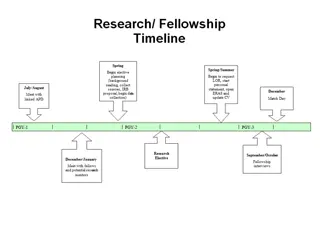
DNP Scholarly Project Proposal Defense Overview
This scholarly project proposal defense covers essential aspects including background, problem description, evidence synthesis, theoretical framework, methods, DNP essentials, references, and Q&A session.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Recovering from Errors during Programming by Demonstration Jiun-Hung Chen and Daniel S. Weld University of Washington By, Paurav Surendra
INTRODUCTION CHINLE is a automation tool Works across applications Programming by demonstration(PBD) systems are constructed. Provides user ability to interact and correct the system Intuitive interface for the users
AUTOMATIC VERSION-SPACE GENERATION 1/2 What is Version Space ? CHINLE creates the VS automatically, using the interface specification
AUTOMATIC VERSION-SPACE GENERATION 2/2 A version space is executed on an input, by applying every hypothesis in the version space to the input and collecting the set of resulting outputs. The output with the highest probability is chosen
PROBABILISTIC WEIGHTING FOR DISAMBIGUATION Need for a Probabilistic Weighting ? A hypothesis conditioned on the value of the most recently changed variable is more likely If (n+1)staction is being learnt, n variables have been modified. A hypothesis is conditioned on a variable which was changed t steps previously, it is assigned a probability of P/2t All k hypotheses whose conditioning variables haven t changed are assigned the weight P/k2n
CORRECTING DEMONSTRATION ERRORS 1/2
CORRECTING DEMONSTRATION ERRORS 2/2
QUESTIONS Overall reaction to the paper ? Opinion on the techniques used ? Is it better than the existing tools ? Other uses for the system ?