Guidance on Hospice Care and Feeding Tubes for Elderly Patients
Learn about the appropriateness of hospice care for a 74-year-old female with heart failure and the use of feeding tubes for an 89-year-old female with advanced Alzheimer's dementia. Understand important considerations for palliative care decisions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Palliative Care KSA Megan Matott, DO, Hospice and Palliative Medicine Fellow, Rochester Regional Health Greg Faughnan, MD, Faculty, St. Joseph's Family Medicine Residency
A 74-year-old female has been hospitalized three times in the past 6 months for exacerbations of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. During rounds the family medicine resident on the team asks whether a hospice referral would be appropriate. Which one of the following is true about hospice care for this patient? A. Hospice would focus on helping her live well B. She does not qualify for hospice because her ejection fraction is preserved C. Hospice is inappropriate for noncancer diagnoses D. Patients under hospice care die earlier because they lose the will to live
A 74-year-old female has been hospitalized three times in the past 6 months for exacerbations of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. During rounds the family medicine resident on the team asks whether a hospice referral would be appropriate. Which one of the following is true about hospice care for this patient? A. Hospice would focus on helping her live well B. She does not qualify for hospice because her ejection fraction is preserved C. Hospice is inappropriate for noncancer diagnoses D. Patients under hospice care die earlier because they lose the will to live
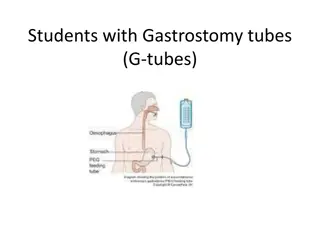
An 89-year-old female with advanced Alzheimers dementia has resided in a skilled nursing facility for the past 5 years. She will eat if she is hand fed but has been hospitalized three times in the past 4 months for aspiration pneumonia. The family asks about tube feedings. Which one of the following would be appropriate advice for this patient s family? A. The risk of aspiration is reduced with a feeding tube B. The quality of life for patients with advanced dementia is so low that a feeding tube is inappropriate C. Feeding tubes increase longevity in patients with advanced dementia D. Feeding tubes prevent pressure ulcers in patients with advanced dementia E. Careful hand feeding has been shown to be as effective as tube feeding
An 89-year-old female with advanced Alzheimers dementia has resided in a skilled nursing facility for the past 5 years. She will eat if she is hand fed but has been hospitalized three times in the past 4 months for aspiration pneumonia. The family asks about tube feedings. Which one of the following would be appropriate advice for this patient s family? A. The risk of aspiration is reduced with a feeding tube B. The quality of life for patients with advanced dementia is so low that a feeding tube is inappropriate C. Feeding tubes increase longevity in patients with advanced dementia D. Feeding tubes prevent pressure ulcers in patients with advanced dementia E. Careful hand feeding has been shown to be as effective as tube feeding
A 51-year-old male with squamous cell cancer of the mouth is considering chemotherapy and radiation therapy. He has seen some information indicating that a feeding tube is sometimes used during this treatment and he asks you for information about this. Which one of the following would be appropriate advice? A. A nasogastric feeding tube is recommended to minimize the need for surgery B. A percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube is a better option than a nasogastric tube C. Total parenteral nutrition would be the preferred route to provide nutrition for this patient D. A feeding tube has not been shown to improve symptoms or longevity in patients with head and neck cancer
A 51-year-old male with squamous cell cancer of the mouth is considering chemotherapy and radiation therapy. He has seen some information indicating that a feeding tube is sometimes used during this treatment and he asks you for information about this. Which one of the following would be appropriate advice? A. A nasogastric feeding tube is recommended to minimize the need for surgery B. A percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube is a better option than a nasogastric tube C. Total parenteral nutrition would be the preferred route to provide nutrition for this patient D. A feeding tube has not been shown to improve symptoms or longevity in patients with head and neck cancer
Although prognostication is often difficult, it promotes thoughtful decision-making, allows for planning, and is often appreciated by patients and families. Which one of the following is true about determining a prognosis? A. A prognosis should be given as a range of time B. Physicians tend to underestimate longevity C. The accuracy of a prognosis improves the longer a physician has known a patient D. Multidisciplinary teams are less accurate than individual physicians when determining a prognosis
