Bonding in Chemistry
Delve into the world of chemical bonding through ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Explore how elements form bonds, from the attraction between sodium and chloride ions to the sharing of electrons in covalent bonds. Witness the formation of compounds like sodium chloride and magnesium oxide, understanding the gains and losses of electrons in the process. Discover the concept of covalent bonds and how shared electrons create stable molecules, providing insights into the essential nature of bonding in chemistry.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic bonding
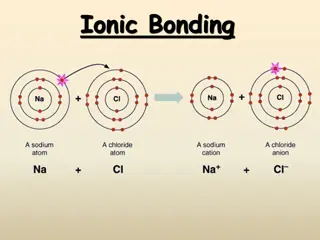
How Elements Bond 2 Bond Formation The positive sodium ion and the negative chloride ion are strongly attracted to each other. This attraction, which holds the ions close together, is a type of chemical bond called an ionic bond.
How Elements Bond 2 Bond Formation The compound sodium chloride, or table salt, is formed. A compound is a pure substance containing two or more elements that are chemically bonded.
How Elements Bond 2 More Gains and Losses Can elements lose or gain more than one electron? The element magnesium, Mg, in Group 2 has two electrons in its outer energy level. Magnesium can lose these two electrons and achieve a completed energy level.
How Elements Bond 2 More Gains and Losses Some atoms, such as oxygen, need to gain two electrons to achieve stability. The two electrons released by one magnesium atom could be gained by a single atom of oxygen. When this happens, magnesium oxide (MgO) is formed.
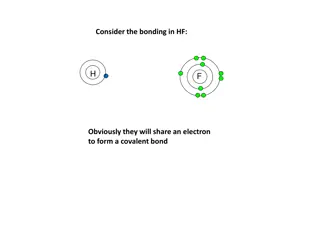
How Elements Bond 2 Convalent Bonds Sharing Some atoms are unlikely to lose or gain electrons because the number of electrons in their outer levels makes this difficult. The alternative is sharing electrons.
How Elements Bond 2 The Convalent Bond The chemical bond that forms between nonmetal atoms when they share electrons is called a covalent bond. Click image to view movie.
How Elements Bond 2 The Convalent Bond Shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms. They move back and forth between the outer energy levels of each atom in the covalent bond. So, each atom has a stable outer energy level some of the time.
How Elements Bond 2 The Convalent Bond The neutral particle is formed when atoms share electrons is called a molecule
How Elements Bond 2 The Convalent Bond A molecule is the basic unit of a molecular compound.
How Elements Bond 2 The Convalent Bond You can see how molecules form by sharing electrons in this figure.
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.