Exploring Multicellular Organisms: Structures and Functions
Learn about multicellular organisms, including examples like humans, animals, and plants, and how their cells, tissues, organs, and systems work together to perform various functions. Understand the difference between single-celled and multicellular organisms and why some require specialized cells to survive. Dive into the world of cell specialization and the importance of different cell types in multicellular organisms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
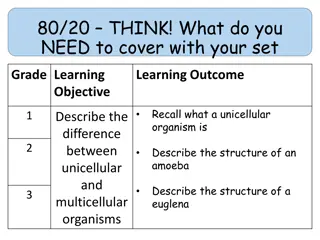
STANDARD: 5.L.1.1 Explain why some organisms are capable of surviving as a single cell while others require many cells that are specialized to survive. I can list examples of multicellular organisms and describe their structures and functions. Clear Learning Goals: List examples of multi cellular organisms and describe their structures and functions.
We have been talking about how cells are the building blocks of all organisms. Yesterday we discussed one celled organisms. What do you remember about yesterday's lesson? Recall those ideas now. Today we will be exploring multicellular organisms.
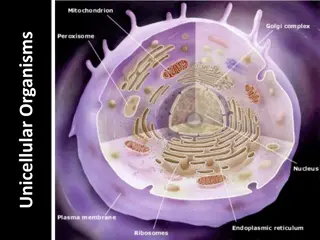
Multicellular Organisms A multicellular organism is made up of more than one cell. Humans, animals, and plants are all examples of multicellular organisms.
Multicellular Organisms Each kind of cell does a different job. It s shape and structure helps it carry out this job.
Multicellular Organisms Groups of cells form tissue, groups of tissue forms organs, groups of organs form systems.
Multicellular Organisms Cell Tissue Organ System Muscle cell Muscle tissue Muscle Muscular system
Comparing Unicellular & Multicellular Single celled organisms take in material directly from their surroundings, while multicellular organisms have systems for moving materials throughout their body. A system is a group of parts that work together.
To summarize: Unicellular (single celled) Organisms can perform all of life s functions within a single cell. Multicellular (many celled) Organisms have many cells that each perform a special task. They need all of these different kinds of cells working together in order to survive.
Exit Ticket 1.What is the correct order for how cells group together in multicellular organisms? 2.How are humans different from amoebas?