Batch Editing Barcodes through ArchivesSpace API Webinar
This webinar covers batch editing of barcodes through ArchivesSpace API, presented by Vakil Smallen from George Washington University. Explore tools like Anaconda Suite and OpenRefine, along with valuable resources and Python scripts for managing barcodes effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression
THINK ABOUT IT How Does A Cell Know? Which Gene To Express & Which Gene Should Stay Silent?
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation @To conserve resources, prokaryotes regulate their activities, producing only those genes necessary for the cell to function.@ It would be wasteful for a bacterium to produce enzymes that are needed to make a molecule that is readily available from its environment. (why waste energy if you already have food?)
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation What is an Operon? Group of Genes That Operate Together For Example: E. coli ferments lactose To Do That It Needs Three Enzymes (Proteins), It Makes Them All At Once! 3 Genes Turned On & Off Together. This is known as the lac Operon (lactose Operon)
The Lac Operon @The lac Operon Regulates Lactose Metabolism@ It Turns On Only When Lactose Is Present & Glucose is Absent. Lactose is a Disaccharide A Combination of Galactose & Glucose To Ferment Lactose E. coli Must: 1. Transport Lactose Across Cell Membrane 2. Separate The Two Sugars
Promoters and Operators The first is a promoter (P), which is a site where RNA-polymerase can bind to begin transcription. The other region is called the operator (O), which is where the lac repressor can bind to DNA.
The Lac Repressor Turns Transcription Off
Gene Regulation: lac Operon Key Concept: The lac Genes Are: Turned Off By Repressors And Turned On By The Presence Of Lactose
Eukaryotic Cell Specialization Most Eukaryotic Genes Are Controlled Individually And Have Regulatory Sequences That Are Much More Complex Than Prokaryotic Gene Regulation
RNA Interference For years, biologists wondered why cells that contain lots of small RNA molecules, only a few dozen bases long, and don t belong to any of the major groups of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, or rRNA)
