Enhancing Health Information Exchange with OpenHIE Approach
The Open Health Information Exchange (OpenHIE) community focuses on interoperable health information sharing by prioritizing security, scalability, and governance. The approach emphasizes internationally recognized standards and optimized infrastructure for secure data exchange. Starting with immunization use cases, OpenHIE streamlines data sharing across various levels of the health system, with dedicated registries for health workers, facilities, and clients ensuring unique identity management for improved service delivery.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Open Health Information Exchange (OpenHIE) Community: A diverse community enabling interoperable health information sharing
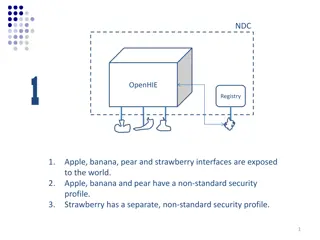
Why OpenHIE? The OpenHIE approach relies on internationally recognized and tested standards. Custom APIs and peer to peer integration is not scalable and difficult to maintain. Information systems are rarely designed to handle high volumes of data exchange. The OpenHIE infrastructure is optimized for scale and increasing volumes of secure data traffic. The OpenHIE model prioritizes security, patient and provider privacy and the role of governance. Governance and security is enforced by the Interoperability layer whereby all data transactions pass through.
Starting with Immunization Use Case Simple data and service delivery that is highly routinized across most developed countries While it is PHI, it is under less scrutiny than other data for example HIV Very broad foot print in country High volumes (relatively speaking to most other screening and interventions) Links all levels of the health system Do not necessarily need to wrestle with some of the more complex issues such as referrals, consent, terminologies etc 4
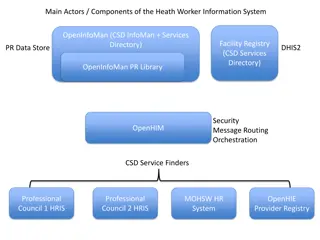
HEALTH WORKER REGISTRY (HWR) FACILITY REGISTRY (FR) ATNA SHARED HEALTH RECORD (SHR) CLIENT REGISTRY (CR) INTERLINKED REGISTRY (IR) HMIS (dhis2) INTEROPERABILITY LAYER (ENSURES SECURE EXCHANGE OF DATA) REGISTRATION INTERFACE TIIS Distribution Resource Planner RAPID PRO TIIS WEB APP MOBILE APP MOBILE PHONE
Client Registry An enterprise master patient index (EMPI), or Client Registry manages the unique identity of citizens receiving health services with the country For whom
Health Worker Registry A Health Worker Registry is the central authority for maintaining the unique identities of health providers within the country By whom
Facility Registry A Health Facility Registry serves as a central authority to uniquely identify all places where health services are administered within the country Where?
Shared Health Record A Shared Health Record is a repository containing the normalized version of content created within the community, after being validated against each of the previous registries. It is a collection of person-centric records for patients with information in the exchange.
Health Management Information System A Health Management Information System is a repository containing the normalized version of aggregate-level content created within the community, after being validated against each of the previous registries. It is a collection of indicator-centric records for cohorts with information in the exchange.
Health Interoperability Layer A Health Interoperability Layer receives all communications from point of service applications within a health geography, and orchestrates message processing among the point of service application and the hosted infrastructure elements.
Recording an Immunization TS CR ILR SHR PDQ IL XDS.b Generate immunization message Who received the vaccine? GIIS eLMIS
Recording an Immunization Health Facility Registry HCMIS HRHIS CSD CR ILR SHR CSD IL Who gave the vaccine? Where was the vaccine given? GIIS eLMIS
What is next? Infrastructure is there to easily allow other health verticals to take advantage of it Many of the issues which were previously more philosophical have real practical significance now as they will be supporting real use cases Forcing function Defacto standards which can be adopted for Tanzania BID is set up to transition to government 14
Questions? 15