Comprehensive Guide to Immune System Glossary Terms
Dive into the world of immune system glossary terms with definitions and visual aids. Explore key concepts such as immune cell activation, adaptive immune response, antibodies, antigens, and more. Understand the complex processes within the immune system through informative images and concise explanations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Immune System Glossary Terms in The Immune System Click & Learn
Immune System Glossary Activation A process by which a cell changes or gains functions in response to a stimulus.
Immune System Glossary Adaptive immune cell An immune cell involved in the adaptive immune response. Includes B cells and T cells.
Immune System Glossary Adaptive immune response One of the two main ways in which the immune system responds to pathogens. Provides long-lasting protection against specific pathogens but may take longer to start.
Immune System Glossary Antibody A small protein that binds to a specific antigen. Antibodies are made by plasma cells and help the immune system fight pathogens in various ways. The human immune system can generate billions of types of antibodies.
Immune System Glossary Antigen A small piece of biological material (protein, carbohydrate, lipid, or nucleic acid) that can be recognized by the immune system. Antigens from pathogens or abnormal cells trigger an immune response.
Immune System Glossary Antigen-MHC complex An antigen bound to an MHC protein on the surface of a cell. T cells must bind to a specific antigen-MHC complex in order to activate.
Immune System Glossary Antigen-presenting cell (APC) A cell with an antigen bound to an MHC protein on its surface. APCs interact with T cells to trigger an immune response. The most common APCs are dendritic cells.
Immune System Glossary Apoptosis A process by which a cell destroys itself. Involves several chemical reactions that make the cell change appearance and then die. Apoptosis is often used to kill cells that are unneeded or abnormal.
Immune System Glossary Autoimmune disease A condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body s healthy, normal cells.
Immune System Glossary Basophil An innate immune cell that circulates in the blood and is involved in inflammation.
Immune System Glossary B cell An adaptive immune cell that helps target and destroy specific pathogens. After being activated by T cells, B cells differentiate into plasma cells to produce antibodies.
Immune System Glossary B cell receptor (BCR) A protein on the surface of a B cell that binds to a specific antigen. Plays a major role in B cell activation.
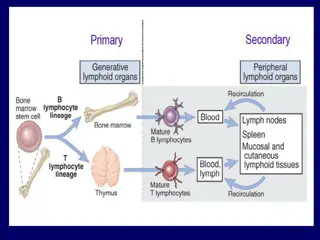
Immune System Glossary Bone marrow A spongy tissue in certain bones. Contains stem cells that develop into immune cells and red blood cells.
Immune System Glossary Cell-mediated immune response The processes of the adaptive immune response that play a major role in destroying infected cells through cytotoxic T cells.
Immune System Glossary Complement proteins A group of proteins in the blood that help destroy pathogens and infected cells. They can damage pathogens directly or attract other immune cells to the site of an infection.
Immune System Glossary Cytokines Small proteins released by cells to communicate with other cells. Some cytokines alert immune cells to an infection or activate certain immune cells.
Immune System Glossary Cytotoxic T cell A type of T cell that kills infected cells by making them undergo apoptosis.
Immune System Glossary Dendritic cell A type of phagocyte (innate immune cell that engulfs and destroys pathogens). Dendritic cells display antigens from the pathogens it engulfs in order to activate other immune cells.
Immune System Glossary Digestive system The organs and tissues involved in eating and breaking down food, absorbing nutrients into cells, and eliminating wastes.
Immune System Glossary Differentiation A process that switches a cell from one type to another, typically more specialized type. Differentiation is caused by changes in gene expression that are often triggered by chemicals, including cytokines and hormones.
Immune System Glossary Engulf A process in which certain cells, called phagocytes, surround and take in large particles (such as pathogens). The phagocyte extends its outer membrane around the particle, forming an enclosed structure called a vesicle that brings the particle into the cell.
Immune System Glossary Eosinophil An innate immune cell that destroys large pathogens, such as parasites, by releasing damaging molecules and chemical signals (cytokines).
Immune System Glossary Helper T cell A type of T cell that activates other immune cells, including B cells and cytotoxic T cells.
