - 32
Suggest: If the above button click is invalid. Please download this document first, and then click the above link to download the complete manual. Thank you so much for reading
15 - Engine 00 - Engine 00 - General Remove and Install Special Tools Description Lifting Brackets to manually lift heavy components on your own. Always use lifting equipment, or obtain the help of an assistant. Inspect the lifting brackets for signs of damage. The brackets must be correctly torqued to the crankcase. Make sure the lifting equipment does not damage any of the engine dressing and the rocker cover. Part No. 892/01160 Qty. 1 Lifting Equipment You can be injured if you use incorrect or faulty lifting equipment. You must identify the weight of the item to be lifted then choose lifting equipment that is strong enough and suitable for the job. Make sure that lifting equipment is in good condition and complies with all local regulations. Component Identification The following component identification is for a typical engine installation. There will be some component differences depending on the machine variant. Before attempting to remove the engine ensure that all the necessary components have either been removed, or safely disconnected from the engine. The lifting equipment used must be an approved type and capable of lifting the engine safely. The recommended lifting equipment is shown. Use a spreader bar when lifting the engine. Never attempt Figure 15. 25 22 14 15 6 7 8 10 23 17 16 18 21 24 12 19 11 20 6 8 11 Engine mounting bolts Lifting bracket fixing bolts Fuel line connector at fuel filter- feed line from fuel pump 7 10 12 Lifting bracket- front Fuel line connector- return to tank line Electrical connector- engine ECM (Engine Control Module) machine side connector (grey) 15 - 33 9806/7000-2 15 - 33
https://www.ebooklibonline.com Hello dear friend! Thank you very much for reading. Enter the link into your browser. The full manual is available for immediate download. https://www.ebooklibonline.com