Aspirin Assay by Direct Acid-Base Titration Experiment Overview
Exploring the process of assessing aspirin purity through direct acid-base titration using sodium hydroxide as a standard solution. The experiment includes details on aspirin properties, dosage, acidity, decomposition, and metabolism. Key aspects covered include the aim of the experiment, the principle of alkalimetry assay, and the overall methodology involved in determining the percentage purity of aspirin tablets.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Assay of aspirin by direct acid- base titration Lecturer Hussien Ali 2021-2022
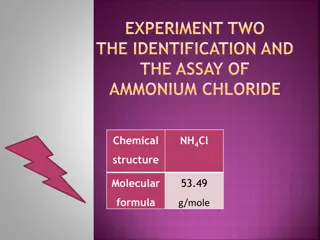
Introduction: Aspirin is acetyl salicylic acid, occurs as white crystals, used as analgesic to relieve minor aches and pain, as antipyretic to reduce fever and as anti- inflammatory medication and also used as prophylaxis of stroke. Its molecular formula (C9H8O4).
Dosage of aspirin Aspirin is pharmacies as tablets (75,81,100 and 300 mg ). Used once dialy dose in prophylaxis of blood coagulation at doses of ( 75,81,100mg). As antipyretic used at dose of 300mg once dialy.
Properties: Aspirin is an aromatic compound containing both a carboxylic acid functional group and an ester functional group. Aspirin can be prepared by reacting salicylic acid and acetic anhydride in the presence of an acid catalyst. It is slightly soluble in water (1:300) and soluble in alcohol (1:5), chloroform (1:17) and ether (l: 15), Also it dissolves easily in glycerin. Its melting point (135 C), and Molecular weight = 180.2 g/mol
Acidity: It is a monoprotic weak acid Ka = 2.8 x 10-4 at 25 degree Celsius, so very little of the molecular aspirin dissociates to form acetylsalicylate ions. Equilibrium dissociation reaction:
It slowly decomposed to acetic acid and salicylic acid in the presence of heat and moisture. It readily absorbed from stomach and small intestine. Their absorption depends strongly on the pH of the environment.
Is aspirin considered to be an acid or a base? Does the co administration of antacid effect the absorption of aspirin? And why? What is the main metabolite of aspirin, mention the type of metabolism and it excreted
Aim of experiment: Apply Alkalimetry assay to determine the percentage purity of aspirin tablet. Principle Inthis experiment you will determine the percentage purity of aspirin by using (Titration method). The aspirin will be titrated against a standard solution of base, 0.1 N NaOH. Base will be dispensed from a burette into a conical flask containing the dissolved acid (in ethanol) and phenolphthalein indicator, which show a faint pink color in basic solutions.
Procedure 1. Fill the burette with 0.1M NaOH solution using the funnel provided. Ensure there are no bubbles by tapping the side of the burette. Take action to do blank titration . 2. Grind up ONE aspirin tablet to a fine powder using the pestle and mortar. 3. Place a clean, dry conical flask on a top balance. Zero the reading. Add all the powder to the conical flask using a spatula and record the weight of the powder 4. Add 10ml of ethanol to the conical flask. 5. Add 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution. 6. Swirl the conical flask carefully until the powder is fully dissolved. Swirl for at least 2 minutes. 7. Titrate carefully with sodium hydroxide. The end point is reached at the first instance of the pink colour persisting. 8. Record the volume of the sodium hydroxide
Procedure: Crush one tablet (100) mg of aspirin 10 ml of ethanol? 3 drops phenolphthalein Swirl to dissolve 0.10N NaOH E.P. pink solution basic medium
why we use ethanol? What is blank titration? Do you think that your results are accurate?
Calculation Recovery % = practical content/ theoretical = ( ?????? ??.??) X 100 ??????????? V(NaOH) = end point ml N(NaOH) = 0.1N Eq.Wt (aspirin) = 180.2 g/mol