Although prognostication is often difficult, it promotes thoughtful decision-making, allows for planning, and is often appreciated by patients and families. Which one of the following is true about determining a prognosis? A. A prognosis should be given as a range of time B. Physicians tend to underestimate longevity C. The accuracy of a prognosis improves the longer a physician has known a patient D. Multidisciplinary teams are less accurate than individual physicians when determining a prognosis
A 79-year-old female with Alzheimers dementia responds to familiar faces and can speak in short sentences. Until recently she has been able to feed herself but she now requires help with eating and other activities of daily living. She is occasionally incontinent of urine and has been hospitalized twice in 3 months for a urinary tract infection (UTI) with fever. Since her last hospitalization for a UTI she has become unable to walk and requires a one-person assist to get into a wheelchair. A home health nurse sees her three times a week to manage pressure sores. Which one of the following is true regarding this patient s qualification for Medicare hospice? A. She does qualify because the natural course of advanced dementia usually leads to death in less than 6 months B. She does qualify because the comorbidity of frequent hospitalization suggests a prognosis of less than 6 months C. She does not qualify because she can speak more than six words D. She does not qualify because she can respond to familiar faces
A 79-year-old female with Alzheimers dementia responds to familiar faces and can speak in short sentences. Until recently she has been able to feed herself but she now requires help with eating and other activities of daily living. She is occasionally incontinent of urine and has been hospitalized twice in 3 months for a urinary tract infection (UTI) with fever. Since her last hospitalization for a UTI she has become unable to walk and requires a one-person assist to get into a wheelchair. A home health nurse sees her three times a week to manage pressure sores. Which one of the following is true regarding this patient s qualification for Medicare hospice? A. She does qualify because the natural course of advanced dementia usually leads to death in less than 6 months B. She does qualify because the comorbidity of frequent hospitalization suggests a prognosis of less than 6 months C. She does not qualify because she can speak more than six words D. She does not qualify because she can respond to familiar faces
A 65-year-old male with metastatic pancreatic cancer is admitted to the hospital for management of a pain crisis. While he is hospitalized his opioid medications are titrated to control his pain. On hospital day 10, after a goals-of-care conversation with his hospital team, he decides to change to comfort-focused treatment. Which one of the following would be most appropriate for this patient? A. Docusate sodium (Colace), 1 tablet orally daily as needed for constipation B. Senna, 2 tablets orally at bedtime daily for constipation C. Psyllium (Metamucil), 1 capful daily with 8 ounces of water for constipation D. Diazepam (Valium), 5 mg orally every 1 hour as needed to control agitation
A 65-year-old male with metastatic pancreatic cancer is admitted to the hospital for management of a pain crisis. While he is hospitalized his opioid medications are titrated to control his pain. On hospital day 10, after a goals-of-care conversation with his hospital team, he decides to change to comfort-focused treatment. Which one of the following would be most appropriate for this patient? A. Docusate sodium (Colace), 1 tablet orally daily as needed for constipation B. Senna, 2 tablets orally at bedtime daily for constipation C. Psyllium (Metamucil), 1 capful daily with 8 ounces of water for constipation D. Diazepam (Valium), 5 mg orally every 1 hour as needed to control agitation
A 72-year-old female has recently been diagnosed with advanced idiopathic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. You explain the diagnosis and prognosis and advise her on breathing exercises. Which one of the following would be most likely to decrease her sense of breathlessness and improve her exertional tolerance without affecting mortality? A. As-needed morphine B. Scheduled morphine C. As-needed lorazepam D. Scheduled lorazepam
A 72-year-old female has recently been diagnosed with advanced idiopathic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. You explain the diagnosis and prognosis and advise her on breathing exercises. Which one of the following would be most likely to decrease her sense of breathlessness and improve her exertional tolerance without affecting mortality? A. As-needed morphine B. Scheduled morphine C. As-needed lorazepam D. Scheduled lorazepam
A 52-year-old female Hmong patient is hospitalized with acute gastrointestinal bleeding, presumably associated with her known colon cancer. Her husband explains that people of their culture believe that spirits are responsible for illness. The patient believes that she brought on her illness by traveling close to a large body of water where the spirits live. Which one of the following would be an appropriate response? A. The bleeding is from your cancer B. The idea of spirits causing your bleeding is unfounded and you should not feel guilty C. I m going to ask my partner from behavioral health to see you D. What else should I know about your culture?
