Computing Tolerance Intervals in JMP: An Add-In for Efficient Data Analysis
Tolerance intervals play a crucial role in statistical analysis, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals. This article introduces an add-in in JMP for computing tolerance intervals, highlighting the significance of understanding and interpreting these intervals correctly. The tool aims to simplify the process for scientists, allowing them to compute tolerance intervals in various configurations without the need for complex scripting, thus saving time for statisticians on more challenging projects.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
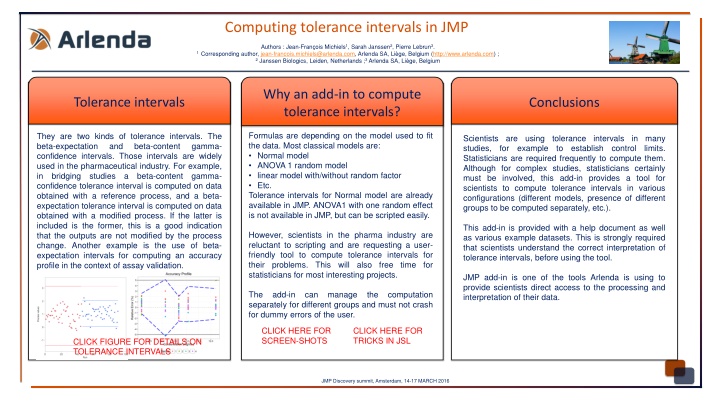
Computing tolerance intervals in JMP Authors : Jean-Fran ois Michiels1, Sarah Janssen2, Pierre Lebrun3. 1 Corresponding author, jean-francois.michiels@arlenda.com, Arlenda SA, Li ge, Belgium (http://www.arlenda.com) ; 2 Janssen Biologics, Leiden, Netherlands ;3 Arlenda SA, Li ge, Belgium Why an add-in to compute tolerance intervals? Tolerance intervals Conclusions Formulas are depending on the model used to fit the data. Most classical models are: Normal model ANOVA 1 random model linear model with/without random factor Etc. Tolerance intervals for Normal model are already available in JMP. ANOVA1 with one random effect is not available in JMP, but can be scripted easily. They are two kinds of tolerance intervals. The beta-expectation and confidence intervals. Those intervals are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry. For example, in bridging studies a confidence tolerance interval is computed on data obtained with a reference process, and a beta- expectation tolerance interval is computed on data obtained with a modified process. If the latter is included is the former, this is a good indication that the outputs are not modified by the process change. Another example is the use of beta- expectation intervals for computing an accuracy profile in the context of assay validation. Scientists are using tolerance intervals in many studies, for example to Statisticians are required frequently to compute them. Although for complex studies, statisticians certainly must be involved, this add-in provides a tool for scientists to compute tolerance intervals in various configurations (different models, presence of different groups to be computed separately, etc.). beta-content gamma- establish control limits. beta-content gamma- This add-in is provided with a help document as well as various example datasets. This is strongly required that scientists understand the correct interpretation of tolerance intervals, before using the tool. However, scientists in the pharma industry are reluctant to scripting and are requesting a user- friendly tool to compute tolerance intervals for their problems. This will also free time for statisticians for most interesting projects. JMP add-in is one of the tools Arlenda is using to provide scientists direct access to the processing and interpretation of their data. The separately for different groups and must not crash for dummy errors of the user. add-in can manage the computation CLICK HERE FOR SCREEN-SHOTS CLICK HERE FOR TRICKS IN JSL CLICK HERE FOR SCREEN-SHOTS CLICK HERE FOR TRICKS IN JSL CLICK FIGURE FOR DETAILS ON TOLERANCE INTERVALS JMP Discovery summit, Amsterdam, 14-17 MARCH 2016
Computing tolerance intervals in JMP -expectation tolerance intervals -content -confidence tolerance intervals -expectation tolerance interval is a statistical interval within which a specified proportion (beta) of the population is expected to fall. The way kEis computed depends on the model -expectation tolerance intervals -content -confidence tolerance intervals -content -confidence tolerance interval that is an interval within which a beta proportion of the population fall, with the confidence level gamma. The way kCis computed depends on the model Example The 95%-proportion tolerance interval computed on new data (blue) fits within the 95%-content 90%-confidence tolerance interval computed on old data (red). This illustrates that either both sets of data originates from the same process or that the known modifications does not affect the results. CLICK HERE TO RETURN JMP Discovery summit, Amsterdam, 14-17 MARCH 2016
CLICK HERE TO RETURN CLICK HERE TO RETURN JMP Discovery summit, Amsterdam, 14-17 MARCH 2016
Expressions to fit by group dt = open("$SAMPLE_DATA/Big Class.jmp"); ::By = {"sex","age"}; distr = expr(distr_platform = dt << Distribution( Continuous Distribution( Column( :height ) ) , bygroupanalysis )); show(distr); if(length(::By)==0, byexpression = expr(by()), if(length(::By)==1, byexpression = eval expr( by( Column( expr(::By[1]) ) ) ), byexpression = eval expr( by( Column( expr(::By[1]) ), Column( expr(::By[2]) ) ) ) ) ); distr2 = substitute(Name expr(distr),expr(bygroupanalysis),name expr(byexpression)); eval(distr2); distr2_reported = distr_platform << report(); if(length(::By)==0, distr2_reported["Summary Statistics"][1][1] << make data table(), distr2_reported[1]["Summary Statistics"][1][1] << make combined data table()); CLICK HERE TO RETURN CLICK HERE TO RETURN JMP Discovery summit, Amsterdam, 14-17 MARCH 2016