Understanding Gene Editing with CRISPR/Cas9 Technology
Explore the fascinating world of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology through sessions led by experts like Roy Campbell and Howard Robinson. Delve into the working of gene editing, the CRISPR system, and the role of Cas9 enzyme. Learn about CRISPR's origin in prokaryotic organisms and its potential f
0 views • 33 slides
Implementing Personal Protective Equipment in Nursing Homes for Preventing XDROs and MDROs
Learn from infection prevention consultant Karen Trimberger about implementing enhanced barrier precautions in nursing homes to prevent the spread of extensively drug-resistant organisms (XDROs) and multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs). Explore the difference between colonization and clinical infec
6 views • 33 slides
Understanding Ecology: Interactions Between Organisms and their Environment
Ecology is the scientific study of how living organisms interact with each other and their environment. It delves into the relationships between biotic and abiotic factors, encompassing topics such as the distribution and abundance of organisms, structural adaptations, behavior under natural conditi
2 views • 42 slides
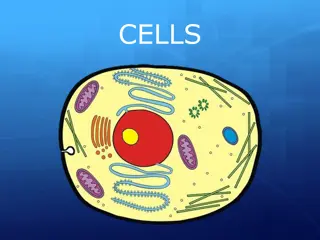
CELLS
Discover the incredible world of cells in the human body, each playing a vital role in sustaining life. Explore the diversity of cell types, learn about the history of microscopy, and delve into the Cell Theory. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, essential building
1 views • 69 slides
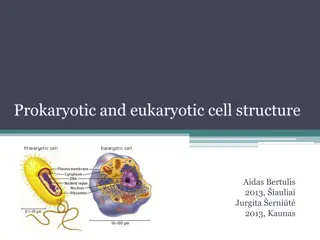
Understanding Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Structure
This comprehensive guide explores the structures and characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Learn about the differences and similarities between these cell types, including features like cell wall composition, membrane-bound organelles, nucleus presence, DNA structure, ribosomes, and m
7 views • 20 slides
Understanding Ecosystems: Ecological Interactions and Dependencies
Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with their environment, influencing their distribution and abundance. This exploration covers terrestrial and aquatic biomes, energy flow, environmental impacts, adaptations, and global ecosystems, emphasizing the interconnectedness of all living organi
2 views • 58 slides
Understanding Applied Microbiology: Insights into Microbial Diversity and Cell Organization
Applied Microbiology focuses on harnessing the capabilities of microorganisms for the production of beneficial products like medicines, vaccines, and biotechnological advancements. This field explores the intricate interactions between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, emphasizing their pivotal
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Homeostasis in Living Organisms
Homeostasis, derived from Greek meaning "standing still", is crucial for maintaining balance in living organisms. It involves regulating internal variables to prevent disease or death. Ancient Greeks emphasized the importance of harmony and equilibrium in life. Claude Bernard and Walter B. Cannon fu
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Levels of Organization in Living Organisms
Explore the levels of organization in living organisms, from atoms to cells, and the differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Learn about prokaryotes, eukaryotes, cell differentiation, chromosomes, and the importance of stem cells in development and repair.
0 views • 17 slides
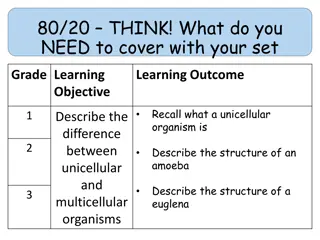
Exploring Unicellular Organisms: Amoeba and Euglena Structures and Characteristics
Journey into the microscopic world of unicellular organisms with a focus on Amoeba and Euglena. Discover the unique structures and behaviors of these tiny creatures, from Amoeba's adaptable pseudopod movements to Euglena's photosynthesis capabilities. Uncover how these organisms survive, feed, and r
0 views • 15 slides
Overview of Bacterial Structure and Morphology in Veterinary Microbiology
Bacteria are single-celled prokaryotic organisms with a simple body design. Their structure includes layers such as the extramural layer, surface appendages like flagella and pili, cell envelop with a cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane, and cytoplasmic inclusions. The capsule and slime layer play es
0 views • 21 slides
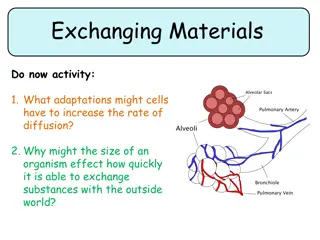
Adaptations for Efficient Material Exchange in Organisms
Understanding how cells and organisms adapt for effective material exchange through diffusion, surface area to volume ratio, and specialized exchange surfaces. Larger organisms require specialized structures for efficient exchanges, in contrast to smaller organisms that can rely on simple diffusion.