A 52-year-old female Hmong patient is hospitalized with acute gastrointestinal bleeding, presumably associated with her known colon cancer. Her husband explains that people of their culture believe that spirits are responsible for illness. The patient believes that she brought on her illness by traveling close to a large body of water where the spirits live. Which one of the following would be an appropriate response? A. The bleeding is from your cancer B. The idea of spirits causing your bleeding is unfounded and you should not feel guilty C. I m going to ask my partner from behavioral health to see you D. What else should I know about your culture?
The table below displays the conversion factors for morphine, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, and oxycodone. Based on this chart, which one of the following statements is accurate? A 2-mg dose of oral hydromorphone is roughly equivalent to 5 mg of oral oxycodone A 5-mg dose of oral oxycodone is roughly equivalent to 15 mg of oral morphine A 45-mg dose of oral hydrocodone is roughly equivalent to 4 mg of oral hydromorphone A 2-mg dose of intravenous morphine is roughly equivalent to 0.1 mg of intravenous hydromorphone A. B. C. D.
The table below displays the conversion factors for morphine, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, and oxycodone. Based on this chart, which one of the following statements is accurate? A 2-mg dose of oral hydromorphone is roughly equivalent to 5 mg of oral oxycodone A 5-mg dose of oral oxycodone is roughly equivalent to 15 mg of oral morphine A 45-mg dose of oral hydrocodone is roughly equivalent to 4 mg of oral hydromorphone A 2-mg dose of intravenous morphine is roughly equivalent to 0.1 mg of intravenous hydromorphone A. B. C. D.
Using the chart provided it is possible to calculate equivalent dosages for opioids. A 20- mg dose of oral oxycodone is equivalent to 30 mg of oral morphine, so multiplying the oxycodone dose by 1.5 will provide the equivalent dose of morphine. A 5-mg dose of oral oxycodone is therefore equivalent to 7.5 mg of oral morphine.
A 57-year-old female with stage IV ovarian cancer presents to the emergency department with a new onset of shortness of breath. She is unable to lie down or complete sentences. A chest radiograph reveals a new large, likely malignant, pleural effusion. Which one of the following is true about this condition? A. Repeated thoracentesis is contraindicated because it increases the mortality risk B. Tunneled pleural catheters are expensive and ineffective for managing this problem C. Chest tube drainage alone prevents re-accumulation of fluid at 30 days 60% 80% of the time D. Systemic chemotherapy or hormonal therapy is the most effective treatment
A 57-year-old female with stage IV ovarian cancer presents to the emergency department with a new onset of shortness of breath. She is unable to lie down or complete sentences. A chest radiograph reveals a new large, likely malignant, pleural effusion. Which one of the following is true about this condition? A. Repeated thoracentesis is contraindicated because it increases the mortality risk B. Tunneled pleural catheters are expensive and ineffective for managing this problem C. Chest tube drainage alone prevents re-accumulation of fluid at 30 days 60% 80% of the time D. Systemic chemotherapy or hormonal therapy is the most effective treatment
A 63-year-old male with advanced lung cancer is admitted to a palliative care unit for pain management. Shortly after admission he develops agitated delirium. He has no contraindications to the use of sedatives or antipsychotics. His behavior is distressing to himself and his family. Nonpharmacologic treatment has not been effective. In addition to adjusting his pain medication, the most appropriate treatment for this patient entering terminal delirium would be A. oral hydroxyzine (Vistaril) B. oral lorazepam (Ativan) C. oral haloperidol and diazepam (Valium) D. oral haloperidol and lorazepam E. intravenous morphine
A 63-year-old male with advanced lung cancer is admitted to a palliative care unit for pain management. Shortly after admission he develops agitated delirium. He has no contraindications to the use of sedatives or antipsychotics. His behavior is distressing to himself and his family. Nonpharmacologic treatment has not been effective. In addition to adjusting his pain medication, the most appropriate treatment for this patient entering terminal delirium would be A. oral hydroxyzine (Vistaril) B. oral lorazepam (Ativan) C. oral haloperidol and diazepam (Valium) D. oral haloperidol and lorazepam E. intravenous morphine
