Economic Policies: Monetary and Fiscal Approaches
Explore the dynamics of economic equilibrium, aggregate demand, and supply while delving into the effectiveness of monetary and fiscal policies. Learn about strategies to tackle inflation and unemployment through contractionary and expansionary measures, and how crowding out can impact the economy. Understand the implications of short-run and long-run aggregate supply on economic growth and stability.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
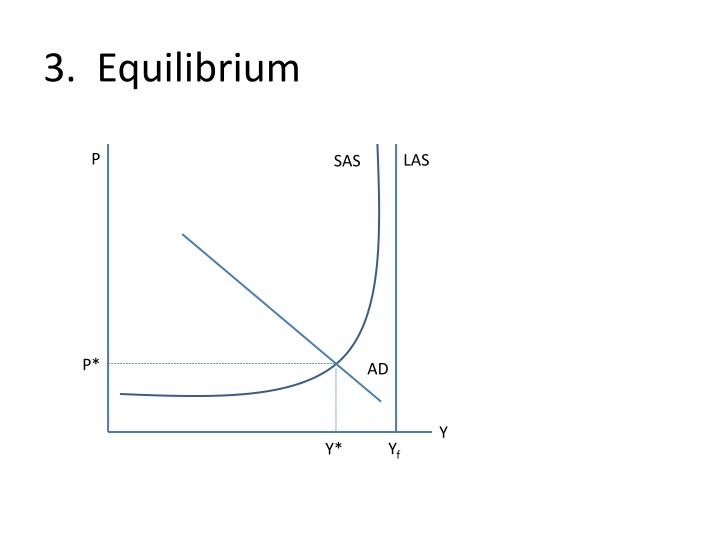
3. Equilibrium P LAS SAS P* AD Y Yf Y*
4.a. Aggregate demand AD0 -> AD1 => P Y P LAS SAS => unemployment decreases but inflation increases AD1 AD0 AD2 P1 AD0 -> AD2 => P Y => unemployment increases but inflation decreases P0 P2 Y Yf Y2 Y0 Y1
4.a.(2)(a) Monetary policy AD0 -> AD1 => P Y P LAS SAS => unemployment decreases but inflation increases AD1 AD0 Use contractionary monetary policy to deal with the problem of inflation AD2 P1 AD0 -> AD2 => P Y => unemployment increases but inflation decreases P0 P2 Use expansionary monetary policy to deal with the problem of unemployment Y Yf Y2 Y0 Y1
Effectiveness of monetary policy r r r0 r0 r1 r1 IRE IRE IRE0 IRE1 IRE IRE0 IRE1 IRE
4.a.(2)(b) Fiscal policy AD0 -> AD1 => P Y P LAS SAS => unemployment decreases but inflation increases AD1 AD0 Use contractionary fiscal policy to deal with the problem of inflation AD2 P1 AD0 -> AD2 => P Y => unemployment increases but inflation decreases P0 P2 Use expansionary fiscal policy to deal with the problem of unemployment Y Yf Y2 Y0 Y1
4.a.(2)(b) i) Crowding out r MS0 MS1 r r1 r1 r0 r0 r2 MD1 IRE MD0 IRE1 M M0 IRE0 IRE Crowding out
b. Short-run aggregate supply SAS1 P Resource costs increase: LAS SAS0 SAS0 -> SAS1 => P Y => unemployment increases and inflation increases Worst possible situation: - Using expansionary policy to deal with unemployment makes inflation worse P1 P0 AD - Using contractionary policy to deal with inflation makes unemployment worse Y Yf Y1 Y0
c. Long-run aggregate supply P SAS LAS0 LAS1 SAS More resources, more efficient use of resources, improved technology => economic growth SAS0 -> SAS1 => P Y P0 => unemployment decreases and inflation decreases P1 AD Y Y1 (Yf)1 Y0(Yf)0
5. Business cycle Y Peak Recession Expansion Turning points Trough Time