Cell Observation Lab for Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Explore the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells through a hands-on lab. Observe, sketch, and label organelles in bacteria (yogurt), protists (pond water), fungi (yeast), and plant cells (onion and anacharis). Learn to differentiate cellular structures and understand the characteristics of different cell types.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cell Observation Lab You will differentiate between a variety of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by observing, sketching and labeling organelles and other cellular structures.
Bacteria Yogurt
Part I: Prokaryotic Cells (Bacterium) Materials: toothpick, yogurt, microscope, water dropper, slide, coverslip. 1. Using a toothpick, place a very small dab of yogurt on a slide. 2. Add a drop of water 3. Carefully add a cover slip 4. Focus on an area where there is some white space between the yogurt. You will see tiny, shimmering bacterial cells (like dust specks). 5. Draw and label the cells under high power.
Part II: Eukaryotic Cells (Protists) Materials: Pond water, pipette, microscope, slide, coverslip. 1. Using the pipette, place a small drop of pond water on a slide. Include some sediment. 2. Carefully add a cover slip 3. Focus on an area around the sediment. 4. Draw and label the cells and observable structures under medium and high power.
Algae Paramecium Water bear
Part III: Eukaryotic Cells (Fungi) Materials: Yeast, pipette, water dropper, microscope, slide, coverslip. 1. Using the pipette, place a tiny drop of yeast solution on a slide. 2. Add a small drop of water from the water dropper. 3. Carefully add a cover slip 4. Draw and label the cells and observable structures under high power.
Part IV: Eukaryotic Plant Cells (Onion) Materials: onion, Iodine, microscope, slide, coverslip. 1. Obtain a piece of onion 2. Fold the onion with the natural curve and peel the thin inside skin from the onion as shown in class. 3. Place the onion skin flat on the slide. 4. Add a drop of iodine on top of the onion skin. 5. Carefully add a cover slip. Wait for 3 minutes. 6. Draw and label the cells and observable structures under medium power.
nucleus cell wall cytoplasm
Part IV: Eukaryotic Plant Cells (Anacharis) Materials: Anacharis (aquatic plant), water dropper, microscope, slide, coverslip. 1. Obtain a single anacharis leaf 2. Place the leaf flat on the slide. 3. Add a drop of water on the leaf 4. Carefully add a cover slip. 5. Draw and label the cells and observable structures under high power.
cell wall chloroplasts cytoplasm
Part V: Eukaryotic AnimalCells (Cheek cells) Materials: toothpick, cheek cells, iodine, microscope, slide, coverslip. 1. Add a drop of iodine on a slide. 2. Obtain a toothpick 3. With the wide side of the toothpick, gently scrape the inside of your cheek. 4. Stir the toothpick in the drop of iodine on the slide. 5. Carefully add a cover slip. 6. Focus on a small cluster of cheek cells. Draw and label the cells and observable structures under high power.
cytoplasm nucleus cell membrane
Clean up! 1. Very carefully rinse all slides and coverslips. Pat dry. 2. Return slides to paper towel on side of room. 3. Return cover slips to petri dish 4. Throw away used materials: toothpicks, leaves, onion, paper towels 5. Turn off and unplug microscopes. Wipe down your area.
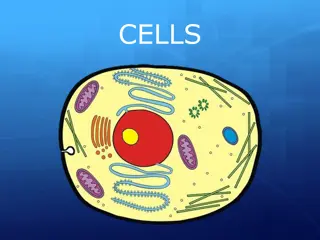
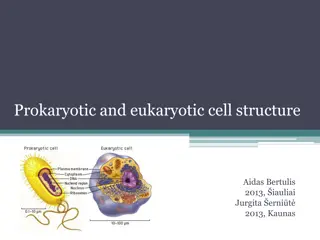
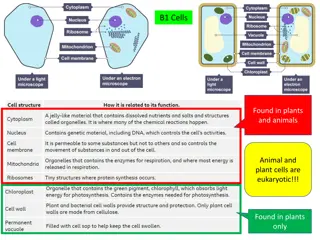
Post-Lab Questions: There are two main types of cells Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells. Name examples of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. List at least three differences you observed between the Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. Two types of eukaryotic cells are plant and animal cells. What differences did you observe between plant and animal cells? You observed plant cells from an onion bulb and a green aquatic plant. What structure was missing from the onion cells? 1. 2. 3. 4.
Post-Lab Questions: 3. Two types of eukaryotic cells are plant and animal cells. What differences did you observe between plant and animal cells? 4. You observed plant cells from an onion bulb and a green aquatic plant. What structure was missing from the onion cells?
Conclusion: 1. Develop a conclusion concerning the diversity of cells you observed. Comment on significant similarities and differences. What were the most interesting observations you made? Make references to your drawings and written observations as you write your conclusion. 2. Staple your Sketches, Answers and Conclusion together. Hand in when complete.