A 55-year-old female with metastatic breast cancer presents with her husband, who reports that for the past 4 months she has had frequent episodes of crying, a feeling of hopelessness, and a lack of interest in activities that used to bring her joy. She is on palliative chemotherapy and her life expectancy is greater than 3 months. Which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point? A. No further evaluation because her symptoms are a normal response to her terminal cancer diagnosis B. Administer a Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9) and a numerical rating scale for pain C. Consider quetiapine (Seroquel) if insomnia is also present D. Offer hospitalization in a behavioral health unit
A 55-year-old female with metastatic breast cancer presents with her husband, who reports that for the past 4 months she has had frequent episodes of crying, a feeling of hopelessness, and a lack of interest in activities that used to bring her joy. She is on palliative chemotherapy and her life expectancy is greater than 3 months. Which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point? A. No further evaluation because her symptoms are a normal response to her terminal cancer diagnosis B. Administer a Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9) and a numerical rating scale for pain C. Consider quetiapine (Seroquel) if insomnia is also present D. Offer hospitalization in a behavioral health unit
A patient with malignant melanoma and a 2-month history of mid-thoracic back pain presents to the emergency department after a fall. She reports significant progressive weakness over the past 3 days and is now unable to climb stairs or to rise off the toilet seat unassisted. The most important initial step for addressing this patient s weakness would be A. plain radiographs of the thoracic spine B. urgent MRI of the thoracic spine C. urgent MRI of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine D. urgent CT myelography
A patient with malignant melanoma and a 2-month history of mid-thoracic back pain presents to the emergency department after a fall. She reports significant progressive weakness over the past 3 days and is now unable to climb stairs or to rise off the toilet seat unassisted. The most important initial step for addressing this patient s weakness would be A. plain radiographs of the thoracic spine B. urgent MRI of the thoracic spine C. urgent MRI of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine D. urgent CT myelography
Which one of the following is true about a 53-year-old female with chronic alcohol abuse who is hospitalized frequently with encephalopathy? A. A medical team may determine whether she is competent to make her own health care decisions B. A judge may determine whether she is competent to make her own health care decisions C. A social worker may determine whether she is capable of making her own health care decisions D. Her health care proxy may automatically make financial decisions for her when she is encephalopathic
Which one of the following is true about a 53-year-old female with chronic alcohol abuse who is hospitalized frequently with encephalopathy? A. A medical team may determine whether she is competent to make her own health care decisions B. A judge may determine whether she is competent to make her own health care decisions C. A social worker may determine whether she is capable of making her own health care decisions D. Her health care proxy may automatically make financial decisions for her when she is encephalopathic
A 74-year-old male is hospitalized with heart failure and an ejection fraction of 14%. He has shortness of breath at rest despite maximal medical therapy. You include the drawing of an illness trajectory as part of your palliative care discussion with the patient and his family. Which one of the illness trajectories shown below would be most likely for this patient? A. Sudden death B. Frailty C. Organ failure D. Cancer/terminal illness
A 74-year-old male is hospitalized with heart failure and an ejection fraction of 14%. He has shortness of breath at rest despite maximal medical therapy. You include the drawing of an illness trajectory as part of your palliative care discussion with the patient and his family. Which one of the illness trajectories shown below would be most likely for this patient? A. Sudden death B. Frailty C. Organ failure D. Cancer/terminal illness
