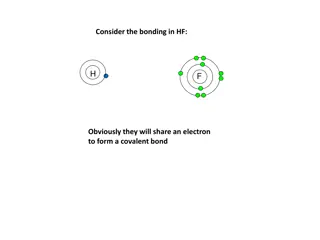
Chemical Properties and Bonding in Xenon: A Study of Noble Gases
Noble gases, including xenon, exhibit unique chemical properties due to their stable electron configurations. Xenon forms compounds like xenon difluoride, xenon tetrafluoride, and xenon hexafluoride, showcasing various hybridization states and geometries. These compounds illustrate the reactivity of noble gases and their ability to form chemical bonds despite their inert nature.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chemical properties of noble gases, structure and bonding in xenon. B. Sc. II SEM, CHEMISTRY REENU MISHRA GUIDED BY- Dr. Dhanesh Sing
The noble Gases Physical properties All colorless, odorless, test less gases low B. P and freezing point chemical properties does not react with other elements monoatomic stable octet except helium, so they are most stable inability to gain or loss electron because they have high ionization value and low electron affinity value
All these gases are chemically unreactive All noble gases(except radon) are found in the atmosphere The noble gases have full valence electron shell Inert gas Atomic number Electronic configuration Helium 2 2 Neon 10 2,8 Argon 18 2,8,8 Krypton 36 2,8,18,8 Xenon 54 2,8,18,18,8 Radon 86 2,8,18,32,18,8
Element having the atomic number close to inert gas are most reactive, as gain the stable configuration by gain or loss of electron. The noble gas exists in the monoatomic gaseous state in the atmosphere. With very high electronegative atom , Xenon, Krypton and Radon forms chemical compounds.
The important fluorides of xenon are xenon difluoride(XeF2), Xenon tetrafluoride(XeF4) and xenon hexafluoride. 1. Xenon difluoride(XeF2) It is prepared by heating a mixture of Xenon and fluorine in the ration 2:1 at 400 degree Celsius . Xe + F2---Ni----> XeF2 On hydrolysis it gives oxygen. 2XeF2+ 2 H2O -------> 2Xe + 4HF + O2 In XeF2Xenon is sp3d hybridized and the molecule has linear structure.
2. Xenon tetrafluoride ( XeF4) It is prepared by heating a mixture of Xe and F2in the molecular ratio 1:5 at 400 degree Celsius and 6 atm . Xe + 2F2---------> XeF4 With water it forms XeO3 . 6 XeF4+ 12 H2O ---------> 2 XeO3+ 4 Xe + 3O2+ 24 HF In XeF4, Xenon is in sp3d2hybridized state and has square planar geometry.
3. Xenon hexafluoride [XeF6] XeF6molecule possesses distorted octahedral structure. The Xe atom in XeF6is in SP3d3 hybridization.
Structure of XeF2- according to VSEPR-2 b.p., 3 l.p., structure -linear
Structure of XeF4 vsepr-4B.P., 2L.P., square pyramidal
3XeF4+ 4 NH3-----> 12 HF +3 Xe + 2N2 XeF4+ 2Hg ---- 2HgF2+ Xe 400OC XeF2+ H2 --------> Xe + 2HF 400OC XeF4+ 2H2 --------> Xe 400OC XeF6+ 3H2 --------> Xe + 4HF + 6HF
3 XeF4+ 4NH3--- 12 HF + 3Xe + 2 N2 Hydrolysis XeF6+ H2O ----- XeO4+ 2HF
XeO4Structure 2. Xenon tetroxide (XeO4) It is prepared by treating barium perxenate (Ba2XeO6) with anhydrous sulfuric acid. Ba2XeO6+ 2H2SO4--------> XeO4+ 2BaSO4+ 2H2O XeO4is highly unstable and has tetrahedral structure