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Ecosystem Organization and Hierarchy
Explore the intricate relationships within ecosystems through the study of organization and hierarchy. From individual organisms to complex communities, learn how biotic and abiotic factors shape these environments. Gain insights into the levels of ecosystem organization, from single organisms to in
5 views • 15 slides
Understanding the Characteristics of Living Organisms
Life is a unique biochemical process expressed through chemical reactions leading to growth, development, responsiveness, adaptation, and reproduction. Living organisms exhibit characteristics such as growth, definite shape and size, reproduction, metabolism, and cellular organization. These traits
4 views • 32 slides
Understanding Gas Exchange in Cells and Organisms
Gas exchange is vital for cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In organisms, specialized structures like alveoli in lungs and stomata in plants facilitate this process. This exchange occurs through diffusion across moist surfaces with large surface areas. In animals, oxygen is taken up by hemogl
0 views • 40 slides
Exploring the Thermophilic Organisms: Thermoplasma Genus
The Thermoplasma genus belongs to Archaea and thrives in acidic, high-temperature environments. These prokaryotic organisms lack a defined nucleus and utilize sulfur and organic carbon for respiration. They possess a unique membrane composition, allowing them to survive in extreme conditions. Specie
0 views • 12 slides
Fundamentals of Taxonomy Explained: From Classification to Nomenclature
Taxonomy, derived from Greek roots, encompasses the science of classifying organisms and understanding their variations, evolutionary relationships, and naming conventions. It involves description, identification, classification, and nomenclature of both living and extinct organisms. The practices o
1 views • 39 slides
Understanding Biosynthetic Pathways in Living Organisms
Biosynthesis, also known as anabolism, involves the formation of complex organic compounds from simple subunits catalyzed by enzymes within living organisms. This process is vital for the development of life and the production of essential compounds like carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, antibiotic
1 views • 21 slides
Exploring Multicellular Organisms: Structures and Functions
Learn about multicellular organisms, including examples like humans, animals, and plants, and how their cells, tissues, organs, and systems work together to perform various functions. Understand the difference between single-celled and multicellular organisms and why some require specialized cells t
0 views • 15 slides
Reproduction in Organisms: Overview and Types
Understanding the concept of reproduction in organisms, this content delves into the different modes of reproduction such as asexual and sexual, with examples and illustrations. It covers the life spans of various organisms and details various methods of asexual reproduction like fission, budding, s
0 views • 23 slides
Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms: A Comparative Analysis
Unicellular and multicellular organisms differ in structure, division of labor, specialization, exposure to environment, response to injury, size limitations, lifespan, and ability to divide. Unicellular organisms have a single-cell body, limited operational efficiency, and face challenges in size a
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Ecosystem Dynamics: The Food Web Explained
An ecosystem comprises various organisms living together in a community. Energy flow through food chains depicts how organisms obtain energy and nutrients from one another. Food chains show the sequence of feeding relationships, while a food web illustrates interconnected chains within a community.
