Assisting with Enteral Tube Feeding and Dysphagia Management
This content covers essential information on assisting with oral feeding for patients at risk of aspiration, managing dysphagia, diet progression, and enteral tube feeding procedures. It emphasizes safety, independence, and dignity in feeding practices. The content includes tips for preventing aspiration, dysphagia management techniques, diet progression options, and complications related to enteral feeding. It serves as a comprehensive guide for healthcare providers involved in providing nutrition support to patients in various settings.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
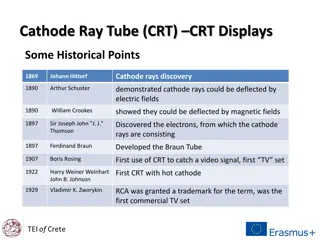
CHAPTER 44 NG TUBE INSERTION, TUBE FEEDING, AND PEG CARE.
ASSISTING WITH ORAL FEEDING 1. Safety 2. Independence 3. Dignity Those at risk for aspiration: decreased level of alertness, decreased gag reflex, or cough reflex, and those who have difficult managing saliva. Skill 44-1 ( Aspiration Precautions)
DYSPHAGIA Identified by speech therapist and recommendations are made: Hand hygiene prior to meals -elevate HOB 30 minutes prior to eating & rest 30 minutes prior to eating. Upright 30 minutes after eating at 90 degrees. Head to chin down position to prevent aspiration Liquids may need to be thickened to consistency of mashed potatoes. Foods may need to be pureed. Place to 1 teaspoon of food on unaffected side of the mouth, allowing the utensil to touch the mouth or tongue. Do NOT use straw. Promote swallowing effort by placing hand on throat to gently palpate swallowing as it occurs. Have patient swallow twice to clear the pharynx. Provide verbal coaching of swallowing process and give positive reinforcement. Observe for coughing, choking, gagging or drooling of food. May need to suction. Provide hand hygiene & oral care after meals
DYSPHAGIA May have to use thicker ( 4 types of liquid thicker) A-thin liquid or low viscosity B-nectar like liquid ( medium viscosity) C-honey like liquid D-Spoon thick liquid ( pudding viscosity) Always feed slowly and allow to empty mouth between feedings. May require verbal couching for each step in process
DIET PROGRESSION ( BOX 44-10) NPO: NOTHING BY MOUTH Clear Liquid ( Broth, Ginger Ale, coffee, tea) Full Liquid ( ice cream, custards, cooked cereal) Pureed- ( scrambled eggs, pureed meats) Mechanical soft ( cottage cheese rice, cooked fruits) Soft-low Residue High Residue Low sodium Low cholesterol Diabetic Regular
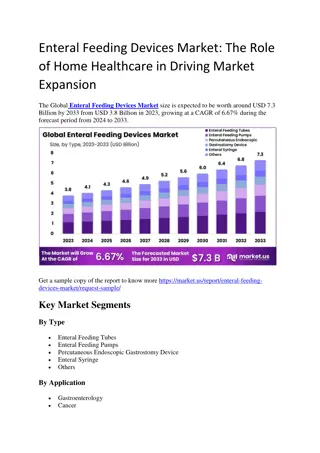
ENTERAL TUBE FEEDING Nutrients given in the GI tract 3 ways to receive nasogastric, jejunal, or gastric tubes. 4 types formula: Milk based blenderized foods, modular formulas, elemental formulas, and specialty formula. Increase rate every 8-12hrs based on dr s order if no intolerance ( Box 44-12) s/s intolerance- high gastric residual, nausea, cramping, vomiting, and diarrhea Box 44-11 indications for eternal and parenteral nutrition.
ENTERAL FEEDING COMPLICATIONS Aspiration Diarrhea Constipation Tube occlusion Tube displacement Delayed gastric emptying Serum electrolyte imbalance ( Table 44-7)
INSERTING NASOENTERIC TUBE FOR ENTERAL FEEDINGS Skill 44-2 Inserting NG Tube for Enteral Feeding Skill 44-3- Administration of Enteral Feedings Insertion of tube will make client gag Must check placement of feeding tube before starting feeding Gastric intestinal aspiration for PH is most accurate for placements after x-ray ( normal ph 0-4 of gastric secretions. ( x-ray most reliable) If complains of cramping then decrease rate, and or fluids may also be to cold.
TUBE FEEDINGS INFUSION PUMPS Tube feedings always on pump Consult doctor rate ( usually 40-60) Good to maintain constant rate Tubing changed every 24hrs Never d/c suddenly will cause hypoglycemic reactions. Mouth care every 2 hrs
PARENTERAL NUTRITION (TPN) Administered to clients who are unable to digest or absorb eternal nutrition Provided Intravenous May also be known as lipid emulsions, run over 24hrs, contain kilo-calories and prevent fatty acid deficiencies.
NASO GASTRIC INTUBATION Decompression-Removal of secretions and gaseous substances from the GI tract Enteral feeding- Installation of liquid nutrition Lavage- irrigation of stomach in cases of active bleeding, poisoning, or gastric dilation.
Creative Commons License This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Except where otherwise noted, this content by Southern Regional Technical College is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, click https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ Healthcare Careers Work!(HCW) is sponsored by a $2.3 million grant from the U.S. Department of Labor, Employment & Training Administration. TAACCCT Grant #TC- 26488-14-60-A-13. Southern Regional Technical College is an equal opportunity employer and will make adaptive equipment available to persons with disabilities upon request. This workforce product was funded by a grant awarded by the U.S. Department of Labor s Employment and Training Administration. The product was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The U.S. Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership.