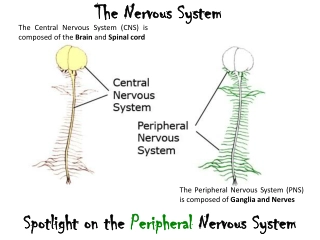
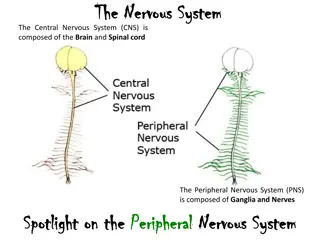
Deep Breathing Tests for Autonomic Nervous System Evaluation
Deep breathing tests are an essential tool for evaluating autonomic nervous system function. They involve controlled breathing patterns to observe changes in heart rate, providing valuable insights into cardiac and vagal nerve responses. These tests are used for various purposes, including assessing autonomic diseases like familial dysautonomia. Learn about the principles, procedures, and benefits of deep breathing tests in this informative guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Deep breathing test 4thSem(Hons) Mr. Debabrata Paria State Aided College Teacher Dept. of Physiology Bajkul Milani Mahavidyalaya
Principle D eepbreathingtestsiscardiacparasym patheticfunctions, becausetheheartresponsestodeepbreathingarem ediated bythevagalnerve,thetestisalsoreferredtoascardiovagal testing. D eep breathing evaluates changes in the instant heart rate that is provoked by deep breathing at 6 breaths/m in. Thetest startsw ith a rest period that gives patienttim etorelax.
Obtain the baseline for one minute, instruct subject to relax. Instruct subject to inhale for 5 seconds and exhale for 5 seconds.. This 10 second respiratory cycle should be repeated 6 times. Patient should breathe continuously and regularly. Respirator movement should resemble a wave. Sudden inhalations/exhalations should be avoided. Care hyperventilate. Preferentially, breathing should be done through nostrils with closed mouth and the end tidal CO2should be monitored to rule out hyperventilation. Deep breathing also activates the vagus nerve, which is like the boss of the parasympathetic4 overseeing things like mood, digestion, and heart rate. It will also send more oxygen to your brain and other organs. or holding be the breath not should taken to nervous system,
Deep breath test for evaluation of autonomic nervous system dysfunction in familial dysautonomia Familial dysautonomia is a genetic disease that affects the sensory and autonomic nervous systems with varying severity. To determine the diagnostic value of the DBT in patients with familial dysautonomia. The deep breath test is one of several measures used to assess the severity of autonomic diseases.
Steps for Deep Breathing 1. Sit or lie down in a quiet, comfortable place. 2. Start by observing your breath for a few moments and take a normal breath (inhale and exhale through your nose). 3. Now take a slow, deep breath. Let the air coming in through nose move downward into lower belly, notice that abdomen do expands fully. 4. Hold this position or breath. 5. Now breathe out through mouth (or your nose, if that feels more natural). This is how simple deep breathing. Remember to pay attention to how feel when inhale and exhale normally and when breathe deeply. Do deep breathing when you are stressed, angry, anxious, feeling low, or tense. Practicing deep breathing for 10 minutes every day, either in the morning, night, or during the day can have a significant impact on overall physical and mental health. Let us look at the benefits of deep breathing and why make it part of our everyday living.
autonomic function tests Heart rate variation during deep breathing: With the subject lying down comfortably on a couch, we instructed him to breathe slowly and deeply (following my count Breathe in, 1 2 3 4 5, breathe out, 1 2 3 4 5 and so on) at about six breaths per minute, 5 seconds each for inspiration and expiration. The maximum of six HR differences (maximum HR minus minimum HR during a deep breathing cycle) was taken as the deep breathing difference.