Immune System Glossary Histamine A small molecule released by mast cells to trigger inflammation. Histamine makes blood vessels leaky, which allows immune cells and fluid to move from the blood vessels into body tissues.
Immune System Glossary Humoral immune response The processes of the adaptive immune response that involve antibodies (also known as the antibody- mediated response). These processes make and use antibodies to fight specific pathogens. They include B cell activation and differentiation into plasma cells, which produce antibodies.
Immune System Glossary Immune cells Cells that are part of the immune system. Sometimes also called white blood cells or leukocytes.
Immune System Glossary Immune response The processes that the immune system uses to fight pathogens. Includes two main parts, the innate and adaptive immune responses, and involves many cells and organs.
Immune System Glossary Immune system A group of organs, tissues, cells, and molecules that protect the body from pathogens.
Immune System Glossary Immunocompromised A condition in which the immune system is weakened and less effective at fighting pathogens. A person could become immunocompromised due to certain medications, medical conditions, viral infections, etc.
Immune System Glossary Inflammation A process in the innate immune response that helps the body fight pathogens and repair tissue damage. Inflammation is triggered by injury or infection and can result in redness, pain, and swelling.
Immune System Glossary Innate immune cell An immune cell involved in the innate immune response. Includes phagocytes (macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells, etc.), mast cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
Immune System Glossary Innate immune response One of the two main ways in which the immune system responds to pathogens. Provides immediate protection but cannot target specific pathogens.
Immune System Glossary Lymph A fluid similar to blood that circulates throughout the body. Lymph contains immune cells but not red blood cells.
Immune System Glossary Lymph nodes Small organs throughout the body that contain many immune cells. Lymphatic vessels connect through lymph nodes.
Immune System Glossary Lymphatic vessels Thin tubes that carry a fluid called lymph throughout the body. Lymphatic vessels are similar to blood vessels but do not contain red blood cells.
Immune System Glossary Lymphocyte A type of immune cell. Includes T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
Immune System Glossary Lymphoid organs A group of organs that produce or contain large numbers of immune cells. Examples include the bone marrow, thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, and tonsils.
Immune System Glossary Macrophage An innate immune cell that plays many roles. Macrophages are phagocytes that engulf and destroy pathogens and abnormal cells. They can also release chemical signals (cytokines) to attract other immune cells.
Immune System Glossary Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein A protein that binds to antigens and displays them on the surface of a cell. Phagocytes use MHC proteins to display antigens from pathogens.
Immune System Glossary Mast cell An innate immune cell that plays a major role in inflammation. Releases chemical signals (histamine) that help fluid and immune cells move from the blood vessels into tissues.
Immune System Glossary Memory cells Long-lived B and T cells that are made the first time a pathogen infects the body. If the body is reinfected by the same type of pathogen, memory cells provide a faster, stronger adaptive immune response.
Immune System Glossary Microbe A microscopic organism. Includes viruses, bacteria, archaea, fungi, and parasites. Some microbes are helpful, and others cause disease.
Immune System Glossary Microbiome The community of microbes that live in and on the body, including fungi, bacteria, protozoa, and viruses. These microbes usually don t cause disease and are sometimes beneficial.
Immune System Glossary Monocyte An innate cell that differentiates into macrophages. Like macrophages, monocytes are phagocytes that engulf and destroy pathogens and abnormal cells.
Immune System Glossary Mucous membrane A thin tissue containing cells that make mucus. Mucous membranes line the digestive system (gut), respiratory system (airways), and urogenital tract.
Immune System Glossary Mucus A sticky, slimy substance produced by certain cells. Protects tissues by trapping pathogens and contains antimicrobial enzymes and antibodies.
Immune System Glossary Natural killer (NK) cell An innate immune cell that kills infected and abnormal cells. Can release chemical signals (cytokines) that cause other cells to undergo apoptosis.
Immune System Glossary Neutralization A process by which antibodies bind to a pathogen and block it from interacting with and infecting the body s cells.
Immune System Glossary Neutrophil An innate immune cell. Typically the first cell type to respond to pathogens, particularly bacteria and fungi. Chemical signals (cytokines) can attract neutrophils and make them multiply.