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding Relationships Between Organisms in Nature
Explore the various relationships between organisms in nature, including intraspecific and interspecific interactions such as competition, predation, and parasitism. Learn how organisms compete for resources, hunt and protect themselves, as well as how parasites survive on host organisms. Delve into
2 views • 13 slides
Understanding Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms in Biology
Explore the basic differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms, including the distinctions between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and amoeba, consist of a single cell and are often microscopic. Examples of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic unicellula
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Taxonomy and Classification in Biology
Scientists use classification to group organisms logically, making it easier to study life's diversity. Taxonomy assigns universally accepted names to organisms using binomial nomenclature. Carolus Linnaeus developed this system, organizing organisms into species, genus, family, order, class, phylum
0 views • 11 slides
Overview of Cell Division in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotic Cells
Cell division plays a crucial role in the growth and reproduction of all organisms. In prokaryotic cells, binary fission is the primary mode of division, while eukaryotic cells undergo a more complex process involving cell growth, DNA replication, chromosome distribution, and cytokinesis. The cell c
0 views • 10 slides
Exploring Molecular Biology and Cell Science
Molecular biology delves into the study of biology at the molecular level, focusing on gene structure and functions to comprehend hereditary traits, genetic variation, and gene expression patterns. Cells, the fundamental units of life, vary in shape and function but share basic structures. The Three
0 views • 31 slides
Comparison of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells in Cell Biology
Cells are the fundamental units of life, but viruses are an exception as they lack cells. Eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus with a nuclear membrane housing chromosomes, while prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger, containing membrane-
0 views • 9 slides
Cell Division Mechanisms in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells divide through binary fission, while eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis with nuclear division and cytokinesis. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and divide by replicating DNA and forming two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic chromosomes, associated with histone proteins, undergo co
0 views • 56 slides
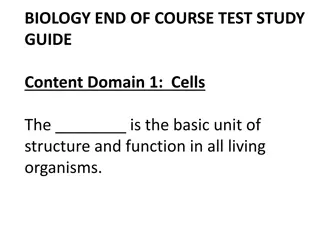
Understanding Cells: The Basic Units of Life
Exploring the fundamental importance of cells in living organisms, this study guide delves into the structure and function of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. It highlights the distinction between these cell types, their respective characteristics, and the defining features of living things. Emphas
0 views • 93 slides
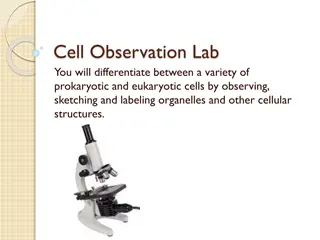
Cell Observation Lab for Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Explore the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells through a hands-on lab. Observe, sketch, and label organelles in bacteria (yogurt), protists (pond water), fungi (yeast), and plant cells (onion and anacharis). Learn to differentiate cellular structures and understand the characterist
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Processes
Cellular respiration is the energy-releasing process in which organisms take in glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. This process is vital for all living organisms. Photosynthesis and respiration are opposite processes, with respiration requiring the products of photosynt
0 views • 10 slides
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: A Comparative Overview
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack membrane-bound organelles, reproducing through binary fission. Eukaryotic cells are more complex, larger, with a nucleus enclosed in a nuclear envelope. They have various organelles and a cell wall. The plasma membrane defines cell boundaries, regulating the pa
0 views • 13 slides
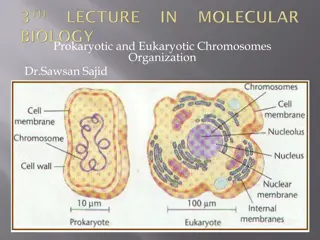
Understanding Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Organization
Chromosomes are vital structures in cells, holding genetic material. Prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid containing DNA while eukaryotic cells have DNA enclosed in a nucleus. Proteins like H-NS, HU, FIS, and IHF play crucial roles in maintaining chromosome structure and gene expression. Unlike eukaryo
0 views • 20 slides
Introduction to Animal Physiology and Cellular Biology Overview
This comprehensive course delves into the fundamental aspects of animal physiology and cellular biology. Topics covered include the characteristics of living organisms, cellular organelles, the cell cycle, division, growth, and death. Additionally, the course introduces the various animal phyla, fro
0 views • 43 slides
Understanding Prokaryotic Gene Regulation: A Teachable Unit
Dive into the world of prokaryotic gene regulation with a focus on the lac operon. This educational unit aims to help students comprehend the mechanisms behind gene regulation, specifically through the example of the lac operon. Explore key terms, models, and outcomes to enhance understanding in an
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Heterotrophic Nutrition in Organisms
Heterotrophic nutrition refers to the process where organisms, such as animals, rely on preformed organic molecules from their environment or other organisms for nutrients and energy. These organisms are unable to produce organic compounds from inorganic sources and must obtain nourishment from exte
0 views • 55 slides
Understanding Biotic Communities and Benthic Ecosystems
Living organisms in an area form biotic communities categorized into producers, consumers, omnivores, detrivores, and decomposers. Aquatic organisms such as plankton, benthos, and nekton play vital roles. Benthic communities refer to organisms attached to or burrowing in aquatic ecosystems, influenc
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding DNA Replication: From Basics to Lab Synthesis
DNA replication is a fundamental process in all living organisms, essential for biological inheritance. This comprehensive guide explores the stages of DNA replication, highlighting key experiments and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic replication. Additionally, it delves into the revol
1 views • 31 slides
Temperature Tolerance of Organisms in the Universe
Life on Earth exists within a range of temperatures, with organisms displaying varied temperature tolerance. Eurythermal organisms can withstand large temperature fluctuations, while stenothermal organisms tolerate only small variations. The temperature range for each species is crucial for their ph
0 views • 8 slides