Influence of GHG and Aerosol Forcings on Pacific Decadal Variability in CESM2
The study investigates how greenhouse gas (GHG) and aerosol forcings impact Pacific decadal variability (PDV) through the analysis of CESM2 full-forcing large ensemble data. It explores the influence on the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) and North Pacific Gyre Oscillation (NPGO) modes, long-term responses in PDV, mean state changes, and variabilities over time. The results highlight the importance of forced mean-state trends in understanding historical PDV behavior in model simulations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
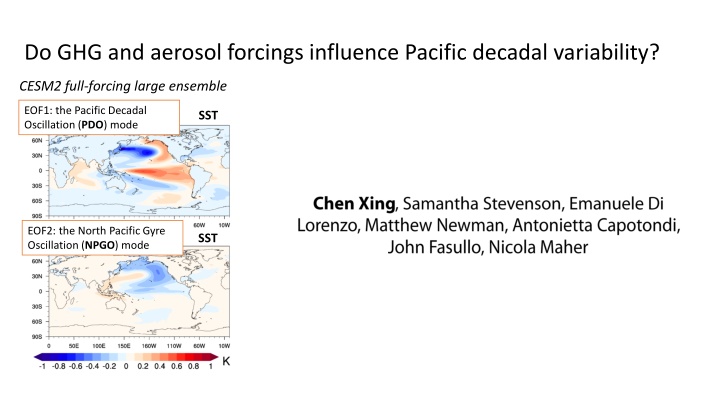
Do GHG and aerosol forcings influence Pacific decadal variability? CESM2 full-forcing large ensemble EOF1: the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) mode SST EOF2: the North Pacific Gyre Oscillation (NPGO) mode SST
Do GHG and aerosol forcings influence Pacific decadal variability? Are there long-term responses in PDV? PC time series in CESM2 full-forcing The PDO-like mode The NPGO-like mode Long-term responses represented by the ensemble mean The PDV definition: Removing global mean SST before applying the EOF
Do GHG and aerosol forcings influence Pacific decadal variability? Are there long-term responses in PDV? The leading EOF of each single forcing ensemble mean SST to represent the mean state change PC in CESM2 full-forcing CESM2- GHG single forcing SST CESM2-AAER single forcing SST Mean state changes from GHG or aerosol forcing could explain the long- term response changes in PDV
Do GHG and aerosol forcings influence Pacific decadal variability? Is variability changed? PC1 in CESM2 full-forcing CESM2 full-forcing large ensemble 30-year moving EOF1: the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) mode SST variance PC2 in CESM2 full-forcing 30-year moving EOF2: the North Pacific Gyre Oscillation (NPGO) mode SST variance The variabilities remain unchanged after removing the ensemble mean Ensemble mean is removed before applying the EOF Solid line: ensemble mean; Shading: one STD across ensembles
PC time series using traditional method Take home message: - Long-term responses of PDV are related to mean state changes from anthropogenic forcings. - While the variability of Pacific decadal variability is not changing from anthropogenic forcings. PC time series, ensemble mean removed first 30-year moving - Forced mean-state trends is critical for capturing the historical behavior of PDV in model simulations. variance