Comprehensive Overview of Jaw Imaging Modalities and Pathologies
Comprehensive overview detailing jaw imaging modalities such as X-Ray, CT, and MRI for evaluating jaw bone and tooth conditions. Covers anatomy, common mandibular lesions, odontogenic cysts, non-odontogenic cysts, and odontogenic benign tumors. Provides details on diagnostic protocols, imaging findings, and differential diagnoses. Includes informative images for better understanding.
Uploaded on Sep 08, 2024 | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
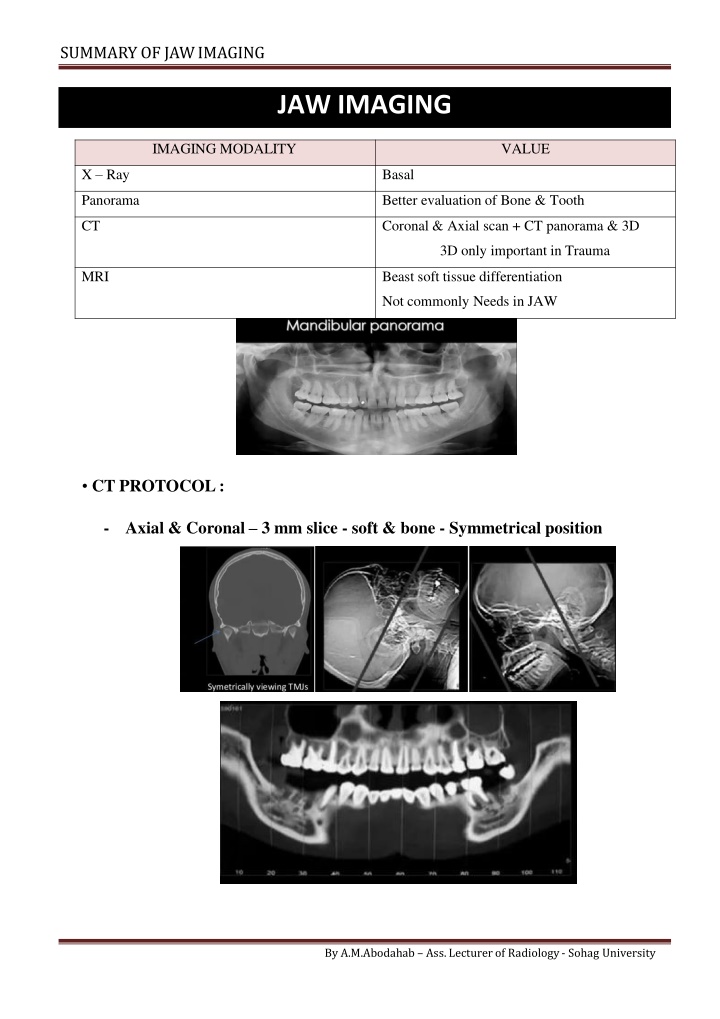
SUMMARY OF JAWIMAGING JAW IMAGING IMAGING MODALITY VALUE X Ray Basal Panorama Better evaluation of Bone & Tooth CT Coronal & Axial scan + CT panorama & 3D 3D only important in Trauma MRI Beast soft tissue differentiation Not commonly Needs in JAW CT PROTOCOL: - Axial & Coronal 3 mm slice - soft & bone - Symmetrical position By A.M.Abodahab Ass. Lecturer of Radiology - Sohag University
SUMMARY OF JAWIMAGING ANATOMY MANDIBULAR LESIONS CYSTS TUMORS Others MANDIBULAR LESIONS CYSTS TUMORS OTHERS ODONTOGENIC Related to atooth mostlyDiseased NON - Benign Malignant ODONTOGENIC Not related to tooth Simple Odont. Non = Lytic Radicular Osteoma Ameloblastoma Myxoma Residual Dentigerous ABC Stafine Chondromas = Sclerotic Cementoma odontoma Mixed Giant Cell Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive By A.M.Abodahab Ass. Lecturer of Radiology - Sohag University
SUMMARY OF JAWIMAGING ODONTOGENICCYSTS Related to a tooth - mostly Diseased ODONTOGENIC Related to a tooth - mostly Diseased Age Age 30:50y Cyst at root of caries tooth Incidence Incidence Commonest 65% Site Site Discretion Discretion Rounded unilocular- <10mm Radicular Cyst related to removed tooth Around crown of un-erupted tooth Mostly to impactedtooth Residual Dentigerous Common Painless usually 3rd molar Root mostly outside cyst Multilocular ,Cheesy Material - @ ramus & angle Young adult 20 :40 th Odontogenic Keratocyst Calcifying Odontogenic 11% Odontogenic Dentigerous Radicular Residual Keratocyst By A.M.Abodahab Ass. Lecturer of Radiology - Sohag University
SUMMARY OF JAWIMAGING Non ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Not Related to a tooth M>F Incisive Commonest Nonodont. At Incisive canal Lucent cyst betweenincisors Not True Cyst Just Medial Bone defect Lucent LobulatedCyst D.D.Odontogen.Keratocyst Lytic - Expansile MRI fluid-fluidlevels Stafine Simple Rare ABC Incisive Stafine ABC Simple Bone Cyst By A.M.Abodahab Ass. Lecturer of Radiology - Sohag University
SUMMARY OF JAWIMAGING ODONTOGENIC BENIGN TUMORS Lytic Sclerotic - MIXED Incidence Age Commonest Beningtumor Mandible 5 : 1 Maxilla Tenis RacketApperance Discretion 30:50y 80 % Ramus Ameloblastoma "Adamantinoma" Odontogenic Myxoma Odontoma Hard-painless-loss teeth Unilocular-Expansile-lytic Slow Expansile Lytic Multi locularseptated 50% with impactedtooth 1:3cm - Painless Benign , may local aggressive Lucent with central calcification Well defined Opaque mass surrounded hallow 2nd Decade Rare Cementoma Mostly 1st molar Attached toroot Odontoma Cementoma Ameloblastoma Odontogenic Myxoma Expansile Lytic Cyst in Mandible .What is your Diagnosis? Adamantinoma or OdontogenicKeratocyst 1. AVASCULARNECROSIS Answer Adamantinoma i.e . Ameloblastoma As it much more common By A.M.Abodahab Ass. Lecturer of Radiology - Sohag University
SUMMARY OF JAWIMAGING NON ODONTOGENIC BENIGN TUMORS Incidence Age Discretion Ball of Bone Osteoma Chondromas Giant Cell + Matrix calcification Lucent Small unilocular, then enlarge multilocular 2nd :3rd Decade D.D. Ameloblastome OdontogenicKeratocyst Osteoma Giant Cell Granuloma By A.M.Abodahab Ass. Lecturer of Radiology - Sohag University
SUMMARY OF JAWIMAGING MALIGNANT JAW TUMORS Malignant Criteria : o Cortical destruction o Peri-osteal reaction o Extraosseous extension o Mets. Malignant Tumors of Jaw: - Osteosarcomas - Chondrosarcomas - Malignant ameloblastoma "rare 1%" - Mets "mandible is common site ofmets" Osteosarcomas Mets "sun rays peri-osteal reaction" By A.M.Abodahab Ass. Lecturer of Radiology - Sohag University