A 59-year-old patient with oxygen- and corticosteroid-dependent COPD is admitted for severe respiratory distress. The pulmonologist recommends intubation for mechanical ventilation and the patient s family asks for your opinion. Which one of the following would be appropriate advice? A. If a ventilator is started it is unlikely to be needed long term B. A tracheostomy will typically be recommended only if intubation is required for longer than 4 weeks C. If the family agrees to short-term intubation, a date should be set for reevaluating the situation D. Withdrawal of mechanical respiratory support in a ventilator- dependent patient would be physician-assisted suicide E. Weaning of ventilator support causes more distress than abrupt withdrawal
A 59-year-old patient with oxygen- and corticosteroid-dependent COPD is admitted for severe respiratory distress. The pulmonologist recommends intubation for mechanical ventilation and the patient s family asks for your opinion. Which one of the following would be appropriate advice? A. If a ventilator is started it is unlikely to be needed long term B. A tracheostomy will typically be recommended only if intubation is required for longer than 4 weeks C. If the family agrees to short-term intubation, a date should be set for reevaluating the situation D. Withdrawal of mechanical respiratory support in a ventilator- dependent patient would be physician-assisted suicide E. Weaning of ventilator support causes more distress than abrupt withdrawal
A 68-year-old male is hospitalized with multiple morbidities, including end- stage heart, lung, and renal failure. His condition has been deteriorating since he was admitted, despite optimal aggressive treatment. Family members feel there is an impasse between the primary care physician who suggests palliative treatment and the consulting specialists who encourage aggressive interventions. They request input from the ethics committee but the involved physicians resist. Which one of the following is true in this situation? A. A family member may not request an ethics consult B. An ethics consult is more likely to help if it is obtained early in the hospitalization C. Judges are barred from considering the opinions of the ethics committee in deciding court cases D. The fact that an ethics investigation is conducted reflects poorly on the involved physicians
A 68-year-old male is hospitalized with multiple morbidities, including end- stage heart, lung, and renal failure. His condition has been deteriorating since he was admitted, despite optimal aggressive treatment. Family members feel there is an impasse between the primary care physician who suggests palliative treatment and the consulting specialists who encourage aggressive interventions. They request input from the ethics committee but the involved physicians resist. Which one of the following is true in this situation? A. A family member may not request an ethics consult B. An ethics consult is more likely to help if it is obtained early in the hospitalization C. Judges are barred from considering the opinions of the ethics committee in deciding court cases D. The fact that an ethics investigation is conducted reflects poorly on the involved physicians
Many conversion charts suggest that a 12 g/hour fentanyl transdermal patch (Duragesic) is roughly equivalent to 30 mg of morphine in 24 hours. Which one of the following would be the most appropriate fentanyl starting dose for a person taking morphine sulfate (MS Contin), 30 mg every 8 hours, and immediate-release morphine, 7.5 mg two times daily? A. Half of a 12 g/hour patch every 72 hours B. One 12 g/hour patch every 72 hours C. One 25 g/hour patch every 72 hours D. One 37.5 g/hour patch every 72 hours E. One 50 g/hour patch every 72 hours
Many conversion charts suggest that a 12 g/hour fentanyl transdermal patch (Duragesic) is roughly equivalent to 30 mg of morphine in 24 hours. Which one of the following would be the most appropriate fentanyl starting dose for a person taking morphine sulfate (MS Contin), 30 mg every 8 hours, and immediate-release morphine, 7.5 mg two times daily? A. Half of a 12 g/hour patch every 72 hours B. One 12 g/hour patch every 72 hours C. One 25 g/hour patch every 72 hours D. One 37.5 g/hour patch every 72 hours E. One 50 g/hour patch every 72 hours
The total daily dose of oral opioid in this scenario is 105 milligrams morphine equivalent (MME). An approximately equivalent fentanyl dose would be 40 g/hour every 3 days. This should be decreased by 25% to 50% to allow for incomplete cross- tolerance, which would be 21 32 g/hour. Incomplete cross tolerance refers to the fact that in any individual, one opioid might have a stronger effect than another. The patch should never be cut.