RNA Interference @Blocking gene expression by means of an miRNA silencing complex is known as RNA interference (RNAi).@
Genetic Control of Development As an embryo develops, different sets of genes are regulated by transcription factors, enhancers, and repressors. Gene regulation helps cells undergo differentiation, becoming specialized in structure and function.
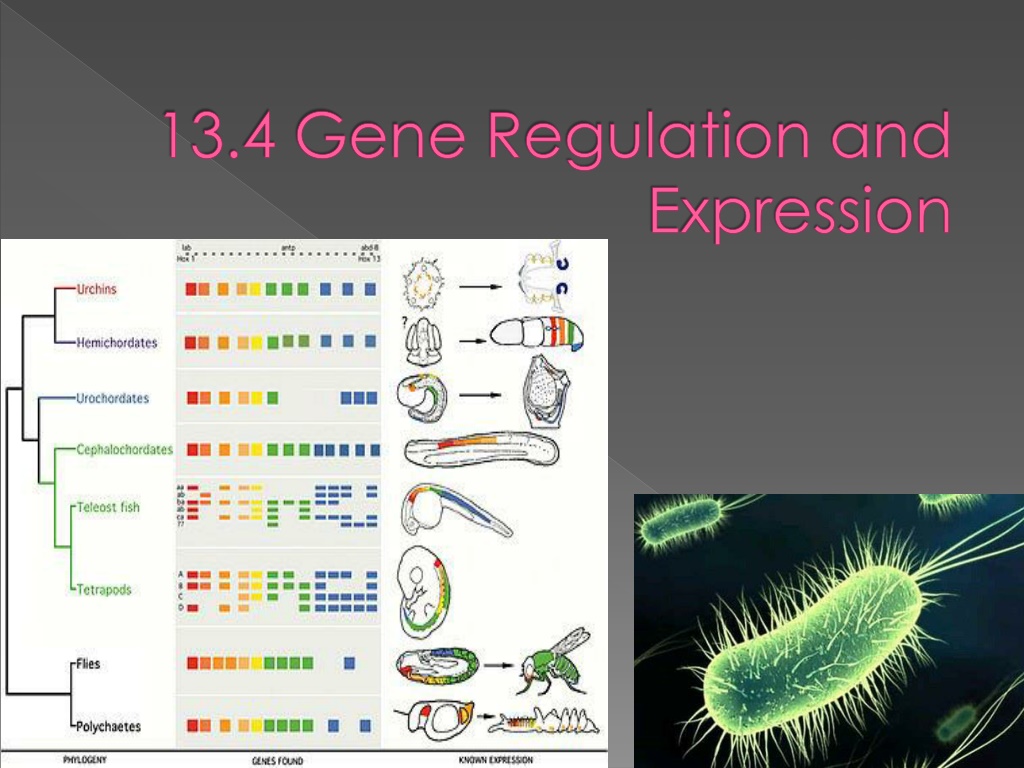
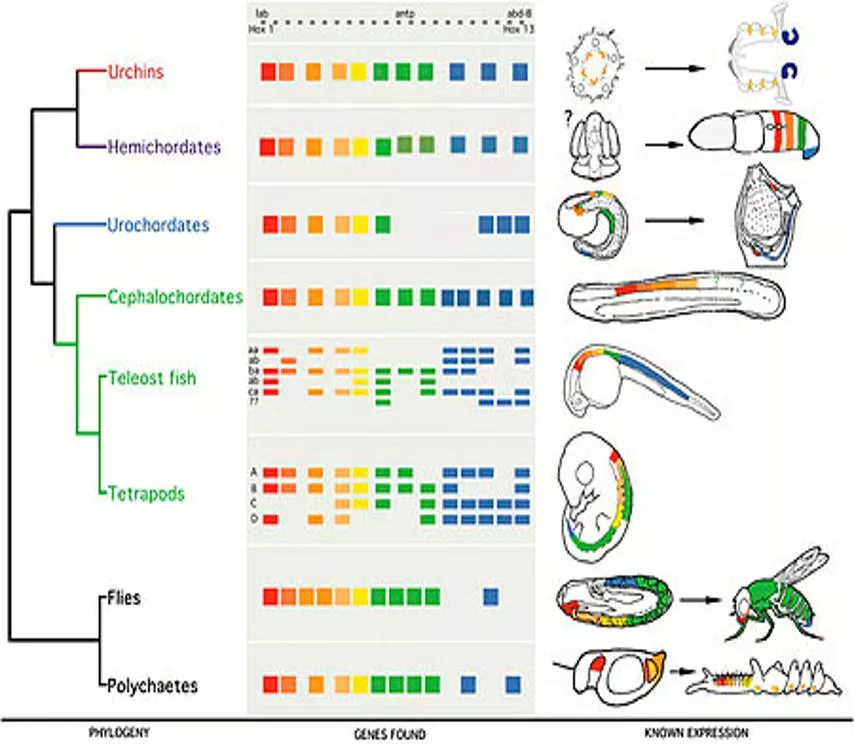
Homeotic Genes Edward B. Lewis was the first to show that a specific group of genes controls the identities of body parts in the embryo of the common fruit fly. Lewis found that a mutation in one of these genes actually resulted in a fly with a leg growing out of its head in place of an antenna! These master control genes, homeobox genes, activate genes important in cell development
Regulation & Development Hox Genes @Control Organ & Tissue Development In The Embryo@ Mutations Lead To Major Changes Drosophila With Legs In Place of Antennae
Regulation & Development Hox Genes Present In All Eukaryotes Shows Common Ancestry Pax 6 hox gene Controls eye growth in Drosophila, Mice & Man Pax 6 from Mouse Placed In Knee Development Sequence Of Drosophila Developed Into Eye Tissue. Common Ancestor >600M Years Ago
Homeobox and Hox Genes Nearly all animals, share the same basic tools for building the different parts of the body. Common patterns of genetic control exist because all these genes have descended from the genes of common ancestors.
Environmental Influences @In prokaryotes and eukaryotes, environmental factors can influence gene expression.@ Ex: temperature, salinity, nutrient availability Ex: The lac operon in E. coli is switched on only when lactose is the only food source in the bacteria s environment.
This type of RNA is used to block gene expression 1. rRNA 2. tRNA 3. mRNA 4. miRNA
In the Lac operon, if lactose is not present what happens to the operon? The Lac operon turns off
In the Lac operon, if lactose is present what happens to the operon? The Lac operon turns on
These determine factors like presence of wings or legs 1. miRNA 2. Homeobox Genes 3. Operator 4. Promoter