A better state-of-mind: deep breathing reduces state anxiety and enhances test performance through regulating test cognitions. Taking deep breaths before a timed math test significantly reduced self- reported feelings of anxiety and improved test performance. There was a statistical trend towards greater effectiveness in reducing state anxiety for boys compared to girls, and in enhancing test performance for students with higher autonomic reactivity in test-like situations. The latter moderation was significant when comparing high-versus-low autonomic reactivity groups. Mediation analyses suggest that deep breathing reduces state anxiety in test-like situations, creating a better state-of-mind by enhancing the regulation of adaptive-maladaptive thoughts during the test, allowing for better performance. The quick and simple technique can be easily learnt and effectively applied by most children to immediately alleviate some of the adverse effects of test anxiety on psychological well- being and academic performance.
Deep Breathing Benefits 1) Decreases stress, increases calm. ... 2) Relieves pain. ... 3) Stimulates the lymphatic system (Detoxifies the body). ... 4) Improves immunity. ... 5) Increases energy. ... 6) Lowers blood pressure. ... 7) Improves digestion.
Breathing detoxifies and releases toxins. 1. our body is designed to release 70% of its toxins (harmful, unwanted substances) through breathing. If we are not breathing effectively, its toxins and thus, other systems of our body must work overtime to release the toxins, which could eventually lead to an illness.
2. Deep breathing releases tension. Think how our body feels when we are tense, angry, scared, constricts. our muscles get tight and our breathing becomes shallow. When, breathing is shallow(superficial), we are not getting the amount of oxygen that our body needs. Deep breathing helps more oxygen enter your body, releasing the tension in our muscles. or stressed. It
3. Breathing relieves emotional problems. Deep breathing feelings out of body body. It disengages our mind from disturbing and negative thoughts. When we are breathe properly, our body sends signals to our brain asking it to calm down and relieves depression, and other emotions that our might be carrying around. will help clear uneasy stress, anxiety,
4. Breathing relieves pain. What happens to your breathing when you anticipate pain? You probably hold your breath. Yet studies show that breathing into your pain helps to ease it. Understand that when muscles are tense, they increase pressure on our nerves, which can make the pain exercises can help Conscious or deep breathing will relax our body and release tension around the pain site. worse. break Breathing this cycle.
5. Breathing massages our organs. The movements of the diaphragm during deep breathing massages our stomach, small intestine, liver, and pancreas. The upper movement of the diaphragm also massages the heart. When we inhale descends and abdomen expands. By this action, our massage to reach of vital organs and improve circulation in them. Controlled breathing also strengthens and tones our abdominal muscles. air, our diaphragm
6. Breathing strengthens our immune system. Deep breathing increases efficiency in oxygen absorption and supply. Oxygen travels through our bloodstream by attaching to heamoglobin (a type of protein that carries oxygen) in our red blood cells. This in turn then enriches our body to metabolize nutrients and vitamins, strengthens the muscles of the chest, improves digestion and quality of sleep. As a result, it strengthens our overall immune system by reducing stress and allowing enough rest. expands our lungs and
7. Breathing improves posture Good breathing techniques over a sustained period of time will encourage good posture and vice versa. Bad body posture will result in incorrect breathing. Diaphragmatic breathing body s balance and wrong/slouching posture. improves helps our correct
8. Breathing increases digestion and assimilation of food. The digestion is enhanced by the fact that the food is oxygenated more, allowing for faster and quicker absorption of nutrients and vitamins in our blood.
9. Breathing improves the nervous system. Deep, long breaths activate our nervous system and increase its efficiency responses. in handling the stress 10. Proper breathing makes the heart stronger. Breathing exercises reduce the workload on the heart in two ways. Deep breathing leads to more efficient lungs, which means more oxygen is brought into contact with blood sent to the lungs by our heart. So, the heart doesn t have to work as hard to deliver oxygen to the tissues.
11. Proper breathing assists in weight control. Deep breathing increases the supply of oxygen in our body and this extra oxygen supplied to our body helps in burning the extra fat that is deposited in our body.
Thank you Schedule your deep breathing exercise just as you would schedule important functional appointments. Set aside a minimum of two 10 minute segments of time everyday although you can begin with two five minutes segments if you prefer. Make deep breathing a part of daily life to stay healthy, longer, and livelier.