An 86-year-old female with a history of COPD and long-term tobacco use is treated for recurrent pneumonia, which fails to improve despite multiple courses of antibiotics. CT of the chest reveals multiple spiculated lesions throughout the lungs, as well as partially visualized lesions in the dome of the right side of the liver suspicious for metastatic cancer. She decides not to proceed with aggressive treatment and requests your help in filling out her advance directive, which includes a discussion of CPR. Which one of the following would be accurate advice when counseling this patient? A. Television shows depicting CPR have helped to promote widespread public understanding of the procedure B. In the United States about 45% of all patients who receive CPR leave the hospital alive C. In the United States about 20% of frail elderly who receive CPR leave the hospital alive D. In the United States <1% of patients with advanced chronic disease who receive CPR leave the hospital alive
An 86-year-old female with a history of COPD and long-term tobacco use is treated for recurrent pneumonia, which fails to improve despite multiple courses of antibiotics. CT of the chest reveals multiple spiculated lesions throughout the lungs, as well as partially visualized lesions in the dome of the right side of the liver suspicious for metastatic cancer. She decides not to proceed with aggressive treatment and requests your help in filling out her advance directive, which includes a discussion of CPR. Which one of the following would be accurate advice when counseling this patient? A. Television shows depicting CPR have helped to promote widespread public understanding of the procedure B. In the United States about 45% of all patients who receive CPR leave the hospital alive C. In the United States about 20% of frail elderly who receive CPR leave the hospital alive D. In the United States <1% of patients with advanced chronic disease who receive CPR leave the hospital alive
A 43-year-old male is treated for squamous cell carcinoma of the throat using chemotherapy and radiation to his neck. Several days after radiation treatment is started he begins to have pain with swallowing and develops sensitivity and blistering of his oral cavity. Which one of the following is true regarding this problem? A. A thorough dental examination is recommended before neck radiation B. All chemotherapeutic agents are associated with the same risk of mucositis C. Prophylactic antifungal mouthwash should be used to decrease the risk of mucositis D. Combination topical agents should not be used for pain relief of mucositis
A 43-year-old male is treated for squamous cell carcinoma of the throat using chemotherapy and radiation to his neck. Several days after radiation treatment is started he begins to have pain with swallowing and develops sensitivity and blistering of his oral cavity. Which one of the following is true regarding this problem? A. A thorough dental examination is recommended before neck radiation B. All chemotherapeutic agents are associated with the same risk of mucositis C. Prophylactic antifungal mouthwash should be used to decrease the risk of mucositis D. Combination topical agents should not be used for pain relief of mucositis
A 45-year-old female with diffuse but treatable lymphoma asks you for a referral to a palliative care specialist. You advise her that A. a palliative care specialist is appropriate at this time and you will arrange it B. a palliative care specialist is appropriate only after radiation therapy is completed C. a palliative care specialist is not appropriate because her life expectancy may be greater than 6 months D. a palliative care specialist is not appropriate because there are still treatment options available
A 45-year-old female with diffuse but treatable lymphoma asks you for a referral to a palliative care specialist. You advise her that A. a palliative care specialist is appropriate at this time and you will arrange it B. a palliative care specialist is appropriate only after radiation therapy is completed C. a palliative care specialist is not appropriate because her life expectancy may be greater than 6 months D. a palliative care specialist is not appropriate because there are still treatment options available
A 94-year-old female nursing home resident has ischemic cardiomyopathy, occasional angina, and an ejection fraction of 25%. She uses a wheelchair but is able to pivot transfer. She is seen in the emergency department with a new minimally displaced right hip fracture. The orthopedist has offered to perform surgery to stabilize the fracture and reduce pain. Which one of the following would be appropriate advice? A. The 1-year mortality rate for nonoperative management is similar to that of surgery B. Early mobilization is appropriate if the hip is not repaired C. The risk of a heart attack automatically precludes hip surgery D. Surgery is the only option that will adequately address the pain
A 94-year-old female nursing home resident has ischemic cardiomyopathy, occasional angina, and an ejection fraction of 25%. She uses a wheelchair but is able to pivot transfer. She is seen in the emergency department with a new minimally displaced right hip fracture. The orthopedist has offered to perform surgery to stabilize the fracture and reduce pain. Which one of the following would be appropriate advice? A. The 1-year mortality rate for nonoperative management is similar to that of surgery B. Early mobilization is appropriate if the hip is not repaired C. The risk of a heart attack automatically precludes hip surgery D. Surgery is the only option that will adequately address the pain
For more than 2 months, a 52-year-old female with an unresectable glioblastoma multiforme has been using extended-release morphine sulfate (MS Contin), 60 mg orally every 8 hours, plus immediate-release morphine, 20 mg three times a day as needed for breakthrough pain. This regimen provided good control of her pain until the last 2 weeks. During that time she has had severe pain even with light touch, including moving the blankets over her. Her pain has continued to increase despite escalating doses of morphine. Which one of the following is most likely to help her symptoms? A. Continuing to increase the morphine dosage until the pain is controlled B. Switching to continuous morphine subcutaneously at an equivalent dosage C. Adding diphenhydramine (Benadryl) D. Decreasing the morphine dosage and considering a change to a different opioid